
The long-tailed goral or Amur goral is a species of ungulate of the family Bovidae found in the mountains of eastern and northern Asia, including Russia, China, and Korea. A population of this species exists in the Korean Demilitarized Zone, near the tracks of the Donghae Bukbu Line. The species is classified as endangered in South Korea, with an estimated population less than 250. It has been designated South Korean natural monument 217. In 2003, the species was reported as being present in Arunachal Pradesh, in northeast India.

The buff-necked ibis, also known as the white-throated ibis, is a fairly large ibis found widely in open habitats of eastern and northern South America. It formerly included the similar black-faced ibis as a subspecies, but that species is almost entirely restricted to colder parts of South America, has a buff lower chest, and lacks the contrasting large white wing-patches.
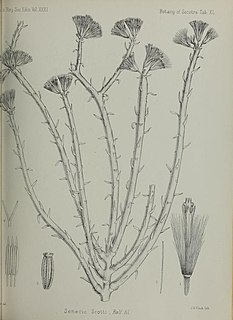
Kleinia scottii is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only in Yemen. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests.
The Cuban pine toad, or Schwartz's Caribbean toad, is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Cuba and found in western Cuba and on the Isla de la Juventud, below 70 m (230 ft) above sea level. Its natural habitats are savannas with pinewood, palms, and sandy soils. Breeding takes place in temporary pools, flooded pastures, and other shallow bodies of standing water; it can be abundant at breeding aggregations, but is otherwise hard to see. It is threatened by habitat loss caused by agriculture and sand extraction. Its habitat is also threatened by the invasive tree, Dichrostachys cinerea.
Eleutherodactylus counouspeus is a species of frog in the family Eleutherodactylidae endemic to the Massif de la Hotte, Haiti. Its natural habitats are limestone caves and crevices in closed, humid forest at elevations of 300–760 m (980–2,490 ft) asl. It is a moderately common species but threatened by habitat loss. The species occurs in the Pic Macaya National Park, but there is no active management for conservation, and habitat loss continues in the park.
Eleutherodactylus wetmorei is a species of frog in the family Eleutherodactylidae.
Odorrana trankieni is a species of frogs in the family Ranidae. It is endemic to Vietnam, only known from vicinity of its type locality in Phu Yen District of Sơn La Province. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forests and rivers. Its status is insufficiently known.

The rufous-throated wren-babbler is a species of bird in the family Timaliidae. It is found in Bhutan, India, and Nepal.
Aneilema silvaticum is a species of plant in the Commelinaceae family. It is found in Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Nigeria. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Euphorbia pellegrinii is a species of plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry lowland grassland. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Helicia is a genus of 110 species of trees and shrubs, constituting part of the plant family Proteaceae. They grow naturally in rainforests throughout tropical South and Southeast Asia, including India, Sri Lanka, Indochina, Peninsular Malaysia to New Guinea and as far south as New South Wales.
Vepris lecomteana, synonym Oricia lecomteana, is a species of plant in the family Rutaceae. It is found in Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, Gabon and Nigeria. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Placodiscus attenuatus is a species of plant in the family Sapindaceae. It is found in Ivory Coast and Ghana. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Placodiscus is a genus of plant in family Sapindaceae. The following species are accepted by Plants of the World Online:
Placodiscus bancoensis is a species of plant in the family Sapindaceae. It is found in Ivory Coast and Ghana. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Placodiscus boya is a species of plant in the family Sapindaceae. It is found in Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Placodiscus bracteosus is a species of plant in the family Sapindaceae. It is found in Ivory Coast and Ghana. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Placodiscus opacus is a species of plant in the family Sapindaceae. It is found in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Placodiscus pseudostipularis is a species of plant in the family Sapindaceae. It is found in Ivory Coast, Ghana, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Tabernaemontana pandacaqui, known as windmill bush and banana bush, is a species of plant in the dogbane family Apocynaceae.






