Related Research Articles

Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.

Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most common. It may also refer to the use of a computer to assist in all operations of a manufacturing plant, including planning, management, transportation and storage. Its primary purpose is to create a faster production process and components and tooling with more precise dimensions and material consistency, which in some cases, uses only the required amount of raw material, while simultaneously reducing energy consumption. CAM is now a system used in schools and lower educational purposes. CAM is a subsequent computer-aided process after computer-aided design (CAD) and sometimes computer-aided engineering (CAE), as the model generated in CAD and verified in CAE can be input into CAM software, which then controls the machine tool. CAM is used in many schools alongside CAD to create objects.
Creo Parametric, formerly known, together with Creo Elements/Pro, as Pro/Engineer and Wildfire, is a solid modeling or CAD, CAM, CAE, and associative 3D modeling application, running on Microsoft Windows.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes, and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises.
JT is an openly-published ISO-standardized 3D CAD data exchange format used for product visualization, collaboration, digital mockups, and other purposes. It was developed by Siemens.

Solid Edge is a 3D CAD, parametric feature and synchronous technology solid modeling software. It runs on Microsoft Windows and provides solid modeling, assembly modelling and 2D orthographic view functionality for mechanical designers. Through third party applications it has links to many other Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) technologies.
Digital Prototyping gives conceptual design, engineering, manufacturing, and sales and marketing departments the ability to virtually explore a complete product before it's built. Industrial designers, manufacturers, and engineers use Digital Prototyping to design, iterate, optimize, validate, and visualize their products digitally throughout the product development process. Innovative digital prototypes can be created via CAutoD through intelligent and near-optimal iterations, meeting multiple design objectives, identifying multiple figures of merit, and reducing development gearing and time-to-market. Marketers also use Digital Prototyping to create photorealistic renderings and animations of products prior to manufacturing. Companies often adopt Digital Prototyping with the goal of improving communication between product development stakeholders, getting products to market faster, and facilitating product innovation.
Femap is an engineering analysis program sold by Siemens Digital Industries Software that is used to build finite element models of complex engineering problems ("pre-processing") and view solution results ("post-processing"). It runs on Microsoft Windows and provides CAD import, modeling and meshing tools to create a finite element model, as well as postprocessing functionality that allows mechanical engineers to interpret analysis results. The finite element method allows engineers to virtually model components, assemblies, or systems to determine behavior under a given set of boundary conditions, and is typically used in the design process to reduce costly prototyping and testing, evaluate differing designs and materials, and for structural optimization to reduce weight.

CD-adapco was a multinational computer software company that authored and distributed applications used for computer-aided engineering, best known for its computational fluid dynamics (CFD) products. In 2016 the company was acquired by Siemens Digital Industries Software.

WorkNC is a Computer aided manufacturing (CAM) software developed by Sescoi for multi-axis machining.
FlexSim is a discrete-event simulation software package developed by FlexSim Software Products, Inc. The FlexSim product family currently includes the general purpose FlexSim product and healthcare systems modeling environment.

NX, formerly known as "unigraphics", is an advanced high-end CAD/CAM/CAE, which has been owned since 2007 by Siemens Digital Industries Software. In 2000, Unigraphics purchased SDRC I-DEAS and began an effort to integrate aspects of both software packages into a single product which became Unigraphics NX or NX.

