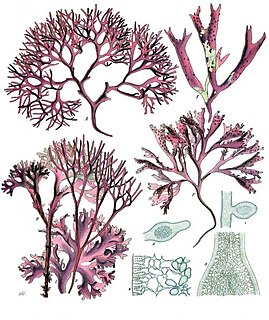
Chondrus crispus—commonly called Irish moss or carrageen moss —is a species of red algae which grows abundantly along the rocky parts of the Atlantic coast of Europe and North America. In its fresh condition this protist is soft and cartilaginous, varying in color from a greenish-yellow, through red, to a dark purple or purplish-brown. The principal constituent is a mucilaginous body, made of the polysaccharide carrageenan, which constitutes 55% of its dry weight. The organism also consists of nearly 10% dry weight protein and about 15% dry weight mineral matter, and is rich in iodine and sulfur. When softened in water it has a sea-like odour and because of the abundant cell wall polysaccharides it will form a jelly when boiled, containing from 20 to 100 times its weight of water.

The beardfishes consist of a single extant genus, Polymixia, of deep-sea marine ray-finned fish named for their pair of long hyoid barbels. They are classified in their own order Polymixiiformes. But as Nelson says, "few groups have been shifted back and forth as frequently as this one, and they were recently added to Paracanthoptergii". For instance, they have previously been classified as belonging to the Beryciformes. They are of little economic importance.

Grenadiers or rattails are generally large, brown to black gadiform marine fish of the subfamily Macrourinae, the largest subfamily of the family Macrouridae. Found at great depths from the Arctic to Antarctic, members of this subfamily are amongst the most abundant of the deep-sea fish.
Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae is a myxozoan parasite of salmonid fish. It is the only species currently recognized in the monotypic genus Tetracapsuloides. It is the cause of proliferative kidney disease (PKD), one of the most serious parasitic diseases of salmonid populations in Europe and North America that can result in losses of up to 90% in infected populations.

Coelorinchus is a genus of rattail fish.

Coryphaenoides is a genus of rattails which is found in all oceans of the world. They are found in deep waters and C. yaquinae, recorded to 7,012 m (23,005 ft), is the only member in the family known from the hadal zone.

Miletus is a genus of butterflies sometimes called brownies. Its species are found in the eastern Palearctic realm and the Indomalayan realm, and some stray east of the Wallace Line. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner around 1819. Miletus is the type genus of the subfamily Miletinae.

Nezumia is a genus of rattails. The generic name derives from the Japanese 鼠 (nezumi), meaning "mouse".

Hymenocephalus is a genus of rattails.

Ventrifossa is a genus of rattails in the family Macrouridae.

Physiculus is a genus of morid cods.

Chondrus is a genus of red algae containing 11 accepted species:

Rhodymenia is a genus of red algae, containing the following species:

Alepocephalus is a genus of slickheads found in all oceans.

Chlorophthalmus is a genus of greeneyes

Laemonema is a genus of morid cods.
Ecklonia kurome is a brown alga species in the genus Ecklonia found in the Sea of Japan.
The Tokunoshima language, also Toku-No-Shima, is a dialect cluster spoken on Tokunoshima, Kagoshima Prefecture of southwestern Japan. It is part of the Amami–Okinawan languages, which are part of the Japonic languages.
Saccosporidae is a family of myxozoans. It is the only family within the class Malacosporea and has only three species, while the other class of Myxozoa, Myxosporea, includes more than a thousand.
Paracetonurus flagellicauda is a species of fish in the subfamily Macrourinae. Some sources place it in the genus Pseudonezumia.














