
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA).

The ostium primum atrial septal defect is a defect in the atrial septum at the level of the tricuspid and mitral valves. This is sometimes known as an endocardial cushion defect because it often involves the endocardial cushion, which is the portion of the heart where the atrial septum meets the ventricular septum and the mitral valve meets the tricuspid valve.

A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure.

Ebstein's anomaly is a congenital heart defect in which the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced downwards towards the apex of the right ventricle of the heart. EA has great anatomical heterogeneity that generates a wide spectrum of clinical features at presentation and is complicated by the fact that the lesion is often accompanied by other congenital cardiac lesions. It is classified as a critical congenital heart defect accounting for less than 1% of all congenital heart defects presenting in around 1 per 200,000 live births. Ebstein's anomaly usually presents with a systolic murmur and frequently with a gallop rhythm.

The atrium is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.

Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" or "endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the heart that creates connections between all four of its chambers. It is a very specific combination of 3 defects:

The fossa ovalis is a depression in the right atrium of the heart, at the level of the interatrial septum, the wall between right and left atrium. The fossa ovalis is the remnant of a thin fibrous sheet that covered the foramen ovale during fetal development.
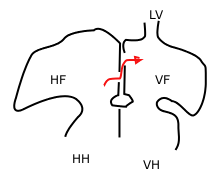
In the fetal heart, the foramen ovale, also foramen Botalli or the ostium secundum of Born, allows blood to enter the left atrium from the right atrium. It is one of two fetal cardiac shunts, the other being the ductus arteriosus. Another similar adaptation in the fetus is the ductus venosus. In most individuals, the foramen ovale closes at birth. It later forms the fossa ovalis.

The interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.

The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart.

Balloon septostomy is the widening of a foramen ovale, patent foramen ovale (PFO), or atrial septal defect (ASD) via cardiac catheterization using a balloon catheter. This procedure allows a greater amount of oxygenated blood to enter the systemic circulation in some cases of cyanotic congenital heart defect (CHD).

The primitive atrium is a stage in the embryonic development of the human heart. It grows rapidly and partially encircles the bulbus cordis; the groove against which the bulbus cordis lies is the first indication of a division into right and left atria.

During heart development of a human embryo, the single primitive atrium becomes divided into right and left by a septum, the septum primum. The septum primum grows downward into the single atrium.
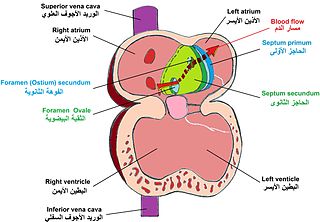
The septum secundum is a muscular flap that is important in heart development. It is semilunar in shape, and grows downward from the upper wall of the atrium immediately to the right of the septum primum and ostium secundum. It is important in the closure of the foramen ovale after birth.

The foramen secundum or ostium secundum is a foramen in the septum primum, a precursor to the interatrial septum of the human heart.
The proper development of the atrioventricular canal into its prospective components to create a clear division between the four compartments of the heart and ensure proper blood movement through the heart, are essential for proper heart function. When this process does not happen correctly, a child will develop atrioventricular canal defect which occurs in 2 out of every 10,000 births. It also has a correlation with Down syndrome because 20% of children with Down syndrome have atrioventricular canal disease as well. This is a very serious condition and surgery is necessary within the first six months of life for a child. Half of the children who are untreated with this condition die during their first year due to heart failure or pneumonia.
The heart is the first functional organ in a vertebrate embryo. There are 5 stages to heart development.

Lutembacher's syndrome is a very rare form of congenital heart disease that affects one of the chambers of the heart as well as a valve. It is commonly known as both congenital atrial septal defect (ASD) and acquired mitral stenosis (MS). Congenital atrial septal defect refers to a hole being in the septum or wall that separates the two atria; this condition is usually seen in fetuses and infants. Mitral stenosis refers to mitral valve leaflets sticking to each other making the opening for blood to pass from the atrium to the ventricles very small. With the valve being so small, blood has difficulty passing from the left atrium into the left ventricle. Septal defects that may occur with Lutembacher's syndrome include: Ostium primum atrial septal defect or ostium secundum which is more prevalent.

The atrioventricular septum is a septum of the heart between the right atrium (RA) and the left ventricle (LV).

Heart development, also known as cardiogenesis, refers to the prenatal development of the heart. This begins with the formation of two endocardial tubes which merge to form the tubular heart, also called the primitive heart tube. The heart is the first functional organ in vertebrate embryos.














