
Gadiformes, also called the Anacanthini, are an order of ray-finned fish that include the cod, hakes, pollock, haddock, burbot, rocklings and moras, many of which are food fish of major commercial value. They are mostly marine fish found throughout the world and the vast majority are found in temperate or colder regions while a few species may enter brackish estuaries. Pacific tomcods, one of the two species that makes up the genus Microgadus, are able to enter freshwater, but there is no evidence that they breed there. Some populations of landlocked Atlantic tomcod on the other hand, complete their entire life cycle in freshwater. Yet only one species, the burbot, is a true freshwater fish.

The beardfishes consist of a single extant genus, Polymixia, of deep-sea marine ray-finned fish named for their pair of long hyoid barbels. They are classified in their own order Polymixiiformes. But as Nelson says, "few groups have been shifted back and forth as frequently as this one, and they were recently added to Paracanthoptergii". For instance, they have previously been classified as belonging to the Beryciformes, and are presently considered either paracanthopterygians or the sister group to acanthopterygians. They are of little economic importance.

Acropomatidae is a family of ray-finned fish in the order Acropomatiformes, commonly known as lanternbellies. Acropoma species are notable for having light-emitting organs along their undersides. They are found in all temperate and tropical oceans, usually at depths of several hundred meters. There are about 32 species in as many as 9 genera, although some authorities recognise fewer genera than Fishbase does.

The viviparous brotulas form a family, the Bythitidae, of ophidiiform fishes. They are known as viviparous brotulas as they generally bear live young, although there are indications that some species do not. They are generally infrequently seen, somewhat tadpole-like in overall shape and mostly about 5–10 cm (2–4 in) in length, but some species grow far larger and may surpass 60 cm (2 ft).

Amblyeleotris is a genus of fish in the family Gobiidae found throughout the Indo-Pacific region. This is the largest genus of the shrimp gobies or prawn gobies, so-called because of their symbiotic relationship with certain alpheid shrimps. The shrimp excavates and maintains a burrow used by both animals while the goby, which has far superior eyesight, acts as a lookout for predators. The shrimp maintains almost constant contact with the fish with an antenna. Fossil Amblyeleotris otoliths have been found together with alpheid shrimp remnants from as early as late early Miocene (Burdigalian) suggesting a possible mutualistic association since then.

Ogilbia is a genus of viviparous brotulas. The generic name honours the Australian naturalist James Douglas Ogilby (1853-1925), for his contribution to the knowledge of the fishes of Australia.

Dysomma is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. These eels are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

The spotted seabass is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Moronidae, the temperate basses. This species is found in the marine and brackish waters of the coastal eastern Atlantic Ocean from the English Channel to the Canary Islands and Senegal, as well as through the Mediterranean Sea.

Polymixia is the only extant genus of the order Polymixiiformes and family Polymixiidae. It contains 10 species, all of which live in deepwater marine environments. They are found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Indian and western Pacific Oceans. They are bottom-dwelling fish, found down to about 800 m (2,600 ft). Most are relatively small fish, although one species is over 40 cm (16 in) in length. They can be considered "living fossils" due to being the only surviving members of the once-diverse order Polymixiiformes.

Oneirodes is a genus of is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep sea anglerfishes. These predatory, deep-sea fishes are found around the world. This is the type genus, and the most speciose genus, of the family Oneirodidae. They are sexually dimorphic but, like most taxa within their family, the small males are free living and are not sexual parasites on the larger females. Only the females are used to identify the species in this genus as no species specific charaxcters have been found for males.
Eusurculus are fish species of viviparous brotula.
Majungaichthys is a genus of viviparous brotulas native to the western Indian Ocean. The generic name refers to Majunga in Madagascar where the type was collected.
Mascarenichthys is a genus of viviparous brotulas. They have mostly been collected from the region of Mascarene Plateau in the Indian Ocean and this is referred to in their generic name.
Ogilbichthys is a genus of viviparous brotulas found in the central-western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. The generic name refers to the resemblance of these fish to those in the genus Ogilbia, a name honours the Australian naturalist James Douglas Ogilby (1853-1925), combined with ichthys which means "fish" in Greek.

Malakichthys is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Malakichthyidae. They are native to the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.
Parascombrops analis, the threespine seabass, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae.
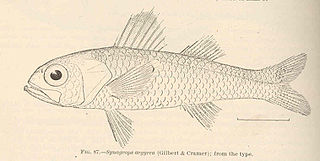
Parascombrops argyreus is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae. They usually live in waters 168–620 metres (551–2,034 ft) deep.
The thinlip splitfin is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae. It lives around Africa's Atlantic coast at a depth of 50–500 m and can grow up to 16.5 cm long.

Parascombrops philippinensis, the sharptooth seabass, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae. It usually inhabits a depth of 180–220 metres and lives in and around the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, where it reaches a length of around 13 centimetres.
Parascombrops serratospinosus, the roughspine seabass is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Synagropidae. It is found in the Western Pacific commonly from Taiwan and the Philippines to northwestern Australia and Vanuatu but it is rare in the waters off Japan












