
A midshipman fish is any species of toadfish belonging to the genus Porichthys. Historically, there have been two common names. Porichthys refers to the well developed pores on the fish, and this led to the common name "Porous Catfish". The other common name, "Midshipman" is based on the pattern of button-like luminous spots (photophores) which resemble the buttons on the uniforms of young naval officers known as midshipmen.

Amphibious fish are fish that are able to leave water for extended periods of time. About 11 distantly related genera of fish are considered amphibious. This suggests that many fish genera independently evolved amphibious traits, a process known as convergent evolution. These fish use a range of methods for land movement, such as lateral undulation, tripod-like walking, and jumping. Many of these methods of locomotion incorporate multiple combinations of pectoral-, pelvic-, and tail-fin movement.
Asymbolus is a genus of catsharks in the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks.
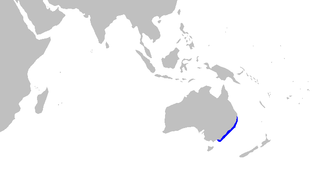
The Australian spotted catshark is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. This species is found only around Australia between 32 and 38°S, at depths between 10 and 180 m. It can grow up to 90 cm (35 in). Females of this species were observed as being reproductive year round. They are also confirmed as being a single oviparous species.
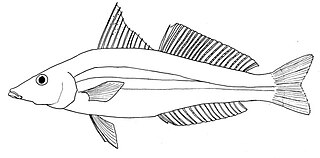
The golden lined whiting, also known as the Tin Can Bay whiting or rough-scale whiting, is a species of inshore marine fish of the smelt whiting family, Sillaginidae that inhabits the coastlines of northern Australia and lower Papua New Guinea. The golden lined whiting can be more readily distinguished by its colour than other whitings in the genus Sillago, although swim bladder morphology and spine and ray counts are the most precise method of identification. S. analis is an opportunistic predator, taking a variety of crustaceans, polychaetes and molluscs, with a transition of diet seen as the fish mature. One unusual aspect about the species diet is the large amounts of molluscan siphons it takes. The species spawns between January and March, with juvenile fish inhabiting the shallow protected coastal waters. Golden lined whiting is important to fisheries centered on Shark Bay in Western Australia and also in Queensland, although makes up a relatively minor component of the whiting fishery.

The mutton snapper is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a snapper belonging to the family Lutjanidae. It is found in the Western Atlantic Ocean.
Yunnanilus analis is a species of ray-finned fish, a stone loach, in the genus Yunnanilus. The type locality is Xingyun Lake in Yunnan, southern China. The specific name analis means "of the anus" and refers to the six branched rays in the anal fin, a unique feature among the species classified under Yunnanilus.

Anchoa is a genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Engraulidae. It currently consists of 35 species.

Clinocottus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. They are nearshore benthic fishes native to the northeastern Pacific Ocean. They are mentioned as sharpnose sculpins.

The yellow chromis, also known as the yellow puller, is a species of marine fish in the family Pomacentridae. It is widespread throughout the tropical waters of the central Indo-Pacific region. A small fish, it can reach a maximum size of 17 cm in length.

The woolly sculpin is a species of ray-finned marine fish belonging to the family Cottidae, or the typical sculpins. It is found in the eastern Pacific Ocean, where it occurs along the coastline of California south to Baja California.
Parascombrops pellucidus is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae.
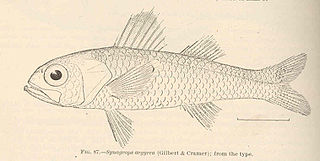
Parascombrops argyreus is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae. They usually live in waters 168–620 metres (551–2,034 ft) deep.

Parascombrops philippinensis, the sharptooth seabass, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae. It usually inhabits a depth of 180–220 metres and lives in and around the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, where it reaches a length of around 13 centimetres.
Parascombrops serratospinosus, the roughspine seabass is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae. It is found in the Western Pacific commonly from Taiwan and the Philippines to northwestern Australia and Vanuatu but it is rare in the waters off Japan

Parascombrops spinosus, the keelcheek bass, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae. It is native to the western Atlantic Ocean from Canada to Uruguay.
Selenanthias is a genus of fish in the family Serranidae native to the western and central Pacific Ocean.

Paracombrops is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes from the family Synagropidae. The fish in this genus are found in the Indo-Pacific.
Abantennarius analis, the tailjet frogfish, tailjet anglerfish or dwarf frogfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. This species is found in the eastern Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Icelus uncinalis, is a marine fish in the family Cottidae. It can be found throughout the Northeast Pacific, Bering Sea and Alaska.












