
Aurora is a Russian protected cruiser, currently preserved as a museum ship in Saint Petersburg. Aurora was one of three Pallada-class cruisers, built in Saint Petersburg for service in the Pacific. All three ships of this class served during the Russo-Japanese War. Aurora survived the Battle of Tsushima and was interned under US protection in the Philippines, and eventually returned to the Baltic Fleet. One of the first incidents of the October Revolution in Russia took place on the cruiser Aurora, which reportedly fired the first shot, signalling the beginning of the attack on the Winter Palace.

The Bayern class was a class of four dreadnought battleships built by the German Kaiserliche Marine. The class comprised Bayern, Baden, Sachsen, and Württemberg. Construction started on the ships shortly before World War I; Baden was laid down in 1913, Bayern and Sachsen followed in 1914, and Württemberg, the final ship, was laid down in 1915. Only Baden and Bayern were completed, due to shipbuilding priorities changing as the war dragged on. It was determined that U-boats were more valuable to the war effort, and so work on new battleships was slowed and ultimately stopped altogether. As a result, Bayern and Baden were the last German battleships completed by the Kaiserliche Marine.

The Battle of the Yellow Sea was a major naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 10 August 1904. In the Russian Navy, it was referred to as the Battle of 10 August. The battle foiled an attempt by the Russian fleet at Port Arthur to break out and form up with the Vladivostok squadron, forcing them to return to port. Four days later, the Battle off Ulsan similarly ended the Vladivostok group's sortie, forcing both fleets to remain at anchor.

Asama (淺間) was the lead ship of her class of armored cruisers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the late 1890s. As Japan lacked the industrial capacity to build such warships herself, the ship was built in Britain. She served in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05 during which she participated in the Battle of Chemulpo Bay and the Battle of the Yellow Sea without damage, although her luck did not hold out during the Battle of Tsushima. Early in World War I, Asama unsuccessfully searched for German commerce raiders until she was severely damaged when she ran aground off the Mexican coast in early 1915. Repairs took over two years to complete and she was mainly used as a training ship for the rest of her career. The ship made a total of 12 training cruises before she was crippled after running aground again in 1935. Asama then became a stationary training ship until she was broken up in 1946–1947.

Tsesarevich was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the Imperial Russian Navy, built in France at the end of the 19th century. The ship's design formed the basis of the Russian-built Borodino-class battleships. She was based at Port Arthur, northeast China, after entering service and fought in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. Tsesarevich was torpedoed during the surprise attack on Port Arthur and was repaired to become the flagship of Rear Admiral Wilgelm Vitgeft in the Battle of the Yellow Sea and was interned in Qingdao after the battle.

Rurik was the last armored cruiser to be built for the Imperial Russian Navy. The ship was designed by the British firm Vickers and built in their shipyard, being laid down in 1905 and completed in 1908. She was armed with a main battery of four 254 mm (10 in) guns and a secondary battery of eight 203 mm (8 in) guns; her top speed was rated at 21 knots. Despite her powerful gun armament, Rurik was rendered obsolescent even before she was completed by the advent of the British battlecruisers of the Invincible class, which were more powerfully armed and faster. Her design is nevertheless well regarded and naval historians rate her as one of the best vessels of her type ever built.

Rossia was an armored cruiser of the Imperial Russian Navy built in the 1890s. She was designed as a long-range commerce raider and served as such during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05. She was based in Vladivostok when the war broke out and made a number of sorties in search of Japanese shipping in the early months of the war without much success.

The Bayan class was a group of four armored cruisers built for the Imperial Russian Navy around the beginning of the 20th century. Two of the ships were built in France, as Russian shipyards had no spare capacity. The lead ship, Bayan, was built several years earlier than the later three. The ship participated in several of the early naval battles of the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05, and provided naval gunfire support for the Imperial Russian Army until she struck a mine. Bayan was trapped in harbor during the subsequent Siege of Port Arthur, and was sunk by Japanese artillery. She was salvaged and put into service with the Imperial Japanese Navy with the name of Aso. She mostly served as a training ship before she was converted into a minelayer in 1920. The ship was sunk as a target in 1932.

Yakumo was an armored cruiser built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the late 1890s. As Japan lacked the industrial capacity to build such warships itself, the ship was built in Germany. She participated in most of the naval battles of the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05, and was lightly damaged during the Battle of the Yellow Sea and the Battle of Tsushima. Yakumo saw no combat during World War I and began the first of many training cruises in 1917, although she was not officially reclassified as a training ship until 1931. Her last training cruise was in 1939, but the ship continued to conduct training in home waters throughout the Pacific War. Yakumo became a repatriation transport after the war and was broken up in 1946–47.

