Structure
UML class and sequence diagram

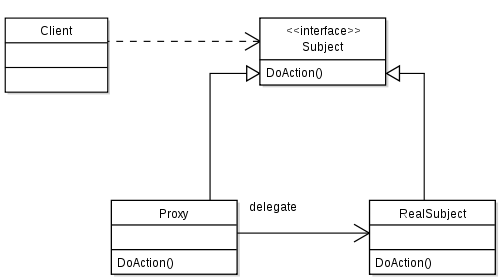
In the above UML class diagram, the Proxy class implements the Subject interface so that it can act as substitute for Subject objects. It maintains a reference (realSubject) to the substituted object (RealSubject) so that it can forward requests to it (realSubject.operation()).
The sequence diagram shows the run-time interactions: The Client object works through a Proxy object that controls the access to a RealSubject object. In this example, the Proxy forwards the request to the RealSubject, which performs the request.
Class diagram