
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram. In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate.

Phosphine is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula PH3, classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane. With traces of P2H4 present, PH3 is spontaneously flammable in air (pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure.
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning as a Lewis acid. Acidic oxides will typically have a low pKa and may be inorganic or organic. A commonly encountered acidic oxide, carbon dioxide produces an acidic solution when dissolved.

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moisture-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.
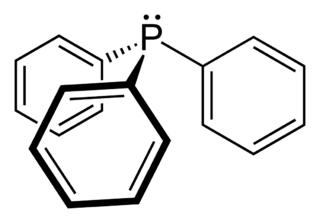
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.
Phosphorous acid (or phosphonic acid (singular)) is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds. Organic derivatives of phosphorous acid, compounds with the formula RPO3H2, are called phosphonic acids.
Po2, pO2, PO2, or PO2 may refer to:
Hypophosphorous acid (HPA), or phosphinic acid, is a phosphorus oxyacid and a powerful reducing agent with molecular formula H3PO2. It is a colorless low-melting compound, which is soluble in water, dioxane and alcohols. The formula for this acid is generally written H3PO2, but a more descriptive presentation is HOP(O)H2, which highlights its monoprotic character. Salts derived from this acid are called hypophosphites.
Phosphinates or hypophosphites are a class of phosphorus compounds conceptually based on the structure of hypophosphorous acid. IUPAC prefers the term phosphinate in all cases, however in practice hypophosphite is usually used to describe inorganic species, while phosphinate typically refers to organophosphorus species.
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.
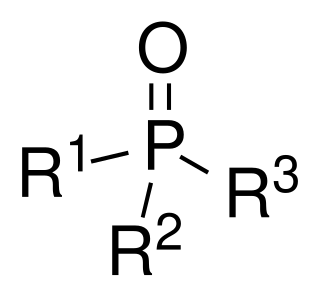
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3).

Triphenylphosphine oxide (often abbreviated TPPO) is the organophosphorus compound with the formula OP(C6H5)3, also written as Ph3PO or PPh3O (Ph = C6H5). This colourless crystalline compound is a common but potentially useful waste product in reactions involving triphenylphosphine. It is a popular reagent to induce the crystallizing of chemical compounds.
Deoxygenation is a chemical reaction involving the removal of oxygen atoms from a molecule. The term also refers to the removal of molecular oxygen (O2) from gases and solvents, a step in air-free technique and gas purifiers. As applied to organic compounds, deoxygenation is a component of fuels production as well a type of reaction employed in organic synthesis, e.g. of pharmaceuticals.
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PRnH3−n, where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of n: primary phosphines (n = 1), secondary phosphines (n = 2), tertiary phosphines (n = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3).

The phosphorus cycle is the biogeochemical cycle that describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Unlike many other biogeochemical cycles, the atmosphere does not play a significant role in the movement of phosphorus, because phosphorus and phosphorus-based compounds are usually solids at the typical ranges of temperature and pressure found on Earth. The production of phosphine gas occurs in only specialized, local conditions. Therefore, the phosphorus cycle should be viewed from whole Earth system and then specifically focused on the cycle in terrestrial and aquatic systems.

A metal-phosphine complex is a In coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).
The Allen–Millar–Trippett rearrangement is a ring expansion reaction in which a cyclic phosphine is transformed into a cyclic phosphine oxide. This name reaction, first reported in the 1960s by David W. Allen, Ian T. Millar, and Stuart Trippett, occurs by alkylation or acylation of the phosphorus, followed by reaction with hydroxide to give a rearranged product. The hydroxide first attacks the phosphonium atom, followed by collapse to the phosphine oxide with one of the groups migrating off of the phosphorus.
Phosphinous acids are usually organophosphorus compounds with the formula R2POH. They are pyramidal in structure. Phosphorus is in the oxidation state III. Most phosphinous acids rapidly convert to the corresponding phosphine oxide, which are tetrahedral and are assigned oxidation state V.

Phosphorus monoxide is an unstable radical inorganic compound with molecular formula PO.










