
The sea lettuces comprise the genus Ulva, a group of edible green algae that is widely distributed along the coasts of the world's oceans. The type species within the genus Ulva is Ulva lactuca, lactuca being Latin for "lettuce". The genus also includes the species previously classified under the genus Enteromorpha, the former members of which are known under the common name green nori.

Cystophora is a genus of brown algae found mostly in temperate waters around Australia. Most of the southern Australian species can be immediately recognised as belonging to this genus by their characteristic zigzag branching pattern. Identification of individual species is generally more difficult and relies on the size and shape of branches, particularly terminal branches, which are specialised reproductive structures known as receptacles. Due to their local diversity and dominance in southern Australia, they are regarded by some as 'the eucalypts of the underwater world'.

Porphyra is a genus of coldwater seaweeds that grow in cold, shallow seawater. More specifically, it belongs to red algae phylum of laver species, comprising approximately 70 species. It grows in the intertidal zone, typically between the upper intertidal zone and the splash zone in cold waters of temperate oceans. In East Asia, it is used to produce the sea vegetable products nori and gim. There are considered to be 60–70 species of Porphyra worldwide and seven around Britain and Ireland, where it has been traditionally used to produce edible sea vegetables on the Irish Sea coast. The species Porphyra purpurea has one of the largest plastid genomes known, with 251 genes.
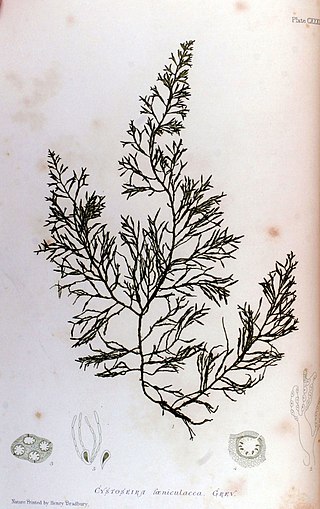
Cystoseira is a genus of brown algae in the order Fucales.

Halymenia a genus of a macroscopic red algae that grows in oceans worldwide.

Rhodymenia is a genus of red algae, containing the following species:

Plocamium is a genus of red algae in the family Plocamiaceae. It contains around 40 species and has a cosmopolitan distribution in temperate seas, although it is most diverse in the southern hemisphere. It is widely distributed in tropical and also warm-temperate and cold-temperate seas, such as northern Europe, the northern Arabian Sea and western Australia. They are also found in the Antarctic regions of Admiralty Bay and Terra Nova Bay.
Martensia is a genus of red algae, containing the following species:

Wrangeliaceae is a red alga family in the order Ceramiales. It was published by J.Agardh in 1851 in his book Species, genera et ordines algarum : seu descriptiones succinctae specierum.
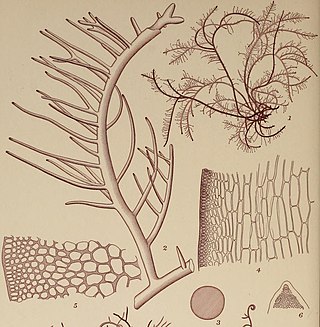
Hypnea is a genus of red algae, and a well known carrageenophyte.

Caulerpa sedoides, also known as mini-grapes or bubble caulerpa, is a species of seaweed in the Caulerpaceae family native to Australia.

Callithamniaceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Ceramiales. The family was first described by Friedrich Traugott Kützing in 1843.

Wrangelia is a genus of red algae in the family Wrangeliaceae.
Gongolaria is a genus of brown algae in the family Sargassaceae. It was formerly included in Cystoseira, but was recently found not to be closely related to it.
Ericaria is a genus of brown algae in the family Sargassaceae. It was formerly included in Cystoseira, but was recently found not to be closely related to it.











