
Starfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea. Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish are also known as asteroids due to being in the class Asteroidea. About 1,900 species of starfish live on the seabed in all the world's oceans, from warm, tropical zones to frigid, polar regions. They are found from the intertidal zone down to abyssal depths, at 6,000 m (20,000 ft) below the surface.

The Forcipulatida are an order of sea stars, containing three families and 49 genera.

Lepetodrilus sp. East Scotia Ridge is an as yet undescribed species of small, deep-sea sea snail, a hydrothermal vent limpet, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Lepetodrilidae.

Kiwa tyleri, the Hoff crab, is a species of deep-sea squat lobster in the family Kiwaidae, which lives on hydrothermal vents near Antarctica. The crustacean was given its English nickname in 2010 by UK deep-sea scientists aboard the RRS James Cook, owing to resemblance between its dense covering of setae on the ventral surface of the exoskeleton and the hairy chest of the actor David Hasselhoff. The 2010 expedition to explore hydrothermal vents on the East Scotia Ridge was the second of three expeditions to the Southern Ocean by the UK led research consortium, ChEsSo.

Hippasteria is one of 70 genera of sea stars in the diverse family Goniasteridae.

Fromia monilis, common name necklace starfish or tiled starfish, is a species of starfish belonging to the family Goniasteridae.

Iconaster longimanus, the icon star or double star, is a species of starfish in the family Goniasteridae. It is found in the west and central Indo-Pacific Ocean. The genus name comes from the Greek eikon, meaning portrait or image and possibly referring to the way the marginal plates frame the disc, and aster, meaning star. The specific name comes from the Latin longus manus and refers to the long, slender arms.

Sea star wasting disease or starfish wasting syndrome is a disease of starfish and several other echinoderms that appears sporadically, causing mass mortality of those affected. There are approximately 40 species of sea stars that have been affected by this disease. At least 20 of these species were on the Northwestern coast of Mexico to Alaska. The disease seems to be associated with increased water temperatures in some locales, but not others. It starts with the emergence of lesions, followed by body fragmentation and death. In 2014 it was suggested that the disease is associated with a single-stranded DNA virus now known as the sea star-associated densovirus (SSaDV). However, this hypothesis was refuted by recent research in 2018 and 2020. Sea star wasting disease is still not fully understood.
Trophodiscus almus is a species of starfish in the family Astropectinidae. It is found in fairly deep waters in the Sea of Okhotsk, the Sea of Japan and around the Japanese island of Hokkaido. It is very unusual among starfish in that it broods its young on its upper surface. Its common name in Japanese is "Komochi-momiji".
Trophodiscus is a genus of starfish in the family Astropectinidae. There are only two species, both found in fairly deep waters in the Sea of Okhotsk. Trophodiscus almus is also found in the Sea of Japan and around the Japanese island of Hokkaido. These starfish are very unusual in that the young are brooded on the upper surface of the female.

Pterasteridae is a family of sea stars in the order Velatida, consisting of eight genera.
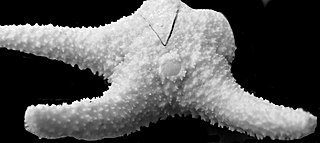
Bathyporania ascendens is a species of starfish in the family Poraniidae, and the only species of the genus Bathyporania. It is native to the Pacific Ocean and is found in deep water off the coast of North America.

Clavaporania fitchorum is a species of starfish in the family Poraniidae. It is the only known species of the genus Clavaporania. It is native to the South Pacific Ocean and is found in deep water off the coast of Australia.

Evoplosoma is a genus of deep-sea sea star in the family Goniasteridae.
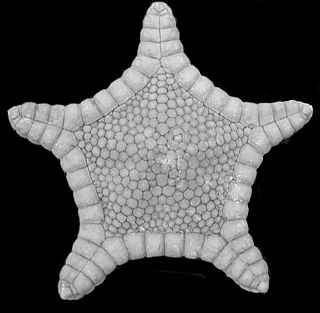
Astroceramus is a genus of abyssal sea stars in the family Goniasteridae.

Apollonaster is a genus of abyssal sea stars in the family Goniasteridae. They can be identified by their bare abactinal plate surfaces and multiple accessory granule rows on their abactinal plates. To date, Apollonaster has been found in the tropical Atlantic region and Hawaiian Islands region oceans, with no other locations or species being known as of 2015.

Hippasteria muscipula is one of twelve species of deep-sea sea star in the genus Hippasteria, which is in the family Goniasteridae.
Parvulastra vivipara, the Tasmanian live-bearing seastar, is a tiny, uniformly orange-yellow seastar, up to 15 mm (0.6 in) across. The species usually has five short arms and is a rounded, pentagon shape. Morphological variation is common and three, four or six arms are occasionally present. It is endemic to coastal waters in southeast Tasmania.
Paulasterias tyleri is a species of starfish in the family Paulasteriidae. It is found in deep water at hydrothermal vents in the Antarctic. It is the type species of the newly erected genus Paulasterias, the only other member of the genus being Paulasterias mcclaini.

Asterodiscides truncatus, the firebrick starfish, is a species of five-armed starfish in the family Asterodiscididae. It is native to eastern and southern Australia, the Norfolk Ridge and the Kermadec Islands of New Zealand.















