Related Research Articles

Libya's history covers its rich mix of ethnic groups added to the indigenous Berbers/Amazigh people. Amazigh have been present throughout the entire history of the country. For most of its history, Libya has been subjected to varying degrees of scholar control, from Europe, Asia, and Africa. The modern history of independent Libya, as reflected in the many revolutions denoted under many moons began before Romantic time or Justinian scribing.

Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad to the south, Niger to the southwest, Algeria to the west, and Tunisia to the northwest. It has maritime borders with Malta, Greece, and Turkey in the eastern Mediterranean. Libya is made of three historical regions: Tripolitania, Fezzan, and Cyrenaica. With an area of almost 700,000 square miles, it is the fourth-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the 16th-largest in the world. Libya has the 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world. The largest city and capital, Tripoli, is located in western Libya and contains over three million of Libya's seven million people.

Libya is fourth in size among the countries of Africa and sixteenth among the countries of the world. It is on the Mediterranean between Egypt and Tunisia, with Niger and Chad to the south and Sudan to the southeast. Although the oil discoveries of the 1960s have brought immense wealth, at the time of its independence it was an extremely poor desert state whose only important physical asset appeared to be its strategic location at the midpoint of Africa's northern rim.

The foreign relations of Libya under Muammar Gaddafi (1969–2011) underwent much fluctuation and change. They were marked by severe tension with the West and by other national policies in the Middle East and Africa, including the Libyan government's financial and military support for numerous paramilitary and rebel groups.

The Arab League, formally the League of Arab States, is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, Eastern Africa, and Western Asia. The Arab League was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 initially with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. Yemen joined as a member on 5 May 1945. Currently, the League has 22 members, but Syria's participation has been suspended since November 2011.

Cyrenaica is the eastern coastal region of Libya. Also known as Pentapolis in antiquity, it formed part of the Roman province of Crete and Cyrenaica, later divided into Libya Pentapolis and Libya Sicca. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as Barqa, after the city of Barca.
The Arab world, formally the Arab homeland, also known as the Arab nation, the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, consists of the 22 Arab countries which are members of the Arab League. A majority of these countries are located in Western Asia, Northern Africa, Western Africa, and Eastern Africa. The region stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Indian Ocean in the southeast. The eastern part of the Arab world is known as the Mashriq, and the western part as the Maghreb. Arabic is used as the lingua franca throughout the Arab world.
Tribalism is the state of being organized by, or advocating for, tribes or tribal lifestyles. Human evolution has primarily occurred in small hunter-gatherer groups, as opposed to in larger and more recently settled agricultural societies or civilizations. With a negative connotation and in a political context, tribalism can also mean discriminatory behavior or attitudes towards out-groups, based on in-group loyalty.
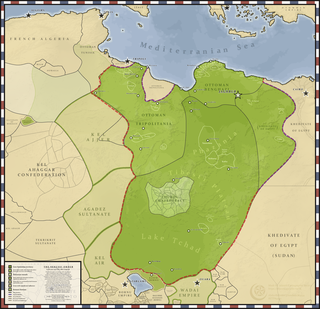
The Senusiyya, Senussi or Sanusi are a Muslim political-religious tariqa and clan in colonial Libya and the Sudan region founded in Mecca in 1837 by the Grand Senussi, the Algerian Muhammad ibn Ali as-Senussi. Senussi was concerned with what he saw as both the decline of Islamic thought and spirituality and the weakening of Muslim political integrity.

The Libyan Desert is a geographical region filling the north-eastern Sahara Desert, from eastern Libya to the Western Desert of Egypt and far northwestern Sudan. On medieval maps, its use predates today's Sahara, and parts of the Libyan Desert include the Sahara's most arid and least populated regions; this is chiefly what sets the Libyan Desert apart from the greater Sahara. The consequent absence of grazing, and near absence of waterholes or wells needed to sustain camel caravans, prevented Trans-Saharan trade between Kharga close to the Nile, and Murzuk in the Libyan Fezzan. This obscurity saw the region overlooked by early European explorers, and it was not until the early 20th century and the advent of the motor car before the Libyan Desert started to be fully explored.

