 | |
Panama | Taiwan |
|---|---|
Panama was once an important diplomatic source of support for Taiwan. In June 2017, it broke off relations with Taiwan and established diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China.
 | |
Panama | Taiwan |
|---|---|
Panama was once an important diplomatic source of support for Taiwan. In June 2017, it broke off relations with Taiwan and established diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China.

Panama was an important source of diplomatic support for the Republic of China for 106 years. [1]
According to diplomatic cables published by WikiLeaks, in 2009, after President Ricardo Martinelli took office, Panama wished to switch diplomatic relations from the ROC to the People's Republic of China (PRC). [2] This was rejected by the PRC, which did not want to disrupt its improving diplomatic relations with the ROC during the ROC Presidency of Ma Ying-jeou. [2]
On 13 June 2017, Panama and the People's Republic of China issued a joint declaration of establishing diplomatic relations with each other. Simultaneously, Panama severed official relations and official contacts with Taiwan. [1]
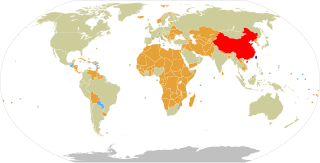
Foreign relations of the Republic of China (ROC), more commonly known as Taiwan, are accomplished by efforts of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China, a cabinet-level ministry of the Government of the Republic of China. As of January 2024, the ROC has formal diplomatic relations with 11 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs the Vatican City State. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories (Guam, Hong Kong, and Macau), and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates. In 2021, the Government of the Republic of China had the 33rd largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.
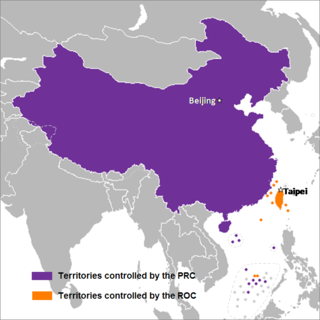
Chinese unification, also known as Cross-Strait unification or Chinese reunification, is the potential unification of territories currently controlled, or claimed, by the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China ("Taiwan") under one political entity, possibly the formation of a political union between the two republics. Together with full Taiwan independence, unification is one of the main proposals to address questions on the political status of Taiwan, which is a central focus of Cross-Strait relations.
The political status of Taiwan or the Taiwan issue is an ongoing geopolitical dispute about Taiwan, currently controlled by the Republic of China (ROC), that arose in the mid-twentieth century. Originally based in mainland China before and during World War II, the ROC government retreated to Taiwan in 1949 after it was defeated by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) during the Chinese Civil War and the subsequent establishment of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Since then, the effective jurisdiction of the ROC has been limited to Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu, and smaller islands.
One China is a phrase describing the relationship between the People's Republic of China (PRC) based on Mainland China, and the Republic of China (ROC) based on the Taiwan Area. "One China" asserts that there is only one de jure Chinese nation despite the de facto division between the two rival governments in the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. The term may refer, in alphabetical order, to one of the following:
China is one of the members of the United Nations and is one of five permanent members of its Security Council. One of the victorious Allies of World War II, the Republic of China (ROC) joined the UN as one of its founding member countries in 1945. The subsequent resumption of the Chinese Civil War between the government of Republic of China and the rebel forces of the Chinese Communist Party, led to the latter's victory on the mainland and the establishment of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949. Nearly all of mainland China was soon under its control and the ROC government retreated to the island of Taiwan.

Since its founding in 1949, the People's Republic of China (PRC) has had a diplomatic tug-of-war with its rival in Taiwan, the Republic of China (ROC). Throughout the Cold War, both governments claimed to be the sole legitimate government of all China and allowed countries to recognize either one or the other. Until the 1970s, most Western countries in the Western Bloc recognized the ROC while the Eastern Bloc and Third World countries generally recognized the PRC. This gradually shifted and today only 11 UN member states recognize the ROC while the PRC is recognized by the United Nations, as well as 181 UN member states, Cook Islands, Niue and the State of Palestine. Both the ROC and the PRC maintain the requirement of recognizing its view of the One China policy to establish or maintain diplomatic relations.

