
Odonata is an order of flying insects that includes the dragonflies and damselflies. Like most other flying insects, they evolved in the early Mesozoic era. Their prototypes, the giant dragonflies of the Carboniferous, 325 mya, are no longer placed in the Odonata but included in the Protodonata or Meganisoptera.

The Carolina mantis is a species of praying mantis of the subfamily Stagmomantinae.

The Chinese mantis is a species of mantis native to Asia and the nearby islands. In 1896 this species was accidentally introduced by a nurseryperson at Mt. Airy near Philadelphia, United States. Tenodera sinensis often is erroneously referred to as Tenodera aridifolia sinensis because it was at first described as a subspecies of Tenodera aridifolia, but Tenodera sinensis is now established as a full species.

The European mantis is a large hemimetabolic insect in the family of the Mantidae ('mantids'), which is the largest family of the order Mantodea (mantises). Their common name praying mantis is derived from the distinctive posture of the first pair of legs that can be observed in animals in repose. It resembles a praying attitude. Both males and females have elongated bodies with two pairs of wings. The most striking features that all Mantodea share are a very mobile, triangular head with large compound eyes and their first pair of legs, which is highly modified for the efficient capture and restraint of fast-moving or flying prey.

Hymenopodidae is a family of the order Mantodea (mantises), which contains six subfamilies. Some of the species in this family mimic flowers and are found camouflaged among them; these are called flower mantises. Their coloration is aggressive mimicry, luring prey to approach close enough to be seized and eaten.

Miomantis caffra is a species of praying mantis native to southern Africa. It appeared in New Zealand in 1978, and was found more recently in Portugal and Los Angeles, USA, likely spread through the exotic pet trade. Females are facultatively parthenogenetic and unmated females can produce viable offspring.

Hierodula membranacea is a large praying mantis, sharing its common name giant Asian mantis with other large members of genus Hierodula: of which it is the type species. Its colours vary from green to yellow-green, or even brown to reddish-brown, similar to those of the giant Indian mantis and the giant Malaysian mantis. As the name suggests, it originates from south-eastern Asia and is among the largest of mantises. Male and female adults reach around 7–9 centimetres (2.8–3.5 in), excluding extended forelegs. It is a cannibalistic species, with the females sometimes eating the males after mating.

Phyllocrania paradoxa, common name ghost mantis, is a small species of mantis from Africa remarkable for its leaf-like body. It is one of the three species in the genus Phyllocrania. It is known for its distinct and exclusive camouflaged appearance of a dry weathered leaf.

Litaneutria minor, or the agile ground mantis, is native to the drier regions of North America. L. minor is found in the United States in Colorado, Arizona to Mexico, and the eastern regions of Washington to California. They also can be found in Canada in the southern Okanagan Valley and are Canada's only native mantis. They are very active hunters and will be seen running across the ground from early spring to late summer.

Sphodromantis viridis is a species of praying mantis that is kept worldwide as a pet. Its common names include African mantis, giant African mantis, and bush mantis.

Deroplatys lobata, common name Southeast Asian dead leaf mantis or dead leaf mantis, is a species of praying mantis that inhabits Thailand, Java, Borneo, Indonesia, Sumatra and the Malay Peninsula.
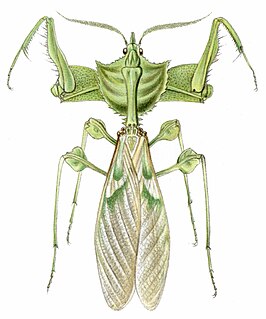
Idolomantis is a genus of praying mantises in the family Empusidae. It is represented by a single species, Idolomantis diabolica, commonly known as the devil's flower mantis or giant devil's flower mantis. It is one of the largest species of praying mantises, and is possibly the largest that mimics flowers

Empusa pennata, or the conehead mantis, is a species of praying mantis in genus Empusa native to the Mediterranean Region. It can be found in Portugal, Spain, southern France, Italy and on the mediterranean coasts of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya and Egypt. Because of its fragmented, low density populations, it is very rarely found in nature.

Orthodera novaezealandiae, known as the New Zealand mantis or the New Zealand praying mantis, is a species of praying mantis which is, as both the scientific name and common names suggest, indigenous and endemic to New Zealand.

Chloroharpax is a genus of praying mantis in the family Hymenopodidae. The genus is monotypic, being represented by a single species, Chloroharpax modesta, commonly called the Nigerian flower mantis, and is found across West Africa.

Empusa fasciata is a species of praying mantis in the genus Empusa in the order Mantodea.

Pseudocreobotra wahlbergii, or the spiny flower mantis, is a small flower mantis native to southern and eastern Africa.

Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They have triangular heads with bulging eyes supported on flexible necks. Their elongated bodies may or may not have wings, but all Mantodea have forelegs that are greatly enlarged and adapted for catching and gripping prey; their upright posture, while remaining stationary with forearms folded, has led to the common name praying mantis.

Phymata crassipes is a species of assassin and thread-legged bugs belonging to the family Reduviidae, subfamily Phymatinae.

Pseudoharpax is an African genus of praying mantids in the family Galinthiadidae.
