The Bogatyr class were a group of protected cruisers built for the Imperial Russian Navy. Unusually for the Russian navy, two ships of the class were built for the Baltic Fleet and two ships for the Black Sea Fleet.

Pallada was the lead ship in the Pallada class of protected cruisers in the Imperial Russian Navy. She was built in the Admiralty Shipyard at Saint Petersburg, Russia. The new class was a major improvement on previous Russian cruisers, although the armor protection was light.

Diana was the second of three Pallada-class protected cruisers built for the Imperial Russian Navy. The cruiser served during the Russo-Japanese War and took part in the Battle of the Yellow Sea on 10 August 1904. Later, she served as part of the Russian Baltic Fleet during World War I.

Pallada was the last of the four Bayan-class armored cruisers built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. She was assigned to the Baltic Fleet during World War I where she captured codebooks from the German cruiser Magdeburg that had run aground during the first month of the war. The ship was torpedoed by a German submarine in October 1914 and exploded; none of the crew survived. Pallada was the first warship lost by the Russians during the war.

The Roon class was a pair of armored cruisers built for the German Kaiserliche Marine in the 1900s. The two ships of the class, Roon and Yorck, closely resembled the earlier Prinz Adalbert-class cruisers upon which they were based. The Roon class incorporated slight incremental improvements, including a pair of extra boilers. The ships were easily distinguished from their predecessors by the addition of a fourth funnel. Though the additional boilers were meant to increase the ships' speed, both vessels failed to reach their designed top speed. In addition, the ships had comparatively light armament and thin armor protection, so they compared poorly with their foreign contemporaries, particularly the armored cruisers of their primary opponent, the British Royal Navy.

The Prinz Adalbert class was a group of two armored cruisers built for the German Kaiserliche Marine under the terms of the Second Naval Law. Two ships of the class were built, Prinz Adalbert and Friedrich Carl, between 1900 and 1904. The two ships were heavily based on the previous armored cruiser, Prinz Heinrich, with a series of incremental improvements. Their armor layout was revised slightly to improve internal protection and their main battery consisted of four 21 cm (8.3 in) guns instead of the two 24 cm (9.4 in) carried by Prinz Heinrich. The new ships also received more powerful propulsion systems, making them slightly faster. Prinz Adalbert spent her peacetime career as a gunnery training ship while Friedrich Carl initially served as the flagship of the fleet's reconnaissance forces. By 1909, she had been replaced by more modern cruisers and joined Prinz Adalbert as a training vessel.

The Wiesbaden class of light cruisers was a class of ships built by the German Kaiserliche Marine shortly before the outbreak of World War I. Two ships were built in this class, Wiesbaden and Frankfurt. They were very similar to the preceding design, the Graudenz class, though they were armed with eight 15 cm SK L/45 guns instead of the twelve 10.5 cm SK L/45 guns on the earlier vessels. The ships had a top speed of 27.5 knots.

The Königsberg class of light cruisers was a group of four ships commissioned into Germany's Kaiserliche Marine shortly before the end of World War I. The class comprised Königsberg, Karlsruhe, Emden, and Nürnberg, all of which were named after light cruisers lost earlier in the war. The ships were an incremental improvement over the preceding Wiesbaden-class cruisers, and were armed with a main battery of eight 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/45 guns and had a designed speed of 27.5 knots.
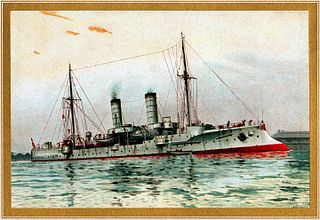
The Gazelle class was a group of ten light cruisers built for the Imperial German Navy at the turn of the 20th century. They were the first modern light cruiser design of the Imperial Navy, and set the basic pattern for all future light cruisers in Imperial service. The design of the Gazelle class attempted to merge the fleet scout with the colonial cruiser. They were armed with a main battery of ten 10.5 cm (4.1 in) guns and a pair of torpedo tubes, and were capable of a speed of 21.5 knots.

The Kolberg class was a group of four light cruisers built for the German Imperial Navy and used during the First World War. The class comprised four vessels: SMS Kolberg, the lead ship, Mainz, Cöln, and Augsburg. The ships were built between 1908 and 1910, and two, Kolberg and Augsburg, were modernized in 1916–1917. The ships were armed with a main battery of twelve 10.5 cm SK L/45 guns and had a design speed of 25.5 knots. The first three ships were assigned to the reconnaissance forces of the High Seas Fleet; Augsburg was instead used as a torpedo and gunnery training ship.

Admiral Lazarev was a Sverdlov-class cruiser of the Soviet Navy.





















