
The Geoemydidae are one of the largest and most diverse families in the order Testudines (turtles), with about 70 species. The family includes the Eurasian pond and river turtles and Neotropical wood turtles.

The giant Asian pond turtle inhabits rivers, streams, marshes, and rice paddies from estuarine lowlands to moderate altitudes throughout Cambodia and Vietnam and in parts of Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar and Thailand.

The spiny turtle is a South-East Asian turtle species. It inhabits lowland and hill rainforest, usually dwelling in the vicinity of small streams in hill areas up to 1,000 m above sea level. It is found in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.

Rhynchobdellida, the jawless leeches or freshwater leeches, are an order of aquatic leeches. Despite the common name "freshwater leeches", species are found in both sea and fresh water. They are defined by the presence of a protrusible proboscis instead of jaws, and having colourless blood. They move by "inchworming" and are found worldwide. The order contains 110 species, divided into 41 genera and three families. Members of the order range widely in length, usually between 7 and 40 mm. They are hermaphrodite. The order is not monophyletic.

The Asian leaf turtle is a species of turtle found in Southeast Asia. They are quite common in the pet trade; their carapaces resemble that of a Cuora amboinensis hybrid.

The yellow-headed temple turtle is a large species of turtle in the family Geoemydidae. The species is native to Southeast Asia.

Glossiphoniidae are a family of freshwater proboscis-bearing leeches. These leeches are generally flattened, and have a poorly defined anterior sucker. Most suck the blood of freshwater vertebrates like amphibians, crocodilians and aquatic turtles, but some feed on invertebrates like oligochaetes and freshwater snails instead. Although they prefer other hosts, blood-feeding species will opportunistically feed from humans.

Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodies that can lengthen and contract. Both groups are hermaphrodites and have a clitellum, but leeches typically differ from the oligochaetes in having suckers at both ends and ring markings that do not correspond with their internal segmentation. The body is muscular and relatively solid; the coelom, the spacious body cavity found in other annelids, is reduced to small channels.

Cyclemys is a genus of freshwater turtles, commonly referred to as Asian leaf turtles, from the family Geoemydidae. The genus occurs throughout Southeast and South Asia, and currently contains seven species.

Echinostoma revolutum is a trematode parasite of which the adults can infect birds and mammals, including humans. In humans, it causes echinostomiasis.

Turtle leeches are a genus, Ozobranchus, of leeches (Hirudinea) that feed exclusively on the blood of turtles. Only two species – Ozobranchus margoi and Ozobranchus branchiatus – are found in the Atlantic coast of the United States and the Gulf of Mexico. Little is known about these leeches due to difficulties in studying their sea turtle hosts.

The Malayan snail-eating turtle is a species of turtle in Malayemys genus of the family Geoemydidae.

Erpobdella octoculata is a freshwater leech in the Erpobdellidae family. This species can be found in Europe, the Mediterranean, and the Middle East.

The Khorat snail-eating turtle is a species of turtle in the family Geoemydidae. They are freshwater turtles from Khorat Plateau in Thailand but were found for the first time in Udon Thani, Thailand.

Ozobranchus branchiatus is a species of leech in the family Ozobranchidae. It is found in the Atlantic Ocean and is a permanent parasite of sea turtles, mostly the green sea turtle.

Placobdelloides is a genus of glossophoniid leeches.
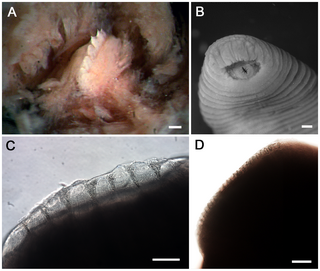
Praobdellidae is a family of hematophagous leeches which live on the mucous membranes of mammals and sometimes invertebrates. These are internal parasites that enter the body through natural orifices, and cause hirudiniases.
Alboglossiphonia heteroclita is a species of leeches belonging to the family Glossiphoniidae. It is distributed across the Holarctic region, in North America and Eurasia. The species is a predator, feeding on freshwater invertebrates, including gastropods, isopods, and certain oligochaetes. They employ a sit-and-wait hunting strategy, and are usually relatively immobile.

Torix is a genus of Rhynchobdellid leeches in the family Glossiphoniidae, found in Eastern Asia and Japan. Rana japonica, the Japanese brown frog, is the main host of T. tagoi.

Myzobdella lugubris, the crab leech, is a species of jawless leech widespread in North America, especially in central and Eastern Canada. It is an ectoparasite of fish and crustaceans, and is responsible for several dangerous conditions in fish, including lesions infected by bacteria and fungi and possibly viral hemorrhagic septicemia. It lays its egg capsules on crabs and possible other arthropods, which then disperse the eggs.



















