In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the elbow and the radiocarpal joint is known as the forearm or "lower" arm, and the extremity beyond the wrist is the hand.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa at the elbow. It then divides into the radial and ulnar arteries which run down the forearm. In some individuals, the bifurcation occurs much earlier and the ulnar and radial arteries extend through the upper arm. The pulse of the brachial artery is palpable on the anterior aspect of the elbow, medial to the tendon of the biceps, and, with the use of a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer, often used to measure the blood pressure.

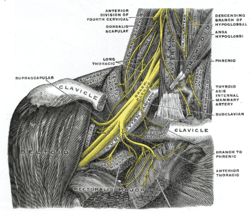
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve. This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit, it supplies afferent and efferent nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna, one of the two long bones in the forearm. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. It originates from the transverse processes of the four uppermost cervical vertebrae; it inserts onto the upper portion of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the cervical nerves C3-C4, and frequently also by the dorsal scapular nerve. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.
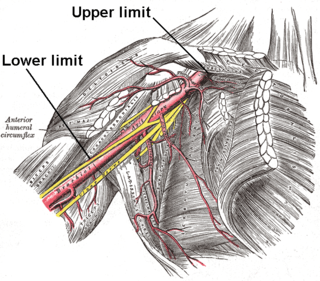
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis.

A nerve plexus is a plexus of intersecting nerves. A nerve plexus is composed of afferent and efferent fibers that arise from the merging of the anterior rami of spinal nerves and blood vessels. There are five spinal nerve plexuses, except in the thoracic region, as well as other forms of autonomic plexuses, many of which are a part of the enteric nervous system. The nerves that arise from the plexuses have both sensory and motor functions. These functions include muscle contraction, the maintenance of body coordination and control, and the reaction to sensations such as heat, cold, pain, and pressure. There are several plexuses in the body, including:

The lateral cord is the part of the brachial plexus formed by the anterior divisions of the upper (C5-C6) and middle trunks (C7). Its name comes from it being lateral to the axillary artery as it passes through the axilla. The other cords of the brachial plexus are the posterior cord and medial cord.

The medial cord is the part of the brachial plexus formed by of the anterior division of the lower trunk (C8-T1). Its name comes from it being medial to the axillary artery as it passes through the axilla. The other cords of the brachial plexus are the posterior cord and lateral cord.

The thoracodorsal nerve is a nerve present in humans and other animals, also known as the middle subscapular nerve or the long subscapular nerve. It supplies the latissimus dorsi muscle.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

The ilioinguinal nerve is a branch of the first lumbar nerve (L1). It separates from the first lumbar nerve along with the larger iliohypogastric nerve. It emerges from the lateral border of the psoas major just inferior to the iliohypogastric, and passes obliquely across the quadratus lumborum and iliacus. The ilioinguinal nerve then perforates the transversus abdominis near the anterior part of the iliac crest, and communicates with the iliohypogastric nerve between the transversus and the internal oblique muscle.

The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.

The medial brachial cutaneous nerve is a sensory branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus derived from spinal nerves C8-T1. It provides sensory innervation to the medial arm. It descends accompanied by the basilic vein.

The lower subscapular nerve, also known as the inferior subscapular nerve, is the third branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It innervates the inferior portion of the subscapularis muscle and the teres major muscle.

The upper (superior) subscapular nerve is the first branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The upper subscapular nerve contains axons from the ventral rami of the C5 and C6 cervical spinal nerves. It innervates the superior portion of the subscapularis muscle. The inferior portion of the subscapularis is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve.
The upper (superior) trunk is part of the brachial plexus. It is formed by joining of the ventral rami of the fifth (C5) and sixth (C6) cervical nerves. The upper trunk divides into an anterior and posterior division.