
The term hake refers to fish in the:

The Merlucciidae are a family of cod-like fish, including most hakes. They are native to cold water in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, and typically are found at depths greater than 50 m (160 ft) in subtropical, temperate, sub-Arctic or sub-Antarctic regions.
Arctogadus glacialis, known also with ambiguous common names Arctic cod and polar cod, is an Arctic species of fish in the cod family Gadidae, related to the true cod. Arctogadus glacialis is found in icy water. They grow to about 30 cm long, and are favorite food of narwhals and other arctic whales.
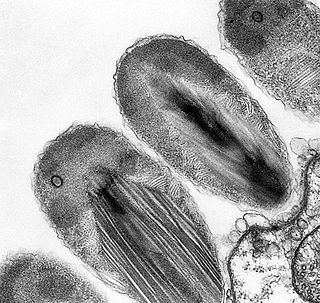
Verrucomicrobia is a phylum of bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated species have been identified in association with eukaryotic hosts including extrusive explosive ectosymbionts of protists and endosymbionts of nematodes residing in their gametes.

The North Pacific hake, Pacific hake, Pacific whiting, or jack salmon is a ray-finned fish in the genus Merluccius, found in the northeast Pacific Ocean from northern Vancouver Island to the northern part of the Gulf of California. It is a silver-gray fish with black speckling, growing to a length of 90 cm (3 ft). It is a migratory offshore fish and undergoes a daily vertical migration from the surface to the seabed at depths down to about 1,000 m (3,300 ft). It is the object of an important commercial fishery off the West Coast of the United States, and annual quotas are used to prevent overfishing.
The white hake or mud hake is a phycid hake of the genus Urophycis, found in the deeper waters in the northwest Atlantic Ocean.

The silver hake, Atlantic hake, or New England hake is a merluccid hake of the genus Merluccius, found in the northwest Atlantic Ocean. It is highly predatory and typically feeds on fish and crustaceans.
A number of Actinopterygiian fish have been given the common name whiting.

Merluccius is a genus of merluccid hakes from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, where mainly found relatively deep.

Merluccius merluccius, the European hake, is a merluccid hake of the genus Merluccius. Other vernacular names include Cornish salmon and herring hake. It is a predatory species which was often netted alongside one of its favoured prey, the Atlantic herring, thus the latter common name. It is found in the eastern Atlantic from the Norway and Iceland south to Mauritania and into the Mediterranean Sea. It is an important species in European fisheries and is heavily exploited with some populations thought to be being fished unsustainably.

Merluccius capensis is a ray-finned fish in the genus Merluccius, found in the south-eastern Atlantic Ocean, along the coast of South Africa. It is a long, lean fish with a large head, similar in appearance to the European hake and the deep-water Cape hake. By day, it lives close to the bottom on the continental shelf and upper slope at depths not usually exceeding 400 m (1,300 ft); it makes a large, daily vertical migration rising at night to feed in the nectonic zone, and it also migrates southwards in spring and northwards in autumn. It is an important commercial fish species in southern Africa.

The Argentine hake is a merluccid hake of the genus Merluccius, found in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean, along the coast of Argentina, and Uruguay. This fish was described by an Argentine ichthyologist, Tomás Marini in 1933.
Merluccius paradoxus, the deep-water Cape hake, is a merluccid hake of the genus Merluccius, found in the south-eastern Atlantic Ocean, along the coast of Southern Africa, south of Angola. Its range extends in decreasing abundance around the southern coast of Africa and into the Indian Ocean, but it is at its most plentiful in the cold, nutrient-rich fishing grounds of the Benguela Current.

Phycita is a genus of small moths belonging to the snout moth family (Pyralidae). They are the type genus of their tribe Phycitini and of the huge snout moth subfamily Phycitinae.
Lyconus is a genus of merluccid hakes known only from the Atlantic Ocean.

Urophycis is a genus of phycid hakes.
The Panama hake, also known as the dwarf hake, is a merluccid hake of the genus Merluccius, found off the west coast of the Americas from Del Mar, California, to Ensenada de Tumaco, Colombia.

Phycis phycis, the forkbeard, is a species of phycid hakes in the family Phycidae.
Lampanyctus festivus is a species of lanternfish. It is found in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. It is a mesopelagic fish that undertakes diel vertical migration. It grows to about 14 cm (5.5 in) standard length. It is an important component in the diet of forkbeard Phycis phycis off the Azores.












