
Barnaviridae is a family of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses. Cultivated mushrooms serve as natural hosts. The family has one genus, Barnavirus, which contains one species: Mushroom bacilliform virus. Diseases associated with this family includes La France disease.

Tymoviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 42 species in this family, assigned to three genera, with two species unassigned to a genus.
Tombusvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 17 species in this genus. Symptoms associated with this genus include mosaic. The name of the genus comes from Tomato bushy stunt virus.
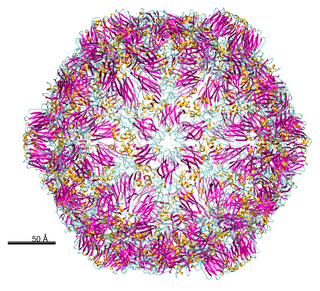
Nepovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae, in the subfamily Comovirinae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 40 species in this genus. Nepoviruses, unlike the other two genera in the subfamily Comovirinae, are transmitted by nematodes.

Ilarvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 22 species in this genus.
Cheravirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are five species in this genus.
Hordeivirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.
Lolavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Plants, specifically ryegrass, serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Lolium latent virus.
Allexivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Shallot, onion, and garlic serve as natural hosts. There are 13 species in this genus, seven of which are assigned to a subgenus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Aureusvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus.
Foveavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are eight species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Marafivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Tymoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 11 species in this genus.
Oleavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Bromoviridae. Olive trees serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Olive latent virus 2.

Tymovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Tymoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 28 species in this genus.

Carmotetraviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses. There is only one genus in this family, Alphacarmotetravirus, which has one species: Providence virus. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts.
Permutotetraviridae is a family of viruses. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts. The family contains one genus that has two species. Diseases associated with this family include: infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.
Alphanecrovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.
Velarivirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Closteroviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are eight species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: GLRaV-7: symptomless in white-berried grapevine cultivar from Albania. However, it induces leafroll symptoms onto grafted cv. cabernet.







