
Albania is a country in southeastern Europe that lies along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas, with a coastline spanning approximately 476 km (296 mi). Situated on the Balkan Peninsula, it is one of the most mountainous countries in Europe. It is bounded by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east and Greece to the southeast and south.

Tourism in Albania has been a key element to the country's economic activity and is constantly developing. Albania is characterized by its rich archaeological and cultural heritage dating back to the classical period when Illyrians and Ancient Greeks inhabited the region. Over the course of history, the territory of Albania was occupied and populated by Romans, Byzantines, Venetians and Ottomans. Notably the country features unspoiled beaches, mountainous landscapes, traditional cuisine, archaeological artifacts, unique traditions, low prices and the wild atmosphere of the countryside.

Barrier islands are a coastal landform, a type of dune system and sand island, where an area of sand has been formed by wave and tidal action parallel to the mainland coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of anything from a few islands to more than a dozen. They are subject to change during storms and other action, but absorb energy and protect the coastlines and create areas of protected waters where wetlands may flourish. A barrier chain may extend for hundreds of kilometers, with islands periodically separated by tidal inlets. The largest barrier island in the world is Padre Island of Texas, United States, at 113 miles (182 km) long. Sometimes an important inlet may close permanently, transforming an island into a peninsula, thus creating a barrier peninsula, often including a beach, barrier beach. Though many are long and narrow, the length and width of barriers and overall morphology of barrier coasts are related to parameters including tidal range, wave energy, sediment supply, sea-level trends, and basement controls. The amount of vegetation on the barrier has a large impact on the height and evolution of the island.

Sazan is an Albanian uninhabited island in the Mediterranean Sea. The largest of Albania's islands, it is a designated military exclusion zone; it lies in a strategically important location between the Strait of Otranto and the mouth of the Bay of Vlorë, marking the border between the Adriatic and Ionian seas.

The littoral zone, also called litoral or nearshore, is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark, to coastal areas that are permanently submerged — known as the foreshore — and the terms are often used interchangeably. However, the geographical meaning of littoral zone extends well beyond the intertidal zone to include all neritic waters within the bounds of continental shelves.

Butrint National Park is a national park in Vlorë County, southern Albania. It is located 18 kilometres (11 mi) south of Sarandë. The park encompasses 9,424 hectares (94.24 km2) of hilly terrain with freshwater lakes, wetlands, salt marshes, open plains, reed beds and islands. The park's significance for conservation is reflected in the large number of species with over 1,200 different animals and plants. Its mandate includes the protection of the lake and lagoon of Butrint, the natural channel of Vivari, the islands of Ksamil and as well the archaeological site, that provides valuable remains of ancient civilisations.

Narta Lagoon is a lagoon of the Adriatic Sea on the Mediterranean Sea in the central coast of Albania. The lagoon extends north of the Bay of Vlorë on the eastern shore of the Strait of Otranto and is separated from the sea by a narrow littoral strip, consisting of an alluvial dune. It has a surface area of 41.8 km2 (16.1 sq mi) with a maximal depth of 1.5 m (4.9 ft).
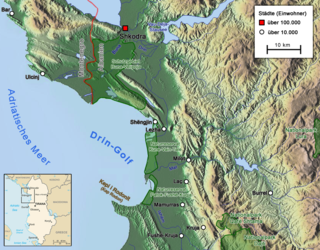
The Gulf of Drin or Bay of Drin is an ocean basin of the Adriatic Sea within the Mediterranean Sea along the northern coast of Albania. Roughly scythe-shaped, it extends immediately from the Delta of the Buna in the north, across the port city of Shëngjin, to the Cape of Rodon in the south. The shoreline of the gulf is a shallow combination of sandy beaches, sand dunes, capes, salty and fresh water wetlands, estuaries, pine and coastal forests, reed beds and coastal meadows.
Akyatan Lagoon is a 14700-hectare wetland ecosystem that is designated as Wetland of International Importance by Ramsar Convention. A major stopover for migrating birds, Akyatan is recognized as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International. It is the single largest green turtle rookery at the Mediterranean, holding 43% of the Mediterranean nesting population.

Karaburun-Sazan Marine Park is a marine park in the Vlorë County of southwestern Albania. The marine park encompasses over 125.70 km2 (48.53 sq mi) and comprises the boundaries of both the Peninsula of Karaburun and the Island of Sazan. It is home to a vast array of landforms, including mountains, caves, islands, depressions, bays, cliffs, canyons and rocky coasts, all contributing to an exceptionally considerable biological diversity. The marine park has been identified as an Important Bird and Plant Area, because it supports immense bird and plant species. Containing ecosystems and habitats that are specific to the Mediterranean Basin, the convention of Barcelona has classified the marine park as a Specially Protected Areas of Mediterranean Importance.

For a small country, Albania is characterised by a considerable wealth of terrestrial and marine ecosystems and habitats with contrasting floral, faunal, and fungal species, defined in an area of 28,748 square kilometres. Most of the country is predominantly of Mediterranean character, comprehending the country's center and south, while the alpine affinity is more visible in the northeast.

Prespa National Park is a national park situated in southeastern Albania on the border triangle shared with Greece and North Macedonia. At approximately 277.5 km2 (107.1 sq mi), the park encompasses the country's sections of the Great and Small Prespa Lake. It is considerably characterised by high mountains, narrow islands, vast freshwater wetlands, salt marshes, meadows, reed beds and dense forests.

Divjakë-Karavasta National Park is a national park in western Albania, sprawling across the Myzeqe Plain in the direct proximity to the Adriatic Sea. The park spans a territory of 222.3 square kilometres (22,230 ha) containing remarkable features such as wetlands, salt marshes, coastal meadows, floodplains, woodlands, reed beds, forests and estuaries. Because of the park's important and great availability of bird and plant species, it has been identified as an important Bird and Plant Area of international importance.

The Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast stretches in the south-eastern Adriatic Sea beginning at the Gulf of Drin in the north, across the port cities of Shëngjin, Durrës, and Vlorë, to the Bay of Vlorë in the south, where the Albanian Riviera and the Albanian Ionian Sea Coast begin.

The Albanian Ionian Sea Coast is a coastline of the north-eastern Ionian Sea, that encompasses the south-western border of the Republic of Albania, stretching from the southern half of Karaburun Peninsula, across the historical region of Labëria, the city of Sarandë, the mountains of the Ceraunians, and the Albanian Riviera, to the Lake of Butrint, where the Strait of Corfu separates the country from Greece.

The Buna River-Velipojë Protected Landscape is a protected landscape area in northwestern Albania, encompassing the estuary of Drin, the lagoon of Viluni, the river of Buna with its estuary, and the gulf of Drin that runs across the city of Velipojë alongside the Adriatic Sea.

The Canyon of Gjipe is a bay and calcareous canyon located between Dhërmi and Vuno carved by the Ionian Sea in Vlorë County, Albania. The canyon occupies a length of 800 metres (2,600 ft) and a width that can varies between 10 metres (33 ft) and 20 metres (66 ft). It represents a narrow strait, created by the activity of the brook flowing through its narrow pass. There are numerous rock formations along the canyon, including a number of caves.
Sri Lanka exhibits a remarkable biological diversity and is considered to be the richest country in Asia in terms of species concentration.

The Étang de Palo is a coastal lagoon beside the Tyrrhenian Sea in the Haute-Corse department on the French island of Corsica. The lagoon is largely unspoiled and is considered ecologically valuable.





















