
Galium odoratum, the sweetscented bedstraw, is a flowering perennial plant in the family Rubiaceae, native to much of Europe from Spain and Ireland to Russia, as well as Western Siberia, Turkey, Iran, the Caucasus, China and Japan. It is also sparingly naturalized in scattered locations in the United States and Canada. It is widely cultivated for its flowers and its sweet-smelling foliage.

Xerophyllum asphodeloides is a North American species of flowering plants in the Melanthiaceae known by the common names turkey beard, eastern turkeybeard, beartongue, grass-leaved helonias, and mountain asphodel. It is native to the eastern United States, where it occurs in the southern Appalachian Mountains from Virginia to Alabama, and also in the Pine Barrens of New Jersey.

Veronica persica is a flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae. It is native to Eurasia and is widespread as an introduced species in the British Isles, North America, and eastern Asia, including Japan and China.

Galium triflorum is a herbaceous plant of the family Rubiaceae. It is widespread in northern Europe, eastern Asia and North America. The plant is considered a noxious weed in New York, Pennsylvania, Vermont, New Hampshire, Connecticut and Massachusetts.

Angelica lucida is a species of angelica known by the common names seacoast angelica and sea-watch. It is also one of many species in the celery family which are casually called wild celery.

Goodyera oblongifolia is a species of orchid known by the common names western rattlesnake plantain and giant rattlesnake plantain. It is native to much of North America, particularly in the mountains of the western United States and Canada, from Alaska to northern Mexico, as well as in the Great Lakes region, Maine, Quebec and the Canadian Maritime Provinces.
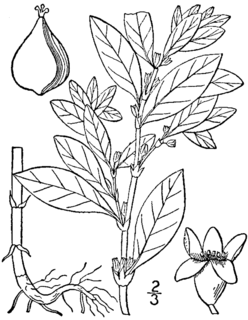
Polygonum erectum is a North American species of annual plant species in the buckwheat family, with upright or ascending stems, called erect knotweed. It was once cultivated for food by Native Americans as part of the group of crops known as the Eastern Agricultural Complex. It is found primarily in the northeastern and north-central parts of the United States, but with scattered populations in other parts of the US and also in Canada.

Nipponanthemum nipponicum, common names "Nippon daisy" or "Montauk daisy," is a plant species native to coastal regions of Japan but cultivated as an ornamental in other regions. It is now naturalized as an escape along seashores in New York and New Jersey. It is the only species in the genus Nipponanthemum, formerly considered part of Chrysanthemum.

Solidago buckleyi, Buckley's goldenrod, is a species of goldenrod native to central North America. It is an uncommon species with a small range, being found mainly in the Ozark Mountains of Arkansas and Missouri, and in the uplands near the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers near southern Illinois and western Kentucky. There are also a few isolated populations reported from Indiana. Its preferred habitat is open oak woodlands.
Vaccinium boreale, common name northern blueberry, sweet hurts or bleuet boréal, is a plant species native to the northeastern United States and eastern Canada. It has been reported from Québec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Newfoundland & Labrador, Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York State. It grows in tundra, rocky uplands and in open conifer forests at elevations up to 2000 m.
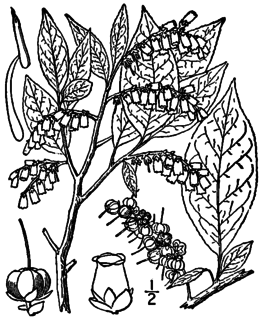
Eubotrys recurva is a plant species native to the eastern United States. Common names include deciduous mountain fetterbush and red-twig doghobble. The plant grows in moist forests, bogs, granitic domes, etc., at elevations up to 1500 m. It has been reported from Alabama, Georgia, North and South Carolina, Tennessee, Kentucky, Ohio, Virginia, West Virginia and New York State.
Clematis coactilis, common name Virginia white-hair leather flower, is a plant species endemic to the western part of the US State of Virginia. It is reported from only Botetourt, Roanoke, Craig, Montgomery, Giles, Wythe, and Pulaski Counties. It is usually found on soils formed from shale, less often dolomite, limestone or sandstone.
Paronychia argyrocoma, the silvery nailwort is a plant species native to the eastern United States. It has a disjunct distribution, found in New England and the Appalachian Mountains of the Southeast but not from New York, New Jersey or Pennsylvania in between. The species grows on rocky sites at elevations of 200–1800 m.
Juncus megacephalus, the bighead rush, is a plant species native to the United States. It is known from every seacoast state from Texas to Maryland, as well as Massachusetts, growing in freshwater marshes, sand dunes, and disturbed sites at elevations less than 100 m.

Cladium mariscoides, called smooth sawgrass, is a plant species native to eastern North America. It has been reported from every US state along the Gulf and Atlantic seashores except Louisiana, as well as every Great Lakes state, plus Vermont, Kentucky and Tennessee. It also occurs in every Canadian province except Alberta, British Columbia and Prince Edward Island. The species generally occurs along the shores of wetlands, including coastal salt marshes.

Iris prismatica, the slender blue flag or cubeseed iris, is a plant species native to parts of the southern and eastern United States from Maine south to Alabama, as well as to the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Nova Scotia.
Sagittaria ambigua, the Kansas arrowhead, is an aquatic plant species native to the central United States. It grows in wet areas, mostly along the shores of ponds and waterways.

Galium concinnum, the shining bedstraw, is a plant species in the Rubiaceae. It is native to the Midwestern United States and central Canada, especially the Great Lakes Region and the Valleys of the Ohio, lower Missouri, and upper Mississippi Rivers. The range extends from eastern Oklahoma to eastern Nebraska, north to Ontario and east to Virginia and New York. It is reportedly naturalized in Utah and considered a noxious weed in Pennsylvania.

Liparis liliifolia, known as the brown widelip orchid, lily-leaved twayblade, large twayblade, and mauve sleekwort, is a species of orchid native to eastern Canada and the eastern United States. In the eastern United States, it is found in the Appalachians, Ozarks, the Great Lakes Region, and the Ohio and Upper Mississippi Valleys, but not the southern coastal plains.

Nuphar sagittifolia, common name arrow-leaved water-lily or Cape Fear spatterdock, is a plant species known only from North Carolina, South Carolina, and Virginia. It is aquatic, found in lakes, ponds, and slow-moving rivers in the coastal plains of those states. It is also sold in pet shops as greenery to grow in aquaria and water-gardens.




















