
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at 419.2 million years ago (Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at 358.9 Ma. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied.

The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

The lycophytes, when broadly circumscribed, are a group of vascular plants that include the clubmosses. They are sometimes placed in a division Lycopodiophyta or Lycophyta or in a subdivision Lycopodiophytina. They are one of the oldest lineages of extant (living) vascular plants; the group contains extinct plants that have been dated from the Silurian. Lycophytes were some of the dominating plant species of the Carboniferous period, and included the tree-like Lepidodendrales, some of which grew over 40 metres (130 ft) in height, although extant lycophytes are relatively small plants.

The embryophytes are a clade of plants, also known as Embryophyta or land plants. They are the most familiar group of photoautotrophs that make up the vegetation on Earth's dry lands and wetlands. Embryophytes have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of freshwater charophyte green algae as a sister taxon of Charophyceae, Coleochaetophyceae and Zygnematophyceae. Embryophytes consist of the bryophytes and the polysporangiophytes. Living embryophytes include hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms. Embryophytes have diplobiontic life cycles.

A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, such as a hand lens, is referred to as a macrofossil.

Charophyta is a group of freshwater green algae, called charophytes, sometimes treated as a division, yet also as a superdivision or an unranked clade. The terrestrial plants, the Embryophyta emerged deep within Charophyta, possibly from terrestrial unicellular charophytes, with the class Zygnematophyceae as a sister group.

Equisetidae is one of the four subclasses of Polypodiopsida (ferns), a group of vascular plants with a fossil record going back to the Devonian. They are commonly known as horsetails. They typically grow in wet areas, with whorls of needle-like branches radiating at regular intervals from a single vertical stem.

The Rhynie chert is a Lower Devonian sedimentary deposit exhibiting extraordinary fossil detail or completeness. It is exposed near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; a second unit, the Windyfield chert, is located some 700 m away. The Rhynie chert contains exceptionally preserved plant, fungus, lichen and animal material preserved in place by an overlying volcanic deposit. The bulk of the Devonian fossil bed consists of primitive plants, along with arthropods, lichens, algae and fungi.

Cooksonia is an extinct group of primitive land plants, treated as a genus, although probably not monophyletic. The earliest Cooksonia date from the middle of the Silurian ; the group continued to be an important component of the flora until the end of the Early Devonian, a total time span of 433 to 393 million years ago. While Cooksonia fossils are distributed globally, most type specimens come from Britain, where they were first discovered in 1937. Cooksonia includes the oldest known plant to have a stem with vascular tissue and is thus a transitional form between the primitive non-vascular bryophytes and the vascular plants.

The zosterophylls are a group of extinct land plants that first appeared in the Silurian period. The taxon was first established by Banks in 1968 as the subdivision Zosterophyllophytina; they have since also been treated as the division Zosterophyllophyta or Zosterophyta and the class or plesion Zosterophyllopsida or Zosteropsida. They were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and had a world-wide distribution. They were probably stem-group lycophytes, forming a sister group to the ancestors of the living lycophytes. By the late Silurian a diverse assemblage of species existed, examples of which have been found fossilised in what is now Bathurst Island in Arctic Canada.
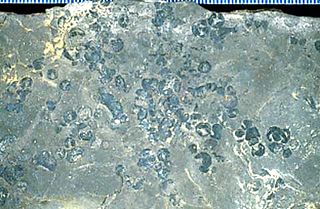
Protosalvinia is a prehistoric plant found commonly in shale from shoreline habitats of the Upper Devonian period. The name Protosalvinia is a misnomer. The name literally means early Salvinia, and was given in the erroneous belief that the fossils were an earlier form of the living aquatic fern Salvinia. It is no longer believed that the fossils come from a fern, but deciding exactly what the fossils represent is still a matter of debate.

Asteroxylon is an extinct genus of vascular plants of the Division Lycopodiophyta known from anatomically preserved specimens described from the famous Early Devonian Rhynie chert and Windyfield chert in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. Asteroxylon is considered a basal member of the Lycopsida.

The evolution of plants has resulted in a wide range of complexity, from the earliest algal mats of unicellular archaeplastids evolved through endosymbiosis, through multicellular marine and freshwater green algae, to spore-bearing terrestrial bryophytes, lycopods and ferns, and eventually to the complex seed-bearing gymnosperms and angiosperms of today. While many of the earliest groups continue to thrive, as exemplified by red and green algae in marine environments, more recently derived groups have displaced previously ecologically dominant ones; for example, the ascendance of flowering plants over gymnosperms in terrestrial environments.

Nematothallus is a form genus comprising cuticle-like fossils. Some of its constituents likely represent red algae, whereas others resemble lichens.

Polysporangiophytes, also called polysporangiates or formally Polysporangiophyta, are plants in which the spore-bearing generation (sporophyte) has branching stems (axes) that bear sporangia. The name literally means 'many sporangia plant'. The clade includes all land plants (embryophytes) except for the bryophytes whose sporophytes are normally unbranched, even if a few exceptional cases occur. While the definition is independent of the presence of vascular tissue, all living polysporangiophytes also have vascular tissue, i.e., are vascular plants or tracheophytes. Extinct polysporangiophytes are known that have no vascular tissue and so are not tracheophytes.
This article attempts to place key plant innovations in a geological context. It concerns itself only with novel adaptations and events that had a major ecological significance, not those that are of solely anthropological interest. The timeline displays a graphical representation of the adaptations; the text attempts to explain the nature and robustness of the evidence.

Fungi diverged from other life around 1.5 billion years ago, with the glomaleans branching from the "higher fungi" (dikaryans) at ~570 million years ago, according to DNA analysis. Fungi probably colonized the land during the Cambrian, over 500 million years ago,, and possibly 635 million years ago during the Ediacaran, but terrestrial fossils only become uncontroversial and common during the Devonian, 400 million years ago.
Discalis is a genus of extinct vascular plants of the Early Devonian. The name is derived from the Greek δίσκος, referring to the disc-shaped sporangia. The genus was first described by Hao in 1989 based on fossil specimens from the Posongchong Formation, Wenshan district, Yunnan, China.
Yarravia is a genus of extinct vascular plants mainly known from fossils found in Victoria, Australia. Originally the rocks in which they were found were considered to be late Silurian in age; more recently they have been found to be Early Devonian. Specimens consist only of incomplete leafless stems, some of which bore groups of spore-forming organs or sporangia which were fused, at least at the base.

The Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution, also known as the Devonian Plant Explosion (DePE) and the Devonian explosion, was a period of rapid colonization, diversification and radiation of land plants and fungi on dry lands that occurred 428 to 359 million years ago (Mya) during the Silurian and Devonian periods, with the most critical phase occurring during the Late Silurian and Early Devonian.

















