
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
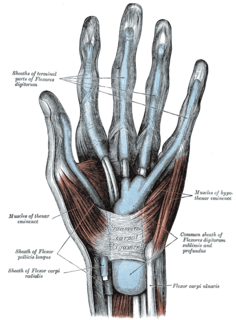
The thenar eminence refers to the group of muscles on the palm of the human hand at the base of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The word thenar comes from Greek θέναρ (thenar) 'palm of the hand'.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

Wrist drop, is a medical condition in which the wrist and the fingers cannot extend at the metacarpophalangeal joints. The wrist remains partially flexed due to an opposing action of flexor muscles of the forearm. As a result, the extensor muscles in the posterior compartment remain paralyzed.

The upper limb or upper extremity is the region in a vertebrate animal extending from the deltoid region up to and including the hand, including the arm, axilla and shoulder.

The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.

In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique.

The opponens digiti minimi is a muscle in the hand. It is of a triangular form, and placed immediately beneath the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of the three hypothenar muscles that control the little finger.

The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles, lying deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis.

The plantar nerves are a pair of nerves innervating the sole of the foot. They arise from the posterior branch of the tibial nerve.

The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the palm that control the motion of the little finger.
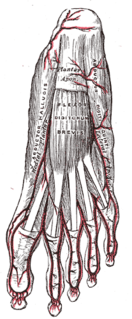
The abductor digiti minimi is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.
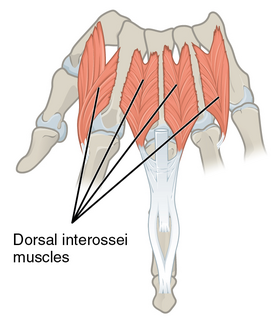
In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.

The flexor digiti minimi brevis is a hypothenar muscle in the hand that flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. It lies lateral to the abductor digiti minimi when the hand is in anatomical position.

The lateral plantar nerve is a branch of the tibial nerve, in turn a branch of the sciatic nerve and supplies the skin of the fifth toe and lateral half of the fourth, as well as most of the deep muscles, its distribution being similar to that of the ulnar nerve in the hand.
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains twelve muscles which are chiefly responsible for extension of the wrist and digits, and supination of the forearm. It is separated from the anterior compartment by the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna.
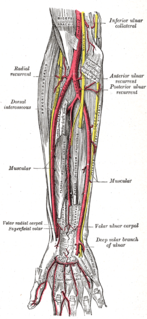
The deep palmar branch of ulnar artery passes between the Abductor digiti minimi and Flexor digiti minimi brevis and through the origin of the Opponens digiti minimi; it anastomoses with the radial artery, and completes the deep volar arch.

The cervical spinal nerve 8 (C8) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment.

The muscles of the thumb are nine skeletal muscles located in the hand and forearm. The muscles allow for flexion, extension, adduction, abduction and opposition of the thumb. The muscles acting on the thumb can be divided into two groups: The extrinsic hand muscles, with their muscle bellies located in the forearm, and the intrinsic hand muscles, with their muscles bellies located in the hand proper.















