A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

Paint is any pigmented liquid, liquefiable, or solid mastic composition that, after application to a substrate in a thin layer, converts to a solid film. It is most commonly used to protect, color, or provide texture. Paint can be made in many colors—and in many different types. Paint is typically stored, sold, and applied as a liquid, but most types dry into a solid. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based and each has distinct characteristics. For one, it is illegal in most municipalities to discard oil-based paint down household drains or sewers. Clean-up solvents are also different for water-based paint than they are for oil-based paint. Water-based paints and oil-based paints will cure differently based on the outside ambient temperature of the object being painted. Usually, the object being painted must be over 10 °C (50 °F), although some manufacturers of external paints/primers claim they can be applied when temperatures are as low as 2 °C (35 °F).

Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575–585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In the RGB color model, used to create colors on television and computer screens, yellow is a secondary color made by combining red and green at equal intensity. Carotenoids give the characteristic yellow color to autumn leaves, corn, canaries, daffodils, and lemons, as well as egg yolks, buttercups, and bananas. They absorb light energy and protect plants from photo damage in some cases. Sunlight has a slight yellowish hue when the Sun is near the horizon, due to atmospheric scattering of shorter wavelengths.

A set of primary colors or primary colours consists of colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color printing, and paintings. Perceptions associated with a given combination of primary colors can be predicted by an appropriate mixing model that reflects the physics of how light interacts with physical media, and ultimately the retina.

A pigment is a colored substance that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compounds. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli.

Cadmium pigments are a class of pigments that contain cadmium. Most of the cadmium produced worldwide has been for use in rechargeable nickel–cadmium batteries, which have been replaced by other rechargeable nickel-chemistry cell varieties such as NiMH cells, but about half of the remaining consumption of cadmium, which is approximately 2,000 tonnes annually, is used to produce colored cadmium pigments. The principal pigments are a family of yellow, orange and red cadmium sulfides and sulfoselenides, as well as compounds with other metals.

Oil paint is a type of slow-drying paint that consists of particles of pigment suspended in a drying oil, commonly linseed oil. The viscosity of the paint may be modified by the addition of a solvent such as turpentine or white spirit, and varnish may be added to increase the glossiness of the dried oil paint film. The addition of oil or alkyd medium can also be used to modify the viscosity and drying time of oil paint. Oil paints were first used in Asia as early as the 7th century AD and can be seen in examples of Buddhist paintings in Afghanistan. Oil-based paints made their way to Europe by the 12th century and were used for simple decoration, but oil painting did not begin to be adopted as an artistic medium there until the early 15th century. Common modern applications of oil paint are in finishing and protection of wood in buildings and exposed metal structures such as ships and bridges. Its hard-wearing properties and luminous colors make it desirable for both interior and exterior use on wood and metal. Due to its slow-drying properties, it has recently been used in paint-on-glass animation. The thickness of the coat has considerable bearing on the time required for drying: thin coats of oil paint dry relatively quickly.
In chemistry, chromism is a process that induces a change, often reversible, in the colors of compounds. In most cases, chromism is based on a change in the electron states of molecules, especially the π- or d-electron state, so this phenomenon is induced by various external stimuli which can alter the electron density of substances. It is known that there are many natural compounds that have chromism, and many artificial compounds with specific chromism have been synthesized to date. It is usually synonymous with chromotropism, the (reversible) change in color of a substance due to the physical and chemical properties of its ambient surrounding medium, such as temperature and pressure, light, solvent, and presence of ions and electrons.

Quinacridone is an organic compound used as a pigment. Numerous derivatives constitute the quinacridone pigment family, which finds extensive use in industrial colorant applications such as robust outdoor paints, inkjet printer ink, tattoo inks, artists' watercolor paints, and color laser printer toner. As pigments, the quinacridones are insoluble. The development of this family of pigments supplanted the alizarin dyes.

