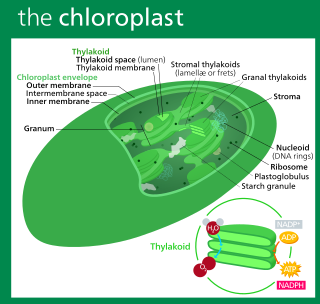
A chloroplast is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like Arabidopsis and wheat.

A mitochondrion is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term mitochondrion was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name.
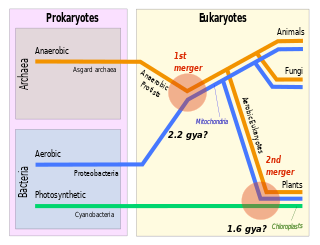
Symbiogenesis is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. Mitochondria appear to be phylogenetically related to Rickettsiales bacteria, while chloroplasts are thought to be related to cyanobacteria.

The alveolates are a group of protists, considered a major clade and superphylum within Eukarya. They are currently grouped with the stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate mitochondria into the SAR supergroup.
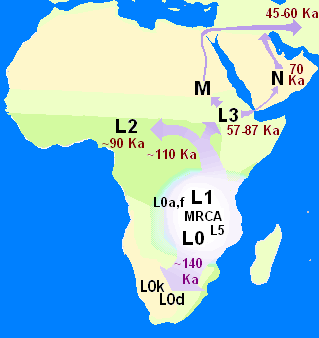
In human genetics, the Mitochondrial Eve is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of all living humans. In other words, she is defined as the most recent woman from whom all living humans descend in an unbroken line purely through their mothers and through the mothers of those mothers, back until all lines converge on one woman.

Mitochondrial DNA is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts.
A plastid, pl. plastids, is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
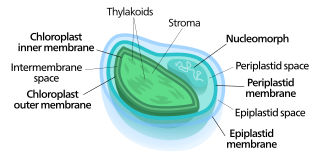
Nucleomorphs are small, vestigial eukaryotic nuclei found between the inner and outer pairs of membranes in certain plastids. They are thought to be vestiges of primitive red and green algal nuclei that were engulfed by a larger eukaryote. Because the nucleomorph lies between two sets of membranes, nucleomorphs support the endosymbiotic theory and are evidence that the plastids containing them are complex plastids. Having two sets of membranes indicate that the plastid, a prokaryote, was engulfed by a eukaryote, an alga, which was then engulfed by another eukaryote, the host cell, making the plastid an example of secondary endosymbiosis.
Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found off the chromosomes, either inside or outside the nucleus of a cell. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes contained in the nucleus. Multiple forms of extrachromosomal DNA exist, and, while some of these serve important biological functions, they can also play a role in diseases such as cancer.
In genetics, paternal mtDNA transmission and paternal mtDNA inheritance refer to the incidence of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) being passed from a father to his offspring. Paternal mtDNA inheritance is observed in a small proportion of species; in general, mtDNA is passed unchanged from a mother to her offspring, making it an example of non-Mendelian inheritance. In contrast, mtDNA transmission from both parents occurs regularly in certain bivalves.
In human mitochondrial genetics, haplogroup E is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup typical for the Malay Archipelago. It is a subgroup of haplogroup M9.

In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup Y is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.

Polytomella is a genus of green algae in the family Dunaliellaceae. Polytomella is a free-living, flagellated, nonphotosynthetic green alga with a highly reduced, linear fragmented mitochondrial genome. Polytomella, as it exists today, bears evidence of once having a functional photosynthetic plastid which has over evolutionary time changed such that it would appear now to have no genome or gene expressing mechanisms remaining to it. Having transitioned completely to heterotrophy, Polytomella uses organic acids, alcohols and monosaccharides as its carbon source. Despite being an evolutionary descendant of the green algae, Polytomella is a colourless organism because it has lost its photosynthetic ability.

HIG1 domain family member 1A (HIGD1A), also known as hypoglycemia/hypoxia inducible mitochondrial protein1-a (HIMP1-a) and hypoxia induced gene 1 (HIG1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIGD1A gene on chromosome 3. This protein promotes mitochondrial homeostasis and survival of cells under stress and is involved in inflammatory and hypoxia-related diseases, including atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease, and Alzheimer's disease, as well as cancer.

Mitochondrial import receptor subunit TOM70, also known as translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane protein 70 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TOMM70 gene.
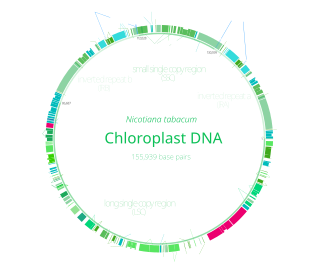
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell nucleus. The existence of chloroplast DNA was identified biochemically in 1959, and confirmed by electron microscopy in 1962. The discoveries that the chloroplast contains ribosomes and performs protein synthesis revealed that the chloroplast is genetically semi-autonomous. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences were published in 1986, Nicotiana tabacum (tobacco) by Sugiura and colleagues and Marchantia polymorpha (liverwort) by Ozeki et al. Since then, a great number of chloroplast DNAs from various species have been sequenced.
Ostreococcus tauri is a unicellular species of marine green alga about 0.8 micrometres (μm) in diameter, the smallest free-living (non-symbiotic) eukaryote yet described. It has a very simple ultrastructure, and a compact genome.

Mitochondrial genome maintenance exonuclease 1, abbreviated as MGME1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MGME1 gene. MGME1 is a 344 amino acids long protein belonging to the PD-(D/E)XK family of nucleases. It localizes to mitochondria where it is important for maintenance of the mitochondrial genome. Loss of function mutations in MGME1 lead to defects in mitochondrial DNA, including mitochondrial DNA depletion, duplications, deletions and increased replication intermediates. Also, there is an accumulation of 7S DNA, a short single stranded linear DNA strand. MGME1 deficiency in humans leads to multisystemic mitochondrial disease.
A linear chromosome is a chromosome which is linear in shape, and contains terminal ends. In most eukaryotic cells, DNA is arranged in multiple linear chromosomes. In contrast, most prokaryotic cells generally contain a singular circular chromosome.













