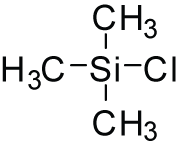
Chloroethane, commonly known as ethyl chloride, is a chemical compound with chemical formula CH3CH2Cl, once widely used in producing tetraethyllead, a gasoline additive. It is a colorless, flammable gas or refrigerated liquid with a faintly sweet odor.
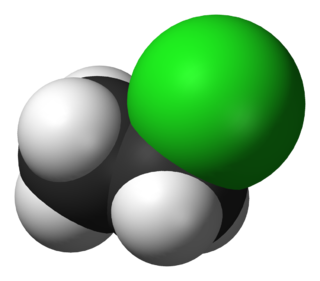
A toluenesulfonyl (shortened tosyl, abbreviated Ts or Tos) group, H3CC6H4SO2, is a univalent organic group that consists of a tolyl group, H3CC6H4, joined to a sulfonyl group, SO2, with the open valence on sulfur. This group is usually derived from the compound tosyl chloride, H3CC6H4SO2Cl (abbreviated TsCl), which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic acid, H3CC6H4SO2OH (abbreviated TsOH). The para orientation illustrated (p-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention tosyl without a prefix refers to the p-toluenesulfonyl group.
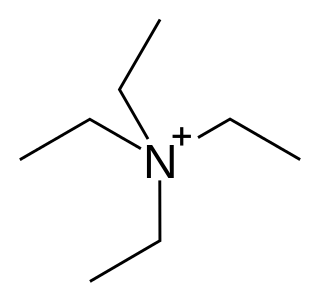
Tetraethylammonium (TEA), (NEt+
4) or (Et4N+) is a quaternary ammonium cation consisting of four ethyl groups attached to a central nitrogen atom, and is positively charged. It is a counterion used in the research laboratory to prepare lipophilic salts of inorganic anions. It is used similarly to tetrabutylammonium, the difference being that its salts are less lipophilic and more easily crystallized.

Phenazone is an analgesic, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and an antipyretic.

Sodium iodide (chemical formula NaI) is an ionic compound formed from the chemical reaction of sodium metal and iodine. Under standard conditions, it is a white, water-soluble solid comprising a 1:1 mix of sodium cations (Na+) and iodide anions (I−) in a crystal lattice. It is used mainly as a nutritional supplement and in organic chemistry. It is produced industrially as the salt formed when acidic iodides react with sodium hydroxide. It is a chaotropic salt.

Copper(I) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CuI. It is also known as cuprous iodide. It is useful in a variety of applications ranging from organic synthesis to cloud seeding.
Cyanines, also referred to as tetramethylindo(di)-carbocyanines are defined as "synthetic dyes with the general formula R2N[CH=CH]nCH=N+R2↔R2N+=CH[CH=CH]nNR2 in which the nitrogen and part of the conjugated chain usually form part of a heterocyclic system, such as imidazole, pyridine, pyrrole, quinoline and thiazole." Cyanines are used in industry biotechnology.
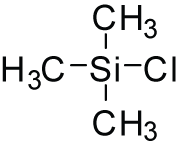
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound (silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.
The Finkelstein reaction named after the German chemist Hans Finkelstein, is an SN2 reaction that involves the exchange of one halogen atom for another. It is an equilibrium reaction, but the reaction can be driven to completion by exploiting the differential solubility of halide salts, or by using a large excess of the halide salt.
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. The list can be found as an appendix to 40 C.F.R. 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121.
Methylmagnesium chloride is an organometallic compound with the general formula CH3MgCl. This highly flammable, colorless, and moisture sensitive material is the simplest Grignard reagent and is commercially available, usually as a solution in tetrahydrofuran.

Phenanthridine is a nitrogen heterocyclic compound that is the basis of DNA-binding fluorescent dyes through intercalation. Examples of such dyes are ethidium bromide and propidium iodide. Acridine is an isomer of phenanthridine.
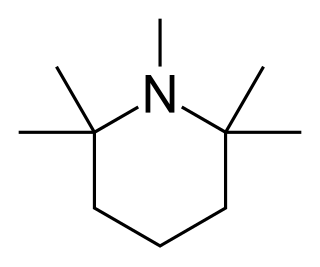
Pempidine is a ganglion-blocking drug, first reported in 1958 by two research groups working independently, and introduced as an oral treatment for hypertension.
Organoiodine compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–iodine bonds. They occur widely in organic chemistry, but are relatively rare in nature. The thyroxine hormones are organoiodine compounds that are required for health and the reason for government-mandated iodization of salt.

Brooker's merocyanine is an organic dye belonging to the class of merocyanines.

Alvameline (Lu 25-109) is a M1 receptor agonist and M2/M3 receptor antagonist that was under investigation for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but produced poor results in clinical trials and was subsequently discontinued.
A J-aggregate is a type of dye with an absorption band that shifts to a longer wavelength of increasing sharpness when it aggregates under the influence of a solvent or additive or concentration as a result of supramolecular self-organisation. The dye can be characterized further by a small Stokes shift with a narrow band. The J in J-aggregate refers to E.E. Jelley who discovered the phenomenon in 1936. The dye is also called a Scheibe aggregate after G. Scheibe who also independently published on this topic in 1937.
Methylammonium halides are organic halides with a formula of CH3NH3X, where X is Cl for methylammonium chloride, Br for methylammonium bromide, or I for methylammonium iodide. Generally they are white or light colored powders. They are used primarily to prepare light absorbing semiconductors for perovskite solar cells.

Decynium-22 is a cationic derivative of quinoline, and a potent inhibitor of the plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT), as well as all members of the organic cation transporter (OCT) family in both human and rat cells. However, it has little effect on high affinity monoamine transporters such as the dopamine transporter and norepinephrine transporter.
Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate or DMAEA is an unsaturated carboxylic acid ester having a tertiary amino group. It is a colorless to yellowish, water-miscible liquid with a pungent, amine-like odor. DMAEA is an important acrylic monomer that gives basic properties to copolymers.