
Pickering Nuclear Generating Station is a Canadian nuclear power station located on the north shore of Lake Ontario in Pickering, Ontario. It is one of the oldest nuclear power stations in the world and Canada's third-largest, with eight CANDU reactors. Since 2003, two of these units have been defueled and deactivated. The remaining six produce about 16% of Ontario's power and employ 3,000 workers.
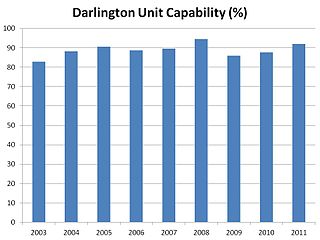
Darlington Nuclear Generating Station is a Canadian nuclear power station located on the north shore of Lake Ontario in Clarington, Ontario. It is a large nuclear facility comprising four CANDU nuclear reactors with a total output of 3,512 MWe when all units are online, providing about 20 percent of Ontario's electricity needs, enough to serve a city of two million people. The reactor design is significantly more powerful than those used in previous CANDU sites at Pickering and Bruce, making its 4-unit plant the second-largest in Canada behind the 8-unit Bruce. It is named for the Township of Darlington, the name of the municipality in which it is located, which is now part of the amalgamated Municipality of Clarington.

The Richard L. Hearn Generating Station is a decommissioned electrical generating station in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The plant was originally fired by coal, but later converted to burn natural gas. The plant has been described as "Pharaonic in scale", and encompasses 650 thousand cubic metres of space—large enough to fit 12 Parthenons inside.

The electricity sector in Canada has played a significant role in the economic and political life of the country since the late 19th century. The sector is organized along provincial and territorial lines. In a majority of provinces, large government-owned integrated public utilities play a leading role in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. Ontario and Alberta have created electricity markets in the last decade to increase investment and competition in this sector of the economy.

The Lakeview Generating Station was an Ontario Power Generation coal-burning power station located in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, in the Lakeview neighbourhood on Lakeshore Road just east of Cawthra Road. The former station, constructed in 1958–1962, had four smokestacks known as the Four Sisters; the eight boilers of the generating plant all 'twinned' their emissions into common stacks. The station was a landmark for years and was shut down in April, 2005, after 43 years of service. The four stacks, which could be seen from as far away as Burlington to the west and downtown Toronto to the east, were demolished on June 12, 2006. The rest of the building was demolished on June 28, 2007.

Bruce Power Limited Partnership is a Canadian business partnership composed of several corporations. It exists as a partnership between TC Energy (31.6%), BPC Generation Infrastructure Trust (61.4%), the Power Workers Union (4%) and The Society of United Professionals (1.2%). It is the licensed operator of the Bruce Nuclear Generating Station, located on the shores of Lake Huron, roughly 250 kilometres northwest of Toronto, between the towns of Kincardine and Saugeen Shores. It is the third-largest operating nuclear plant in the world by capacity.

The Nanticoke Generating Station was a coal-fired power station in Nanticoke, Ontario in operation from 1972 to 2013. It was the largest coal power station in North America and, at full capacity, it could provide 3,964 MW of power into the southern Ontario power grid from its base in Nanticoke, Ontario, Canada, and provided as much as 15% of Ontario's electricity.
The electricity policy of Ontario refers to plans, legislation, incentives, guidelines, and policy processes put in place by the Government of the Province of Ontario, Canada, to address issues of electricity production, distribution, and consumption. Policymaking in the electricity sector involves economic, social, and environmental considerations. Ontario's electricity supply outlook is projected to deteriorate in the near future due to increasing demand, aging electricity supply infrastructure, and political commitments, particularly the phase-out of coal-fired generation. Policymakers are presented with a range of policy choices in addressing the situation, both in terms of overall system design and structure, and specific electricity generating technologies.

Thunder Bay Generating Station is a defunct biomass-fired thermal power station owned by Ontario Power Generation ("OPG"). It is located on Mission Island in Thunder Bay, on the shore of Lake Superior.
Atikokan Generating Station is a biomass power plant owned by Ontario Power Generation (OPG) located 8 km (5 mi) north of Atikokan, Ontario. The plant employs 90 people. The Atikokan Generating Station began operation as a coal fired station in 1985 and underwent an overhaul in the autumn of 2003.

Ontario Power Generation Inc. (OPG) is a Crown corporation and "government business enterprise" that is responsible for approximately half of the electricity generation in the province of Ontario, Canada. It is wholly owned by the government of Ontario. Sources of electricity include nuclear, hydroelectric, wind, gas and biomass. Although Ontario has an open electricity market, the provincial government, as OPG's sole shareholder, regulates the price the company receives for its electricity to be less than the market average, in an attempt to stabilize prices. Since 1 April 2008, the company's rates have been regulated by the Ontario Energy Board.
Through the 1996 Electric Utilities Act the Alberta's deregulated electricity market began.
According to the International Hydropower Association, Canada is the fourth largest producer of hydroelectricity in the world in 2021 after the United States, Brazil, and China. In 2019, Canada produced 632.2 TWh of electricity with 60% of energy coming from Hydroelectric and Tidal Energy Sources).

The Lambton Generating Station was a coal-fuelled power plant located on the St. Clair River near Corunna, Ontario, delivering up to 950 MW of power to the grid. It is owned by Ontario Power Generation.

Capital Power is a North American independent power generation company based in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It develops, acquires, owns and operates power generation facilities using a variety of energy sources.
Brighton Beach Generating Station is a natural gas fired combined cycle fossil fuel power station in the Brighton Beach neighbourhood of Windsor, Ontario, Canada, owned by the Atura Power subsidiary of Ontario Power Generation. The electricity generated is under the control and marketing lead of Coral Energy Canada Inc. Gas for the plant is supplied by Union Gas, and cooling water is drawn from the Detroit River.
Smoky Falls Generating Station is one of four stations in the Lower Mattagami River Hydroelectric Complex owned by Ontario Power Generation (OPG) and the Moose Cree First Nation. The station is approximately 85 km (53 mi) northeast of Kapuskasing in the Cochrane District of Northern Ontario. Smoky Falls was originally commissioned as a 54 MW generating station in 1931 by the Spruce Falls Power and Paper Company but it was sold to OPG's predecessor, Ontario Hydro, in 1991. OPG completed a $2.6 billion upgrade of the four Lower Mattagami dams in 2014 and 2015. The new Smoky Falls was commissioned in late 2014 with a 267.9 MW installed capacity.