The Sahara is a desert on the African continent. With an area of 9,200,000 square kilometres (3,600,000 sq mi), it is the largest hot desert in the world and the third largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Arctic.

The Maghreb, also known as Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco and Tunisia. The Maghreb also includes the disputed territories of Western Sahara and the Spanish cities Ceuta and Melilla. As of 2018, the region had a population of over 100 million people.
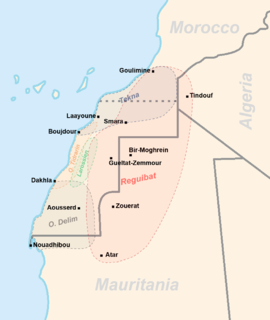
The Sahrawi, or Saharawi people, are an ethnic group and nation native to the western part of the Sahara desert, which includes the Western Sahara, southern Morocco, much of Mauritania, and the extreme southwest of Algeria.

Murzuk, Murzuq, Murzug or Merzug is an oasis town and the capital of the Murzuq District in the Fezzan region of southwest Libya. It lies on the northern edge of the Murzuq Desert, an extremely arid region of ergs or great sand dunes which is part of the greater Sahara Desert.

The Toubou, or Tubu, are a Saharan ethnic group inhabiting northern Chad, southern Libya, northeastern Niger and northwestern Sudan. They live either as herders and nomads or as farmers near oases. Their society is clan-based, with each clan having certain oases, pastures and wells.

Muammar Gaddafi became the de facto leader of Libya on 1 September 1969 after leading a group of young Libyan Army officers against King Idris I in a bloodless coup d'état. After the king had fled the country, the Revolutionary Command Council (RCC) headed by Gaddafi abolished the monarchy and the old constitution and established the Libyan Arab Republic, with the motto "freedom, socialism and unity".

Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area. With 1.3 billion people as of 2018, it accounts for about 16% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita, in part due to geographic impediments, legacies of European colonization in Africa and the Cold War, predatory/neo-colonialistic activities by Western nations and China, and undemocratic rule and deleterious policies. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context.

Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign state in Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to the north and northwest, Algeria to the northeast, Mali to the east and southeast, and Senegal to the southwest. Mauritania is the eleventh largest country in Africa, and 90 percent of its territory is situated in the Sahara. Most of its population of 4.4 million lives in the temperate south of the country, with roughly one third concentrated in the capital and largest city, Nouakchott, located on the Atlantic coast.
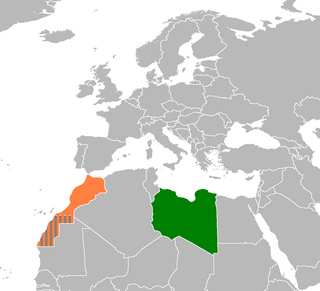
Libya–Morocco relations is the bilateral relations between Libya and Morocco, two Arab-Berber North African and Maghreb countries. Libya has an embassy in Rabat and Morocco has an embassy in Tripoli, which was attacked by ISIS militants in 2015.

During the Trans-Saharan slave trade, slaves were transported across the Sahara desert. Most were moved from Sub-Saharan Africa to North Africa to be sold to Mediterranean and Middle eastern civilizations; some moved the other way.
References
- ↑ Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. OECD. 2014. p. 197. ISBN 978-9264222359 . Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ↑ Hilsum, Lindsay (2012). Sandstorm. Faber and Faber. ISBN 978-0571288052 . Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ↑ "Tripoli, Libye : Ligue populaire et sociale des tribus du Grand Sahara". maliweb.net. September 30, 2008. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ↑ "Niger political party delegation meets Kadhafi". panapress.com. July 27, 2006. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ↑ "League of Great Saraha Tribes advocates preservation of social ties". February 15, 2011.