| Pyramimonas | |
|---|---|
 | |
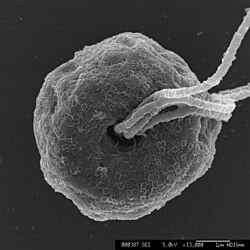
| Pyramimonas tetrarhynchus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Pyramimonadophyceae |
| Order: | Pyramimonadales |
| Family: | Pyramimonadaceae |
| Genus: | Pyramimonas Schmarda, 1849 |
| Species | |
| |
Pyramimonas is a genus of green algae in the order Pyramimonadales. [1] Phototropic euglenids inherited their plastids from a close relative of Pyramimonas which was an endosymbiont inside phagotrophic eukaryovorous euglenids. [2]