Oceania is, to the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China, a stage for continuous diplomatic competition. The PRC dictates that no state can have diplomatic relations with both the PRC and the ROC. As of 2024, eleven states in Oceania have diplomatic relations with the PRC, and three have diplomatic relations with the ROC. These numbers fluctuate as Pacific Island nations re-evaluate their foreign policies, and occasionally shift diplomatic recognition between Beijing and Taipei. The issue of which "Chinese" government to recognize has become a central theme in the elections of numerous Pacific island nations, and has led to several votes of no-confidence.
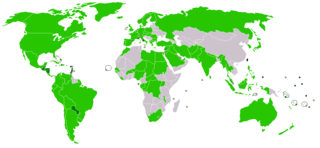
Numerous states have ceased their diplomatic recognition of the Republic of China during the last 70 years, since the founding of the People's Republic of China. Under the One China policy, the ROC is recognized by 11 UN member states and Holy See with 59 UN member states and Somaliland maintaining unofficial cultural and economic relations.
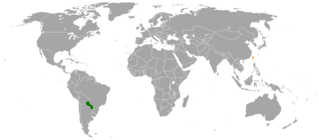
The Republic of Paraguay and the Republic of China (Taiwan) established diplomatic relations on 8 July 1957.

Relations between the Holy See and the Republic of China were established on a non-diplomatic level in 1922 and at a diplomatic level in 1942. The Holy See conducts its relationship with China through formal diplomatic relations with Taiwan. It does not have formal diplomatic relationship with the People's Republic of China.

India and Republic of China (ROC) had formal diplomatic relations from 1942 to 1949. After severing diplomatic relations, the bilateral relations have improved since the 1990s, despite both countries not maintaining official diplomatic relations. India only recognises the People's Republic of China (PRC) since 1949. However, India's economic and commercial links as well as people-to-people contacts with Taiwan have expanded in recent years.

China–Lithuanian relations are the bilateral foreign relations between the People's Republic of China (China) and Lithuania. The PRC has a chargé d'affaires in Vilnius. In December 2021, Lithuania closed its embassy in Beijing
The Republic of the Fiji Islands was the first Pacific Island country to establish diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China, in 1975. China established an embassy in Fiji in 1976, and Fiji opened its embassy in China in 2001.

The Republic of Kiribati and the People's Republic of China (PRC) established diplomatic relations on June 25, 1980, and resumed on September 27, 2019. Between 2003 and 2019, The government of Kiribati recognized the Republic of China, and, in accordance with the "One China" policy, the People's Republic of China did not have diplomatic relations to the country.
The Independent State of Papua New Guinea and China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations in 1976, soon after Papua New Guinea became independent. The two countries currently maintain diplomatic, economic and, to a lesser degree, military relations. Relations are cordial; China is a significant provider of both investments and development aid to Papua New Guinea.

Samoa and China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations in 1976. The two countries currently maintain cordial relations; China provides economic aid to Samoa.
The Republic of Vanuatu and the People's Republic of China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations on March 26, 1982. China established an embassy in Vanuatu in 1989, while Vanuatu established an honorary consulate in China in 1999; it officially became an embassy in 2005. The current Ambassador of China in Vanuatu is Liu Quan. The current Ambassador of Vanuatu in China is former Minister of Finance Willie Jimmy.
Relations between the Commonwealth of Australia and the Republic of China, formerly the Qing dynasty, date back to 1909. The two countries had official diplomatic relations from 1941 to 1972. Since 1972, Australia no longer has formal diplomatic relations with Republic of China (Taiwan). Australia and Taiwan share partnership in the inter-governmental Global Cooperation and Training Framework (GCTF) activities.

Canada and Taiwan have maintained unofficial bilateral relations since 1970. First contacts between Canada and Taiwan began in 1871 with the arrival of George Leslie Mackay.

China–Panama relations are the bilateral relationships between the People's Republic of China and Republic of Panama. Relations between Panama and the Qing dynasty began in 1909 and modern relations between Panama and the Beiyang government of China began on 2 January 1922. After the Chinese Civil War in 1949, relations were maintained with the Nationalist government of the ROC which retreated to the island of Taiwan, a former Qing province and later a dependency of the Empire of Japan that ruled from 1895 to 1945.