| Pimienta Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: | |
| Type | Formation |
| Underlies | Lower Tamaulipas Formation |
| Overlies | Taman Formation |
| Thickness | Over 50 metres |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Limestone, Bentonite, Breccia |
| Location | |
| Country | Mexico |
The Pimienta Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Tithonian-Berriasian. [1] [2] The formation is considered laterally equivalent to the La Casita Formation. The Metriorhynchid Cricosaurus vignaudi is known from the formation. [3]
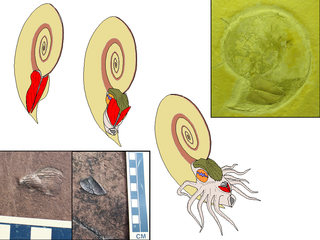
An aptychus is a type of marine fossil. It is a hard anatomical structure, a sort of curved shelly plate, now understood to be part of the body of an ammonite. Paired aptychi have, on rare occasions, been found at or within the aperture of ammonite shells. The aptychus was usually composed of calcite, whereas the ammonite shell was aragonite.
In the geologic timescale, the Bajocian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 170.9 ±0.8 Ma to around 168.2 ±1.2 Ma. The Bajocian Age succeeds the Aalenian Age and precedes the Bathonian Age.

Dakosaurus is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially. The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named Geosaurus maximus by Theodor Plieninger in 1846. Dakosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. The extent of its adaptation to a marine lifestyle means that it is most likely that it mated at sea, but since no eggs or nests have been discovered that have been referred to Dakosaurus, whether it gave birth to live young at sea like dolphins and ichthyosaurs or came ashore like turtles is not known. The name Dakosaurus means "biter lizard", and is derived from the Greek dakos ("biter") and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard").

Geosaurus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform within the family Metriorhynchidae, that lived during the Late Jurassic and the Early Cretaceous. Geosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. No Geosaurus eggs or nests have been discovered, so little is known of the reptile's lifecycle, unlike other large marine reptiles of the Mesozoic, such as plesiosaurs or ichthyosaurs which are known to give birth to live young out at sea. Where Geosaurus mated, whether on land or at sea, is currently unknown. The name Geosaurus means "Mother of Giants lizard", and is derived from the Greek Ge- and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard"). The name Geosaurus was established by the French naturalist Georges Cuvier in 1824.
Cricosaurus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliforms of the Late Jurassic. belonging to the family Metriorhynchidae. The genus was established by Johann Andreas Wagner in 1858 for three skulls from the Tithonian of Germany. The name Cricosaurus means "Ring lizard", and is derived from the Greek Krikos- ("ring") and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard"). It was a relatively small reptile, with C. suevicus and C. araucanensis measuring 2 m (6.6 ft) and 3.2 m (10 ft) in total body length, respectively.

The Cerro del Pueblo Formation is a geological formation in Coahuila, Mexico whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. The formation is believed to correlate with the Baculites reesidesi and Baculites jenseni ammonite zones, which dates it to 73.63-72.74 Ma.
The Jackson Bluff Formation is a geologic formation in Florida. It preserves fossils dating back to the Neogene period.
The Goodland Limestone or Goodland Formation is a geologic formation in Arkansas and Texas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period.
The Ixtaltepec Formation is a geologic formation in Oaxaca state, southwestern Mexico.
The Taraises Formation is a geologic formation in northern Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Early Cretaceous, including ammonites.
The El Abra Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period.
The Mal Paso Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period, Late Albian.
The La Caja Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils dating from the Kimmeridgian to the lower Berriasian. La Caja Formation is widespread in northeastern and central Mexico and known for their abundant and diverse well-preserved ammonites. It was deposited in hemipelagic conditions, and predominantly consists of siliclastic sediments, including marl, with limestone. It is laterally equivalent to the La Casita Formation, which represent more proximal facies. The ichthyosaurs Ophthalmosaurus icenicus and Parrassaurus yacahuitztli, metriorhynchid Cricosaurus saltillensis and the giant pliosaur "Monster of Aramberri" are known from the formation.

The La Casita Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Kimmeridgian to lowermost Berriasian. It is laterally equivalent to the La Caja Formation and the Pimienta Formation. The ichthyosaurs Jabalisaurus and Acuetzpalin are known from the formation, as well as the metriorhynchid Dakosaurus and indeterminate pliosaurs.
The Zorrillo Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico, near Tezoatlán de Segura y Luna, Oaxaca. It preserves fossils dating back to the Jurassic period.
The El Bosque Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils of plants, vertebrates, invertebrates and calcareous algae dating back to the Eocene period.
The Artemisa Formation is a geologic formation in western Cuba. It preserves mainly ammonite fossils dating back to the Late Oxfordian to Tithonian period. The formation is divided into two members; La Zarza and Sumidero Members. Most of the formation was deposited in deeper marine conditions.

Laevapetchyus is a genus of ammonites.
Acuetzpalin is an extinct genus of platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur found in the Kimmeridgian La Casita Formation in Mexico. It is known from a partial skeleton, of which the skull is surprisingly well preserved. Its length is estimated to have been more than 3.1 metres (10 ft) long, considering the missing parts of the holotype. It was the first ichthyosaur described in 2020 and the first new ichthyosaur genus described since 2017.
Parrassaurus is an ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur from the late Jurassic La Caja Formation of Mexico found in 2021. Parrassaurus includes one species, Parrassaurus yacahuitztli. The type specimen was around 5 metres (16 ft) long.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)