
Dactylorhiza fuchsii, the common spotted orchid, is a species of flowering plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae.

Phalaenopsis, also known as moth orchids, is a genus of about seventy species of plants in the family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus are monopodial epiphytes or lithophytes with long, coarse roots, short, leafy stems and long-lasting, flat flowers arranged in a flowering stem that often branches near the end. Orchids in this genus are native to India, Taiwan, China, Southeast Asia, New Guinea and Australia with the majority in Indonesia and the Philippines.

The ornamental orchid species Phalaenopsis hieroglyphica is native to certain islands of the Philippines. Its flowers are creamy white with transverse markings that resemble glyphs. Through hybridization, growers have successfully created flowers with different shapes and colors while retaining the glyphs. Since 1975, the species has been protected under Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).

Phalaenopsis amabilis, commonly known as the moon orchid or moth orchid in India and as anggrek bulan in Indonesia, is a species of flowering plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae. It is native to the East Indies and Australia, and widely cultivated as a decorative houseplant. It is an epiphytic or lithophytic herb with long, thick roots, between two and eight thick, fleshy leaves with their bases hiding the stem and nearly flat, white, long-lasting flowers on a branching flowering stem with up to ten flowers on each branch.

Aphyllorchis, commonly known as pauper orchids or as 無葉蘭屬/无叶兰属 , is a genus of about twenty species of terrestrial leafless orchids in the family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus have fleshy, upright stems and small to medium-sized resupinate flowers with narrow sepals and petals. They are native to a region extending from India east to China and Japan, south to Indonesia, New Guinea and Queensland.

Sarcochilus, commonly known as butterfly orchids or fairy bells is a genus of about twenty species of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Most species are epiphytes but a few species only grow on rocks or in leaf litter. Orchids in this genus usually have short stems, leaves arranged in two rows and flowers arranged along unbranched flowering stems. Most species are endemic to Australia but some are found in New Guinea and New Caledonia.

Luisia, commonly known as velvet orchids or 钗子股属 , is a genus of epiphytic or lithophytic orchids in family Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus have flattened roots, long leafy stems, narrow, thick, leathery leaves and short-lived flowers that open sporadically. There are about forty species found from tropical and subtropical Asia to the Western Pacific.

Pholidota, commonly known as rattlesnake orchids, is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are clump-forming epiphytes or lithophytes with pseudobulbs, each with a single large leaf and a large number of small, whitish flowers arranged in two ranks along a thin, wiry flowering stem that emerges from the top of the pseudobulb. There are about thirty five species native to areas from tropical and subtropical Asia to the southwestern Pacific.

Dendrobium bigibbum, commonly known as the Cooktown orchid or mauve butterfly orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has cylindrical pseudobulbs, each with between three and five green or purplish leaves and arching flowering stems with up to twenty, usually lilac-purple flowers. It occurs in tropical North Queensland, Australia and New Guinea.

Phalaenopsis taenialis, also known as 小尖囊蝴蝶兰 in Chinese, is a species of epiphytic orchid occurring from the eastern Himalaya to China (Yunnan). The specific epthet taenialis is derived from the long, flattened roots, which resemble tapeworms. The specific epithet taenialis, from the Latin taenia, means ribbon or band.

Phalaenopsis deliciosa is a species of orchid occurring from the Indian subcontinent to Malesia and China. The species is a miniature epiphytic herb. The leaves are unique due to their undulate margins. This characteristic greatly simplifies the identification of the species, even when specimens are not currently flowering. The small flowers are usually slightly pink, but white and yellow forms exist as well. Old inflorescences, which are usually panicles or more rarely racemes, may continue to grow and form new flowers over several flowering periods.

Phalaenopsis lobbii, also known as 罗氏蝴蝶兰 in Chinese, is a species of orchid found from the eastern Himalaya to Indochina.It is named in honour of Cornish plant hunter Thomas Lobb. These epiphytic plants have aerial, fleshy, dorsiventrally flattened roots, which radiate from a short stem, which is inclosed by leaf petioles. The stem bears 3-5 slightly fleshy, thin leaves, which are commonly shed in winter. Some plants retain up to two leaves, but most exhibit deciduous leaflessness. Small flowers with reflexed petals of 1.5 cm in diameter are produced between March and May on racemose inflorescences. The midlobe of the labellum shows brown colouration. It is a rare species with extremely small population sizes. It is found in evergreen broad leaved forests on limestone at altitudes of 150–330 m.

Phalaenopsis tetraspis is a species of epiphytic orchid endemic to the Andaman Islands, the Nicobar Islands and northwestern Sumatra. It was originally erroneously published as a Himalayan species by Reichenbach, which was corrected by James Veitch 23 years after Heinrich Gustav Reichenbachs publication. Mature specimens may have up to nine leaves, but usually plants have 4–5, elliptic-obovate, acute to obtuse, 20 cm long and 8 cm wide leaves. Showy, fleshy, fragrant flowers are produced on axillary, arching to subpendent racemes or panicles. A prominent feature of this species is the midlobe of the labellum, which is oblong, obtuse-subacute, and the apex is covered in dense trichomes. The karyotype is asymmetric and nonuniform.

Phalaenopsis sanderiana is an orchid in the genus Phalaenopsis that is native to the Philippines. It was named in honour of M. Fredrick Sander. It is a pendant growing epiphyte with epileptic, rounded tip pendulous leaves. Inflorescence are showy of 15 to 20 on 32 inch long raceme.

Phalaenopsis japonica, also known as 萼脊兰 in Chinese, 나도풍란 (nadopungnan) in Korean and ナゴラン or 名護蘭 (nago-ran) in Japanese, is a species of epiphyte in the family Orchidaceae, native to open forests of China, Japan and Korea, occurring at altitudes of 600–1400 m. It also may grow lithophytically on cliffs along valleys. The 1 to 1.5 cm long stems bear 6–13 cm long and 2–3 cm wide, alternate leaves. Inflorescences are between 17 and 19 cm in length and bear flowers with whitish green, petals and sepals. The lateral sepals bear 1-3 transverse bands of dull brown spots on the adaxial surface. The midlobe is spotted purple to red. The horn-shaped spur ranges from 1.2 to 1.4 cm in length. The plants have four pollinia in two pairs, but previously they have been mistaken as two pollinia.

Phalaenopsis hygrochila, also known as 湿唇兰 in Chinese, is a species of epiphytic orchid native to Assam, Borneo, China South-Central, China Southeast, East Himalaya, Laos, Malaya, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sumatera, Thailand, Vietnam and West Himalaya. This species has a complex taxonomic history and has been previously assigned to several genera. The extensive list of synonyms may be explained by this species wide distribution, its early discovery and unusual morphology compared to other species of the genus Phalaenopsis.

Phalaenopsis corningiana is a species of orchid endemic to the island of Borneo.

Phalaenopsis marriottiana is a species of orchid native to Southeast China and Myanmar. The specific epithet marriottiana honours William Henry Smith-Marriott (1835-1924), who had a considerable orchid collection at Down House, Blandford, Dorsetshire in England.

Phalaenopsis pantherina, also known as the panther-like Phalaenopsis, is a species of orchid endemic to Borneo. The specific epithet pantherina is derived from the leopard-like floral colouration.
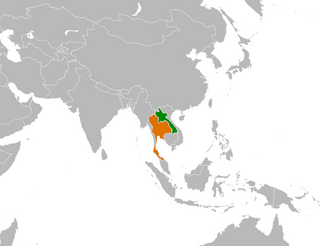
Phalaenopsis ubonensis, is a species of orchid native to Thailand and Laos. The specific epithet ubonensis refers to the Thai province Ubon.





















