Related Research Articles

A road is a thoroughfare for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles and pedestrians. Unlike streets, whose primary function is to serve as public spaces, the main function of roads is transportation.

A sidewalk, pavement, footpath in Australia, India, New Zealand and Ireland, or footway is a path along the side of a road. Usually constructed of concrete, pavers, brick, stone, or asphalt, it is designed for pedestrians. A sidewalk is normally higher than the roadway, and separated from it by a kerb. There may also be a planted strip between the sidewalk and the roadway and between the roadway and the adjacent land.
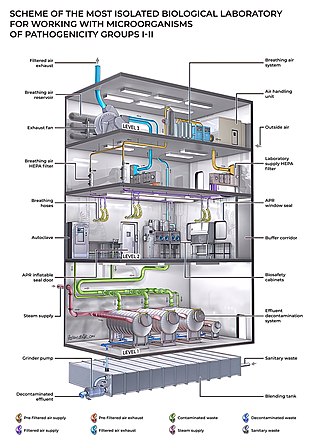
A biosafety level (BSL), or pathogen/protection level, is a set of biocontainment precautions required to isolate dangerous biological agents in an enclosed laboratory facility. The levels of containment range from the lowest biosafety level 1 (BSL-1) to the highest at level 4 (BSL-4). In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have specified these levels in a publication referred to as BMBL. In the European Union, the same biosafety levels are defined in a directive. In Canada the four levels are known as Containment Levels. Facilities with these designations are also sometimes given as P1 through P4, as in the term P3 laboratory.

A pedestrian crossing is a place designated for pedestrians to cross a road, street or avenue. The term "pedestrian crossing" is also used in the Vienna and Geneva Conventions, both of which pertain to road signs and road traffic.

A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, whether walking or running. In modern times, the term usually refers to someone walking on a road or pavement, but this was not the case historically. Pedestrians may also be wheelchair users or other disabled people who use mobility aids.

A street is a public thoroughfare in a built environment. It is a public parcel of land adjoining buildings in an urban context, on which people may freely assemble, interact, and move about. A street can be as simple as a level patch of dirt, but is more often paved with a hard, durable surface such as tarmac, concrete, cobblestone or brick. Portions may also be smoothed with asphalt, embedded with rails, or otherwise prepared to accommodate non-pedestrian traffic.
Pamela is a given name and, rarely, a surname.

Permeable paving surfaces are made of either a porous material that enables stormwater to flow through it or nonporous blocks spaced so that water can flow between the gaps. Permeable paving can also include a variety of surfacing techniques for roads, parking lots, and pedestrian walkways. Permeable pavement surfaces may be composed of; pervious concrete, porous asphalt, paving stones, or interlocking pavers. Unlike traditional impervious paving materials such as concrete and asphalt, permeable paving systems allow stormwater to percolate and infiltrate through the pavement and into the aggregate layers and/or soil below. In addition to reducing surface runoff, permeable paving systems can trap suspended solids, thereby filtering pollutants from stormwater.

A living street is a street designed with the interests of pedestrians and cyclists in mind by providing enriching and experiential spaces. Living streets also act as social spaces, allowing children to play and encouraging social interactions on a human scale, safely and legally. Living streets consider all pedestrians granting equal access to elders and those who are disabled. These roads are still available for use by motor vehicles; however, their design aims to reduce both the speed and dominance of motorized transport. The reduction of motor vehicle dominance creates more opportunities for public transportation.

The Thomas J. Watson Research Center is the headquarters for IBM Research. Its main laboratory is in Yorktown Heights, New York, 38 miles (61 km) north of New York City. It also operates facilities in Cambridge, Massachusetts and Albany, New York.

A greenway is usually a shared-use path along a strip of undeveloped land, in an urban or rural area, set aside for recreational use or environmental protection. Greenways are frequently created out of disused railways, canal towpaths, utility company rights of way, or derelict industrial land. Greenways can also be linear parks, and can serve as wildlife corridors. The path's surface may be paved and often serves multiple users: walkers, runners, bicyclists, skaters and hikers. A characteristic of greenways, as defined by the European Greenways Association, is "ease of passage": that is that they have "either low or zero gradient", so that they can be used by all "types of users, including mobility impaired people".

Shared space is an urban design approach that minimises the segregation between modes of road user. This is done by removing features such as curbs, road surface markings, traffic signs, and traffic lights. Hans Monderman and others have suggested that, by creating a greater sense of uncertainty and making it unclear who has priority, drivers will reduce their speed, in turn reducing the dominance of vehicles, reducing road casualty rates, and improving safety for other road users.

A curb or kerb is the edge where a raised sidewalk or road median/central reservation meets a street or other roadway.

Tactile paving is a system of textured ground surface indicators found at roadsides, by and on stairs, and on railway station platforms, to assist pedestrians who are vision impaired.

Biolab is a single-rack multi-user science payload designed for use in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station. Biolab support biological research on small plants, small invertebrates, microorganisms, animal cells, and tissue cultures. It includes an incubator equipped with centrifuges in which the preceding experimental subjects can be subjected to controlled levels of accelerations.

In urban planning, walkability is the accessibility of amenities by foot. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it should be relatively complete livable spaces that serve a variety of uses, users, and transportation modes and reduce the need for cars for travel.

A sett, also known as a block or Belgian block, is a broadly rectangular quarried stone used in paving roads and walkways. Formerly in widespread use, particularly on steeper streets because setts provided horses' hooves with better grip than a smooth surface, they are now encountered rather as decorative stone paving in landscape architecture. Setts are often referred to as "cobblestones", although a sett is distinct from a cobblestone in that it is quarried or worked to a regular shape, whereas the latter is generally a small, naturally-rounded rock. Setts are usually made of granite.
A walking audit is an assessment of the walkability or pedestrian access of an external environment. Walking audits are often undertaken in street environments to consider and promote the needs of pedestrians as a form of transport. They can be undertaken by a range of different stakeholders including:
The MIT Senseable City Laboratory is a digital laboratory within MIT's City Design and Development group, within the Department of Urban Studies and Planning, which works in collaboration with the MIT Media Lab. The lab aims to investigate and anticipate how digital technologies are changing the way people live and their implications at the urban scale.

Cycling infrastructure is all infrastructure cyclists are allowed to use. Bikeways include bike paths, bike lanes, cycle tracks, rail trails and, where permitted, sidewalks. Roads used by motorists are also cycling infrastructure, except where cyclists are barred such as many freeways/motorways. It includes amenities such as bike racks for parking, shelters, service centers and specialized traffic signs and signals. The more cycling infrastructure, the more people get about by bicycle.
References
- ↑ BBC NEWS | Science/Nature | Scientists walk on tech pavement
- ↑ "First custom-designed pedestrian accessibility lab launched".
- ↑ "PEARL Background Information Document" (PDF). UCL. Retrieved 23 May 2024.