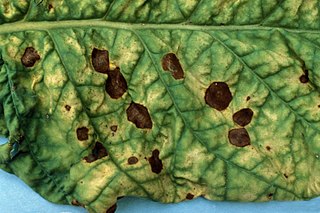
Alternaria alternata is a fungus causing leaf spots, rots, and blights on many plant parts, and other diseases. It is an opportunistic pathogen on over 380 host species of plant.
Cadophora malorum is a saprophytic plant pathogen that causes side rot in apple and pear and can also cause disease on asparagus and kiwifruit. C. malorum has been found parasitizing shrimp and other fungal species in the extreme environments of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, and can be categorized as a halophilic psychrotrophic fungus and a marine fungus.

Plasmopara viticola, the causal agent of grapevine downy mildew, is a heterothallic oomycete that overwinters as oospores in leaf litter and soil. In the spring, oospores germinate to produce macrosporangia, which under wet condition release zoospores. Zoospores are splashed by rain into the canopy, where they swim to and infect through stomata. After 7–10 days, yellow lesions appear on foliage. During favorable weather the lesions sporulate and new secondary infections occur.

Apple mosaic virus (ApMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Bromoviridae. It is named after its symptoms that were first present on apples. ApMV is a positive sense RNA based virus. The disease itself has several synonyms including Mild Apple Mosaic Virus, Hop Virus, Rose Mosaic Virus, and European Plum Line Patten Virus. It causes a severe yield reduction and decreased life-expectancy of fruit trees.
Copper pesticides are copper compounds used as bactericides, algaecides, or fungicides. They can kill bacteria, oomycetes and algae, and prevent fungal spores from germinating. Common forms of fixed copper fungicides include copper sulfate, copper sulfate pentahydrate, copper hydroxide, copper oxychloride sulfate, cuprous oxide, and copper octanoate.
Linear atrophoderma of Moulin, also known as Moulin atrophoderma linearis,) is an acquired unilateral dermatitis localized along the Blaschko lines. It affects children or adolescents of both genders, involving the trunk and the limbs. It is, presumably, a rare cutaneous form of mosaicism. This disease was first referred to as atrophoderma of Moulin after Dr. Moulin who first reported it in 1992 then was renamed as linear atrophoderma of Moulin. Only a few dozen cases have been described; for this reason, LAM is considered to be a very rare disorder.

Richard C. Summerbell is a Canadian mycologist, author and award-winning songwriter. He was editor in chief of an international scientific journal in mycology from 2000 to 2004. In the 1970s and 80s, he was a gay activist and an early commentator on (then) controversial topics such as AIDS and promiscuity and attitudes to homosexuality in organized religion.
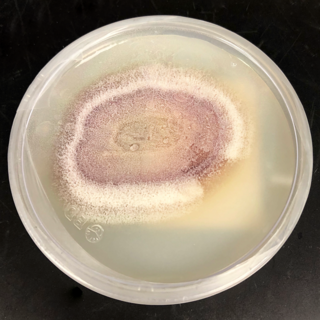
Phaeoacremonium is a fungus genus associated with wilt and decline diseases of woody hosts and human infections.
Bacterial blight of cotton is a disease affecting the cotton plant resulting from infection by Xanthomonas axonopodis pathovar malvacearum (Xcm) a Gram negative, motile rod-shaped, non spore-forming bacterium with a single polar flagellum

Esca is a grape disease of mature grapevines. It is a type of grapevine trunk disease.
Phaeomoniella is a genus of hyphomycete fungi in the family Celotheliaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Pedro Crous and Walter Gams in 2000 to contain the type species, P. chlamydospora, the causal agent of Petro grapevine decline, a disesase in the esca disease complex. Phaeomoniella is similar to Phaeoacremonium, differing in cultural characteristics, and in the morphology of the conidiophores and conidia.
Phaeoacremonium aleophilum is a fungus species in the genus Phaeoacremonium. It is associated with Phaeomoniella chlamydospora in esca in mature grapevines and decline in young vines, two types of grapevine trunk disease.
Grapevine trunk diseases (GTD) are the most destructive diseases of vineyards worldwide. Fungicides with the potential to control GTD have been banned in Europe and there are no highly effective treatments available. Action to develop new strategies to fight these diseases are needed.
Trunk injection or endotherapy also known as vegetative endotherapy, is a method of target-precise application of pesticides, plant resistance activators, or fertilizers into the xylem vascular tissue of a tree with the purpose of protecting the tree from pests, or to inject nutrients to correct for nutrient deficiencies. This method largely relies on harnessing the tree's vascular system to translocate and distribute the active compounds into the wood, canopy and roots where protection or nutrition is needed.
Marinomonas mediterranea is a lysogenic bacterium from the genus of Marinomonas which has been isolated from seawater from the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in Spain.
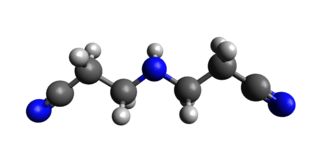
IDPN (3,3'-iminodipropanenitrile) is a neurotoxin with ototoxic and hepatotoxic effects. It causes irreversible movement disorder.
Garlic common latent virus (GarCLV) is a plant virus member of the genus Carlavirus that has been found infecting garlic globally. Detection of the virus in leek and onion has also been reported.
Ernest Charles Snow CBE was born in Woodford, Essex on 12 March 1886. He was educated at East London College. In 1902 Snow won an Open Mathematical Scholarship at The Queen’s College, Oxford.
Celotheliaceae is a family of fungi in the monotypic order Phaeomoniellales. It contains 27 species of crustose lichens with thalli that are more or less immersed in tree bark.

The 2020 table grape harvest was worth $2.12 billion while wine grapes brought in $1.7 billion, down 15.3% year-on-year. By weight this was 17% lower versus 2018. The next year, 2021 saw a much better yield. From 829,000 acres (335,000 ha) viniculturists got 6.94 short tons per acre (15.6 t/ha) for a total harvest of 5,755,000 short tons (5,221,000 t). At an average of $909 per short ton ($1,002/t) they were paid $5,229,902,000 for the season. Of that, 4,844,600 short tons (4,394,900 t) were for destined for processing industries and at $835 per short ton ($920/t) that was worth $4,046,382,000. The fresh harvest was 910,400 short tons (825,900 t) and selling at a price of $1,300 per short ton ($1,433/t), this sector was worth $1,183,520,000 for the season.







