| Pyramimonadales | |
|---|---|
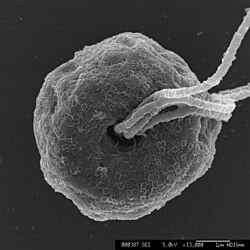 | |
| Pyramimonas sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Pyramimonadophyceae |
| Order: | Pyramimonadales Chadefaud [1] |
| Families | |
| |
Pyramimonadales are an order of green algae in the Chlorophyta. [2] The chloroplasts of phototrophic euglenids probably came from endosymbiosis with a member of this order. [3]