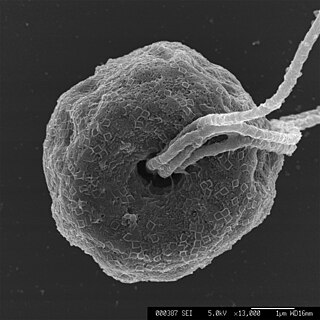
| Pterosperma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | Viridiplantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Pyramimonadophyceae |
| Order: | Pyramimonadales |
| Family: | Pterospermataceae |
| Genus: | Pterosperma Pouchet 1893 |
| Species | |
| |
Pterosperma is a genus of green algae in the order Pyramimonadales. [1]