Gamboge is a deep yellow pigment derived from a species of tree that primarily grows in Cambodia. Popular in east Asian watercolor works, it has been used across a number of media dating back to the 8th century. Easy to transport and manipulate into a durable watercolor paint, Gamboge is notable for its versatility as a pigment in how it has been used in paintings, printing of books, and garment dyes. Though used in a number of different contexts, Gamboge is known not to react well with lime surfaces therefore making it unsuitable for frescos and with white lead. For its popularity, Gamboge has not been extensively identified in works of art from any time period; the few instances wherein art historians have attempted to identify whether or not the pigment was used in a given work have confirmed its widespread use and its longevity as staple within watercolor painting particularly in eastern art.
Chrome yellow is a bright, warm yellow pigment that has been used in art, fashion, and industry for over two centuries. The pigment is derived from lead chromate, a chemical compound that was first synthesized in the early 1800s. The name "chrome yellow" comes from the French chemist Louis Nicolas Vauquelin, who discovered the element chromium in 1797.

A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two separate molecular orbitals falls within the range of the visible spectrum. Visible light that hits the chromophore can thus be absorbed by exciting an electron from its ground state into an excited state. In biological molecules that serve to capture or detect light energy, the chromophore is the moiety that causes a conformational change in the molecule when hit by light.
Arylide yellow, also known as Hansa yellow and monoazo yellow, is a family of organic compounds used as pigments. They are primarily used as industrial colorants including plastics, building paints and inks. They are also used in artistic oil paints, acrylics and watercolors. These pigments are usually semi-transparent and range from orange-yellow to yellow-greens. Related organic pigments are the diarylide pigments. Overall, these pigments have partially displaced the toxic cadmium yellow in the marketplace. Painters such as Alexander Calder and Jackson Pollock are known to have employed arylide yellow in their artworks.
Diarylide pigments are organic compounds that are used as pigments in inks and related materials. They often are yellow or yellow-green. To some extent, these organic compounds have displaced cadmium sulfide from the market. They exist as yellow powders of low solubility in water.
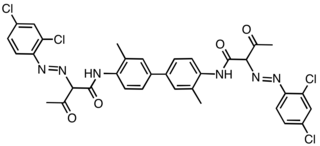
Pigment Yellow 83 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant.

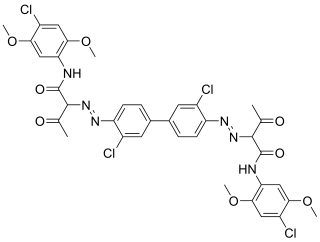
Pigment Yellow 81 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant.
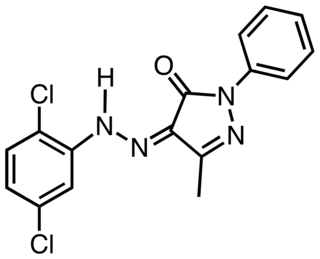
Pigment Yellow 10 is an organic compound that is classified as a Monoazopyrazolone pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant, notably as yellow road marking on highways in the US. The compound is synthesized by coupling the diazonium salt derived from dichloroaniline with the pyrazolone.

Paint mixing is the practice of mixing components or colors of paint to combine them into a working material and achieve a desired hue. The components that go into paint mixing depend on the function of the product sought to be produced. For example, a painter of portraits or scenery on a canvas may be seeking delicate hues and subtle gradiations, while the painter of a house may be more concerned with durability and consistency of colors in paints presented to customers, and the painter of a bridge or a ship may have the weatherability of the paint as their primary concern.
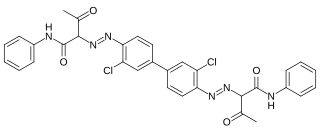
Pigment Yellow 12 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 13, wherein the two phenyl groups are replaced by 2,4-xylyl.
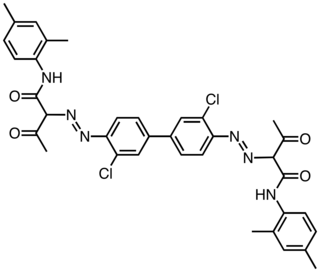
Pigment Yellow 13 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 12, wherein the two xylyl groups are replaced by phenyl.