
Buckminsterfullerene is a type of fullerene with the formula C60. It has a cage-like fused-ring structure (truncated icosahedron) made of twenty hexagons and twelve pentagons, and resembles a football. Each of its 60 carbon atoms is bonded to its three neighbors.
Organic semiconductors are solids whose building blocks are pi-bonded molecules or polymers made up by carbon and hydrogen atoms and – at times – heteroatoms such as nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. They exist in the form of molecular crystals or amorphous thin films. In general, they are electrical insulators, but become semiconducting when charges are injected from appropriate electrodes or are introduced by doping or photoexcitation.
The 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is a chemical reaction between a 1,3-dipole and a dipolarophile to form a five-membered ring. The earliest 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions were described in the late 19th century to the early 20th century, following the discovery of 1,3-dipoles. Mechanistic investigation and synthetic application were established in the 1960s, primarily through the work of Rolf Huisgen. Hence, the reaction is sometimes referred to as the Huisgen cycloaddition. 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is an important route to the regio- and stereoselective synthesis of five-membered heterocycles and their ring-opened acyclic derivatives. The dipolarophile is typically an alkene or alkyne, but can be other pi systems. When the dipolarophile is an alkyne, aromatic rings are generally produced.

In organic chemistry, the Michael reaction or Michael 1,4 addition is a reaction between a Michael donor and a Michael acceptor to produce a Michael adduct by creating a carbon-carbon bond at the acceptor's β-carbon. It belongs to the larger class of conjugate additions and is widely used for the mild formation of carbon-carbon bonds.

The Prato reaction is a particular example of the well-known 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of azomethine ylides to olefins. In fullerene chemistry this reaction refers to the functionalization of fullerenes and nanotubes. The amino acid sarcosine reacts with paraformaldehyde when heated at reflux in toluene to an ylide which reacts with a double bond in a 6,6 ring position in a fullerene via a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition to yield a N-methylpyrrolidine derivative or pyrrolidinofullerene or pyrrolidino[[3,4:1,2]] [60]fullerene in 82% yield based on C60 conversion.

The Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidised, whereas the H2O2 is reduced.

Fullerene chemistry is a field of organic chemistry devoted to the chemical properties of fullerenes. Research in this field is driven by the need to functionalize fullerenes and tune their properties. For example, fullerene is notoriously insoluble and adding a suitable group can enhance solubility. By adding a polymerizable group, a fullerene polymer can be obtained. Functionalized fullerenes are divided into two classes: exohedral fullerenes with substituents outside the cage and endohedral fullerenes with trapped molecules inside the cage.
Organic photovoltaic devices (OPVs) are fabricated from thin films of organic semiconductors, such as polymers and small-molecule compounds, and are typically on the order of 100 nm thick. Because polymer based OPVs can be made using a coating process such as spin coating or inkjet printing, they are an attractive option for inexpensively covering large areas as well as flexible plastic surfaces. A promising low cost alternative to conventional solar cells made of crystalline silicon, there is a large amount of research being dedicated throughout industry and academia towards developing OPVs and increasing their power conversion efficiency.
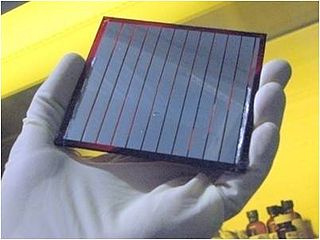
An organic solar cell (OSC) or plastic solar cell is a type of photovoltaic that uses organic electronics, a branch of electronics that deals with conductive organic polymers or small organic molecules, for light absorption and charge transport to produce electricity from sunlight by the photovoltaic effect. Most organic photovoltaic cells are polymer solar cells.

Hagemann's ester, ethyl 2-methyl-4-oxo-2-cyclohexenecarboxylate, is an organic compound that was first prepared and described in 1893 by German chemist Carl Hagemann. The compound is used in organic chemistry as a reagent in the synthesis of many natural products including sterols, trisporic acids, and terpenoids.

Polyfluorene is a polymer with formula (C13H8)n, consisting of fluorene units linked in a linear chain — specifically, at carbon atoms 2 and 7 in the standard fluorene numbering. It can also be described as a chain of benzene rings linked in para positions with an extra methylene bridge connecting every pair of rings.

Photoconductive atomic force microscopy (PC-AFM) is a variant of atomic force microscopy that measures photoconductivity in addition to surface forces.
The Buchner ring expansion is a two-step organic C-C bond forming reaction used to access 7-membered rings. The first step involves formation of a carbene from ethyl diazoacetate, which cyclopropanates an aromatic ring. The ring expansion occurs in the second step, with an electrocyclic reaction opening the cyclopropane ring to form the 7-membered ring.

Polymer-fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells are a type of solar cell researched in academic laboratories. Polymer-fullerene solar cells are a subset of organic solar cells, also known as organic photovoltaic (OPV) cells, which use organic materials as their active component to convert solar radiation into electrical energy. The polymer, which functions as the donor material in these solar cells, and fullerene derivatives, which function as the acceptor material, are essential components. Specifically, fullerene derivatives act as electron acceptors for donor materials like P3HT, creating a polymer-fullerene based photovoltaic cell. The Polymer-fullerene BHJ forms two channels for transferring electrons and holes to the corresponding electrodes, as opposed to the planar architecture when the Acceptor (A) and Donor (D) materials were sequentially stacked on top of each other and could selectively touch the cathode and anode electrodes. Hence, the D and A domains are expected to form a bi-continuous network with Nano-scale morphology for efficient charge transport and collection after exciton dissociation. Therefore, in the BHJ device architecture, a mixture of D and A molecules in the same or different solvents was used to form a bi-continual layer, which serves as the active layer of the device that absorbs light for exciton generation. The bi-continuous three-dimensional interpenetrating network of the BHJ design generates a greater D-A interface, which is necessary for effective exciton dissociation in the BHJ due to short exciton diffusion. When compared to the prior bilayer design, photo-generated excitons may dissociate into free holes and electrons more effectively, resulting in better charge separation for improved performance of the cell.
Diketopyrrolopyrroles (DPPs) are organic dyes and pigments based on the heterocyclic dilactam 2,5-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4-dione, widely used in optoelectronics. DPPs were initially used as pigments in the painting industry due to their high resistance to photodegradation. More recently, DPP derivatives have been also investigated as promising fluorescent dyes for bioimaging applications, as well as components of materials for use in organic electronics.

In organic chemistry, contorted aromatics, or more precisely contorted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in which the fused aromatic molecules deviate from the usual planarity.
Non-fullerene acceptors (NFAs) are types of acceptors used in organic solar cells (OSCs). The name Fullerene comes from another type of acceptor-molecule which was used as the main acceptor material for bulk heterojunction Organic solar cells. Non-fullerene acceptors are thus defined as not being a part of this sort of acceptors.
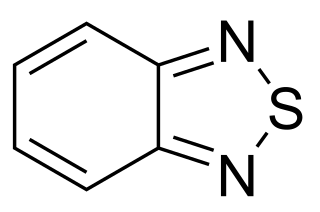
2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole is a bicyclic molecule composed of a benzene ring that is fused to a 1,2,5-thiadiazole.
André Taylor is an American scientist who is an associate professor of chemical engineering at the New York University Tandon School of Engineering. Taylor works on novel materials for energy conversion and storage. He was awarded the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers in 2010, and named as one of The Community of Scholars' Most Influential Black Researchers of 2020.

James D. Wuest is a Canadian chemist, materials scientist and academic. He is a professor of Chemistry at the Université de Montréal, where he teaches and leads a research group.