Simcad Pro simulation software is a product of CreateASoft Inc. used for simulating process-based environments including manufacturing, warehousing, supply lines, logistics, and healthcare. It is a tool used for planning, organizing, optimizing, and engineering real process-based systems. Simcad Pro allows the creation of a virtual computer model, which can be manipulated by the user and represents a real environment. Using the model, it is possible to test for efficiency as well as locate points of improvement among the process flow. Simcad Pro's dynamic computer model also allows for changes to occur while the model is running for a fully realistic simulation. It can also be integrated with live and historical data.
Siemens Digital Industries Software is an American computer software company specializing in 3D & 2D Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software. The company is a business unit of Siemens, operates under the legal name of Siemens Industry Software Inc, and is headquartered in Plano, Texas.
Simcenter Amesim is a commercial simulation software for the modeling and analysis of multi-domain systems. It is part of systems engineering domain and falls into the mechatronic engineering field.
The FORAN system is an integrated CAD/CAM/CAE system developed by SENER for the design and production of practically any naval ship and offshore unit. It is a multidisciplinary and integrated system that can be used in all the ship design and production phases and disciplines. The System collects all the information in a single database. FORAN is mainly focused on the design of:
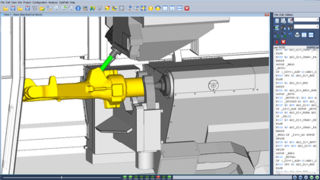
Vericut, is a software program used for simulating CNC machining. It is used to simulate tool motion and the material removal process, detecting errors or areas of inefficiency in NC programs. It was developed by CGTech Inc. and first released in 1988.
Digital manufacturing is an integrated approach to manufacturing that is centered around a computer system. The transition to digital manufacturing has become more popular with the rise in the quantity and quality of computer systems in manufacturing plants. As more automated tools have become used in manufacturing plants it has become necessary to model, simulate, and analyze all of the machines, tooling, and input materials in order to optimize the manufacturing process. Overall, digital manufacturing can be seen sharing the same goals as computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM), flexible manufacturing, lean manufacturing, and design for manufacturability (DFM). The main difference is that digital manufacturing was evolved for use in the computerized world.
References
- ↑ Phelan, Jim (June 23, 2009). "Siemens PLM Software Launches Tecnomatix 10 to Increase Planning and Manufacturing Productivity". Thomson Reuters 2009. Archived from the original on February 1, 2013.
- ↑ "Plant Simulation". Siemens PLM. 2010. Archived from the original on 2009-08-03. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- ↑ "Tecnomatix Plant Simulation". 4D Systems. Archived from the original on 2022-06-29. Retrieved 2022-04-18.
- ↑ Koenig, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Markus. "Visual simulation - an appropriate approach to support execution planning in building engineering" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2009-09-14.
- ↑ Jallas, Eric (February 2009). "Mechanistic Virtual Modeling: Coupling a Plant Simulation Model with a Three-dimensional Plant Architecture Component". Environmental Modeling and Assessment. 14 (1): 29–45. doi:10.1007/s10666-008-9164-4. ISSN 1420-2026. S2CID 110236902.
- ↑ Heinrich, Stephan (2008). "Optimizing the Color Sorting Store" (PDF). Promasim. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-07.
- ↑ Hanreich, Klaus (May 2005). "To shorten process times and retain ontime delivery of maintenanced aerospace engines, MTU Aero Engines built a new assembly hall that it designed to stabilize maintenance processes that are effectively supported by materialflow-oriented production methods" (PDF). Aerospace Engineering. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-05. Retrieved 2009-09-14.
- ↑ Hasenschwanz, Werner (January 2009). "PRACTICAL AND USEFUL RESULTS; Process simulation in a brewery" (PDF). BBII. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-04-15. Retrieved 2009-09-14.
- ↑ Steinhauer, Dirk (2008). "Simulation Aided Production Planning in Shipyards" (PDF). Flensburger Shipyard.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Caprace, Jean-David (December 2006). "Minimization of Production Cost by use of an Automatic Cost Assessment Method and Simulation". Journal of Harbin Engineering University. The AsiaLink-EAMARNET International Conference on Ship Design, Production &Operation. 27 Suppl.: 399–408. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2009-09-14.
- ↑ Park, Eun-Jung (December 2007). "A SIMULATION MODEL WITH A LOW LEVEL OF DETAIL FOR CONTAINER TERMINALS AND ITS APPLICATIONS" (PDF). Proceedings of the 2007 Winter Simulation Conference, page 2004-2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-04-29. Retrieved 2009-09-14.
- ↑ "Siemens AG to buy UGS". Dallas Business Journal. January 25, 2007.[ dead link ]