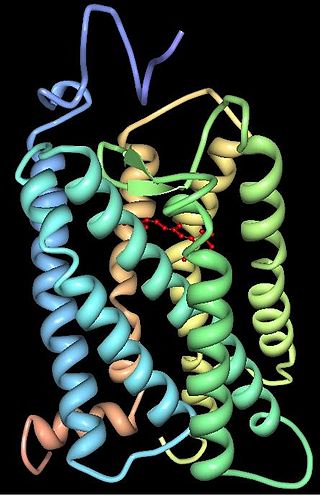
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction in rods. Rhodopsin mediates dim light vision and thus is extremely sensitive to light. When rhodopsin is exposed to light, it immediately photobleaches. In humans, it is regenerated fully in about 30 minutes, after which the rods are more sensitive. Defects in the rhodopsin gene cause eye diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa and congenital stationary night blindness.

Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a genetic disorder of the eyes that causes loss of vision. Symptoms include trouble seeing at night and decreasing peripheral vision. As peripheral vision worsens, people may experience "tunnel vision". Complete blindness is uncommon. Onset of symptoms is generally gradual and often begins in childhood.

Vitelliform macular dystrophy is an irregular autosomal dominant eye disorder which can cause progressive vision loss. This disorder affects the retina, specifically cells in a small area near the center of the retina called the macula. The macula is responsible for sharp central vision, which is needed for detailed tasks such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces. The condition is characterized by yellow, slightly elevated, round structures similar to the yolk of an egg.

The photoreceptor cell-specific nuclear receptor (PNR), also known as NR2E3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2E3 gene. PNR is a member of the nuclear receptor super family of intracellular transcription factors.

X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator is a GTPase-binding protein that in humans is encoded by the RPGR gene. The gene is located on the X-chromosome and is commonly associated with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). In photoreceptor cells, RPGR is localized in the connecting cilium which connects the protein-synthesizing inner segment to the photosensitive outer segment and is involved in the modulation of cargo trafficked between the two segments.

ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 4, also known as ABCA4 or ABCR, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ABCA4 gene.

Bestrophin-1 (Best1) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the BEST1 gene.

PRP31 pre-mRNA processing factor 31 homolog , also known as PRPF31, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PRPF31 gene.

Cone-rod homeobox protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRX gene.

Rod cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit beta is the beta subunit of the protein complex PDE6 that is encoded by the PDE6B gene. PDE6 is crucial in transmission and amplification of visual signal. The existence of this beta subunit is essential for normal PDE6 functioning. Mutations in this subunit are responsible for retinal degeneration such as retinitis pigmentosa or congenital stationary night blindness.

Crumbs homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRB1 gene.

Elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELOVL4 gene.

Tubby-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TULP1 gene.

Rod outer segment membrane protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ROM1 gene.

Oxygen-regulated protein 1 also known as retinitis pigmentosa 1 protein (RP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RP1 gene.

Cyclic nucleotide gated channel beta 1, also known as CNGB1, is a human gene encoding an ion channel protein.

Fascin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FSCN2 gene.

Retinal degeneration is a retinopathy which consists in the deterioration of the retina caused by the progressive death of its cells. There are several reasons for retinal degeneration, including artery or vein occlusion, diabetic retinopathy, R.L.F./R.O.P., or disease. These may present in many different ways such as impaired vision, night blindness, retinal detachment, light sensitivity, tunnel vision, and loss of peripheral vision to total loss of vision. Of the retinal degenerative diseases retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a very important example.
Retinal gene therapy holds a promise in treating different forms of non-inherited and inherited blindness.
Occult macular dystrophy (OMD) is a rare inherited degradation of the retina, characterized by progressive loss of function in the most sensitive part of the central retina (macula), the location of the highest concentration of light-sensitive cells (photoreceptors) but presenting no visible abnormality. "Occult" refers to the degradation in the fundus being difficult to discern. The disorder is called "dystrophy" instead of "degradation" to distinguish its genetic origin from other causes, such as age. OMD was first reported by Y. Miyake et al. in 1989.





















