Plagiaulacida is a group of extinct multituberculate mammals. Multituberculates were among the most common mammals of the Mesozoic, "the age of the dinosaurs". Plagiaulacids, an informal suborder, are the most basal of this order, and ranged from the Middle Jurassic Period to the Lower Cretaceous Period of the northern hemisphere.
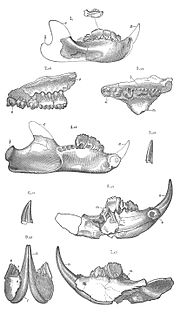
Ctenacodon is a genus of extinct mammal that lived in what is now North America during the Upper Jurassic period. It is a member of the family Allodontidae within the order Multituberculata. Ctenacodon, also known as Allodon, was named by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1879. At least three species are currently recognized.
Zofiabaatar is a genus of extinct mammal from the Upper Jurassic period. It was a relatively early member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder "Plagiaulacida". It lived in North America along with dinosaurs such as Diplodocus and Allosaurus.

Paulchoffatia is a genus of extinct mammal of the Upper Jurassic - Lower Cretaceous. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order Multituberculata, within the suborder "Plagiaulacida" and family Paulchoffatiidae. It lived in Europe during the "age of the dinosaurs."
Henkelodon was a small mammal of the Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the extinct order Multituberculata. Henkelodon was a European herbivore that lived during the "age of the dinosaurs". It lies within the suborder "Plagiaulacida" and family Paulchoffatiidae.
Paulchoffatiidae is a family of extinct mammals that lived predominantly during the Upper Jurassic period, though a couple of genera are known from the earliest Cretaceous. Some undescribed fossils from the Middle Jurassic of England may represent earlier versions. Remains have been reported from Portugal, Spain and England. Paulchoffatiids were members of the order Multituberculata. They were relatively early representatives and are within the informal suborder of "Plagiaulacida". The family was named by G. Hahn in 1969, and it honors the Portuguese geologist Léon Paul Choffat. Two subfamilies are recognized.
Liopleurodon is a genus of large, carnivorous marine reptile belonging to the Pliosauroidea, a clade of short-necked plesiosaurs. The two species of Liopleurodon lived from the Callovian Stage of the Middle Jurassic to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic Period. It was the apex predator of the Middle to Late Jurassic seas that covered Europe. The largest species, L. ferox, is estimated to have grown up to 6.4 metres (21 ft) in length.

The Oxfordian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, the earliest age of the Late Jurassic epoch, or the lowest stage of the Upper Jurassic series. It spans the time between 163.5 ± 4 Ma and 157.3 ± 4 Ma. The Oxfordian is preceded by the Callovian and is followed by the Kimmeridgian.

Phuwiangosaurus is a genus of titanosaur dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (Valanginian-Hauterivian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The type species, P. sirindhornae, was described by Martin, Buffetaut, and Suteethorn in a 1993 press release and was formally named in 1994. The species was named to honor Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn of Thailand, who was interested in the geology and palaeontology of Thailand, while the genus was named after the Phu Wiang area, where the fossil was discovered.
Kepodactylus is an extinct genus of ctenochasmatid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian-age Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of Colorado, United States.

Aegirosaurus is an extinct genus of platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaurs known from the late Jurassic and early Cretaceous of Europe. It was originally named as a species of Ichthyosaurus.

Ginkgo is a genus of highly unusual non-flowering seed plants. The scientific name is also used as the English name. The order to which it belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, 270 million years ago, and is now the only living genus within the order. The rate of evolution within the genus has been slow, and almost all its species had become extinct by the end of the Pliocene; the exception is the sole living species, Ginkgo biloba, which is only found in the wild in China, but is cultivated across the world. The relationships between ginkgos and other groups of plants are not fully resolved.

Hsisosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform from China. Currently there are three species within this genus: H. dashanpuensis is from the Middle Jurassic, while H. chungkingensis and H. chowi are from the Late Jurassic. It is likely to have been a medium-sized predator.

Duriavenator is a genus of theropod dinosaur described in 2008 by Roger Benson; its finds were excavated in England. The only named species in the genus is Duriavenator hesperis, formerly known as Megalosaurus hesperis. Duriavenator lived during the Bajocian stage, between 169.1 and 168.7 million years ago, making it one of the oldest-known Tetanurae. The genus name combines the Latin name of Dorset, Duria, with Latin for "hunter", venator. This genus has also gone under the unofficial name "Walkersaurus", which is a nomen nudum. It has been estimated to be 7 meters in length.

Hauffiosaurus is an extinct genus of Early Jurassic pliosaurid plesiosaur known from Holzmaden of Germany and from Yorkshire of the United Kingdom. It was first named by Frank Robin O’Keefe in 2001 and the type species is Hauffiosaurus zanoni. In 2011, two additional species were assigned to this genus: H. longirostris and H. tomistomimus.
Eopneumatosuchus is an extinct genus of basal crocodyliform. Fossils have been found from two localities within the Kayenta Formation of Arizona. Both localities are around 20 miles southeast of the Grand Canyon and in close proximity to one another. The localities probably date back to the Early Jurassic, most likely during the Sinemurian stage.
Osmakasaurus is a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian dinosaur. It is a basal iguanodontian which lived during the Early Cretaceous period in what is now Buffalo Gap of South Dakota, United States. It is known from the Chilson Member of the Lakota Formation. This genus was named by Andrew T. McDonald in 2011 and the type species is O. depressus.

Stereognathus is an extinct genus of tritylodontid cynodonts from the Middle Jurassic of the United Kingdom. There is a single named species: S. ooliticus, named after the Great Oolite deposits of England. A second species, S. hebridicus, was named after the Hebrides in Scotland, where it was found; it was synonymized with S. ooliticus in 2017.

Pterorigonia is an extinct genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Megatrigoniidae. This genus is known in the fossil record from the Jurassic period Tithonian age to the Cretaceous period Maastrichtian age. Species in this genus were facultatively mobile infaunal suspension feeders. The type species of the genus is Pterotrigonia cristata.
Luopterus is an extinct genus of anurognathid pterosaur containing only the holotype species L. mutoudengensis that is known from the Middle Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation of Qinglong, northern Hebei Province, China. It was originally named as a species of Dendrorhynchoides in 2012 but it was moved to the genus Luopterus in 2020. Luopterus was originally thought to be from the Early Cretaceous, with a wingspan that is about 40 centimeters (16 in), making it one of the smallest known pterosaurs.











