
Phellodendron, or cork-tree, is a genus of deciduous, dioecious trees in the family Rutaceae, native to east and northeast Asia. It has leathery, pinnate leaves and yellow, clumped flowers. The name refers to the thick and corky bark of some species in the genus.

Papilio protenor, the spangle, is a butterfly found in South East Asia belonging to the swallowtail family.

Phellodendron amurense is a species of tree in the family Rutaceae, commonly called the Amur cork tree. It is a major source of huáng bò, one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine. The Ainu people used this plant, called shikerebe-ni, as a painkiller. It is known as hwangbyeok in Korean and (キハダ) kihada in Japanese.
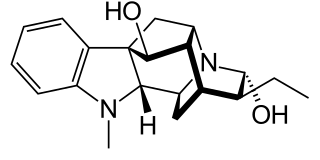
Ajmaline is an alkaloid that is classified as a 1-A antiarrhythmic agent. It is often used to induce arrhythmic contraction in patients suspected of having Brugada syndrome. Individuals suffering from Brugada syndrome will be more susceptible to the arrhythmogenic effects of the drug, and this can be observed on an electrocardiogram as an ST elevation.

Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, occurring naturally as a secondary metabolite in some plants including species of Berberis, from which its name is derived.
Porphyromonas gingivalis belongs to the phylum Bacteroidota and is a nonmotile, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, anaerobic, pathogenic bacterium. It forms black colonies on blood agar.

Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TYK2 gene.

Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LILRB1 gene.

T-box transcription factor TBX21, also called T-bet, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBX21 gene. Though being for long thought of only as a master regulator of type 1 immune response, T-bet has recently been shown to be implicated in development of various immune cell subsets and maintenance of mucosal homeostasis.

Transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13B (TNFRSF13B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF13B gene.

Phellamurin, a flavonoid, is the 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 8-C-prenyl derivative of the flavan-on-ol Aromadendrin, and may be seen as the 7-O-glucoside of noricaritin. Being a flavanonol, it has two stereocenters on the C-ring, so four stereoisomers of phellamurin are possible.
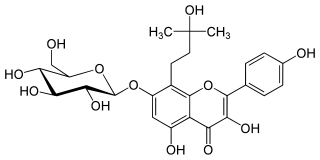
Amurensin is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is the tert-amyl alcohol derivative of kaempferol 7-O-glucoside. It can be found in Phellodendron amurense.

Huáng bǎi, huáng bó or huáng bò is one of the fifty fundamental herbs of traditional Chinese medicine. Known also as Cortex Phellodendri, it is the bark of one of two species of Phellodendron tree: Phellodendron amurense or Phellodendron chinense.
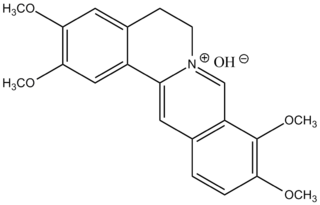
Palmatine is a protoberberine alkaloid found in several plants including Phellodendron amurense, Coptis Chinensis and Corydalis yanhusuo, Tinospora cordifolia, Tinospora sagittata, Phellodendron amurense, Stephania yunnanensis.

Furoquinoline alkaloids are a group of alkaloids with simple structure. Distribution of this group of alkaloids is essentially limited to plant family Rutaceae. The simplest member of this group is dictamnine and most widespread member is skimmianine.
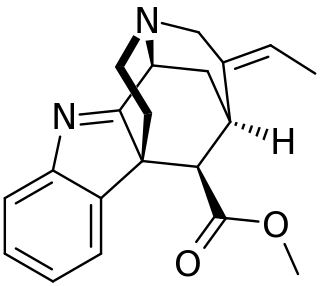
Strictamine is an alkaloid isolated from Alstonia scholaris.

Gigactonine is a naturally occurring diterpene alkaloid first isolated from Aconitum gigas. It occurs widely in the Ranunculaceae plant family. The polycyclic ring system of this chemical compound contains nineteen carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom, which is the same as in aconitine and this is reflected in its preferred IUPAC name.
Corydalis yanhusuo is a plant species in the genus Corydalis. The Chinese name for Corydalis yanhusuo is yan hu suo. The Japanese common name is engosaku (エンゴサク) and the Korean common name is hyeonhosaek (현호색). English common names include yanhusuo, corydalis, and Asian corydalis. The tuber of this plant, frequently mislabeled as the root, is an important therapeutic agent in traditional Chinese medicine. It is native to high-altitude grasslands across China including in the provinces of Anhui, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang, but is more widely cultivated.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid tricyclic indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of indole alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.

















