
Mosasaurus is the type genus of the mosasaurs, an extinct group of aquatic squamate reptiles. It lived from about 82 to 66 million years ago during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. The earliest fossils of Mosasaurus known to science were found as skulls in a chalk quarry near the Dutch city of Maastricht in the late 18th century, which were initially thought to have been the bones of crocodiles or whales. One skull discovered around 1780, and which was seized by France during the French Revolutionary Wars for its scientific value, was famously nicknamed the "great animal of Maastricht". In 1808, naturalist Georges Cuvier concluded that it belonged to a giant marine lizard with similarities to monitor lizards but otherwise unlike any known living animal. This concept was revolutionary at the time and helped support the then-developing ideas of extinction. Cuvier did not designate a scientific name for the new animal, and this was done by William Daniel Conybeare in 1822 when he named it Mosasaurus in reference to its origin in fossil deposits near the Meuse River. The exact affinities of Mosasaurus as a squamate remain controversial, and scientists continue to debate whether its closest living relatives are monitor lizards or snakes.
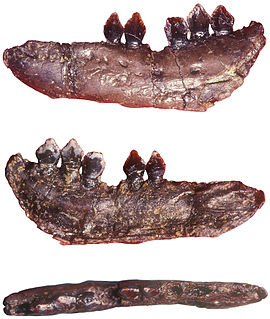
Echinodon is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the earliest Cretaceous of southern England and possibly western France in the Berriasian epoch. The first specimens were jaw bones named Echinodon becklesii by Sir Richard Owen in 1861, and since their original description only additional teeth have been discovered. The specific name honours collector Samuel Beckles who discovered the material of Echinodon and many other taxa from across England, while the genus name translates as "prickly tooth" in reference to the dental anatomy of the taxon.

The Purbeck Group is an Upper Jurassic to Lower Cretaceous lithostratigraphic group in south-east England. The name is derived from the district known as the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset where the strata are exposed in the cliffs west of Swanage.

Nuthetes is the name given to a dubious dromaeosaurid, genus of theropod dinosaur, known only from fossil teeth and jaw fragments found in rocks of the middle Berriasian age in the Cherty Freshwater Member of the Lulworth Formation in England. As a dromaeosaurid, Nuthetes would have been a small predator.

The Wessex Formation is a fossil-rich English geological formation that dates from the Berriasian to Barremian stages of the Early Cretaceous. It forms part of the Wealden Group and underlies the younger Vectis Formation and overlies the Durlston Formation. The dominant lithology of this unit is mudstone with some interbedded sandstones. It is part of the strata of the Wessex Basin, exposed in both the Isle of Purbeck and the Isle of Wight. While the Purbeck sections are largely barren of vertebrate remains, the Isle of Wight sections are well known for producing the richest and most diverse fauna in Early Cretaceous Europe.

The Fossil Forest is the remains of an ancient submerged forest from Jurassic times, located to the east of Lulworth Cove on the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset, England. It lies on the Jurassic Coast, on a wide ledge in the seaside cliff. The site is within the Lulworth Ranges and thus has restricted access. Parts of forest can also be seen on the Isle of Portland and in quarries near the town of Weymouth to the west.
Paramacellodus is an extinct genus of scincomorph lizards from the Early Cretaceous of England and France, and the Late Jurassic of Portugal and the western United States. The type species, Paramacellodus oweni, was named in 1967 from the earliest Cretaceous (Berriasian) Purbeck Group in Dorset, England. Additional material referable to a species of Paramacellodus, possibly P. oweni, has been described from the Morrison Formation, specifically in Como Bluff, Wyoming, and Dinosaur National Monument, Utah. An indeterminate species is known from the Berriasian aged Angeac-Charente bonebed in France. Paramacellodus belongs to an extinct family of scincomorphs called Paramacellodidae, which spanned most of Laurasia during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous and represented one of the earliest evolutionary radiations of lizards.

Dorsetochelys is an extinct genus of turtle from the Early Cretaceous of southern England and northwestern Germany.

Pholidosaurus is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodylomorph. It is the type genus of the family Pholidosauridae. Fossils have been found in northwestern Germany. The genus is known to have existed during the Berriasian-Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. Fossil material found from the Annero and Jydegård Formations in Skåne, Sweden and on the island of Bornholm, Denmark, have been referred to as a mesoeucrocodylian, and possibly represent the genus Pholidosaurus.

Pleurosternon is an extinct genus of freshwater pleurosternid turtle from the late Jurassic period to the early Cretaceous period of Europe. Its type species, P. bullocki was described by the paleontologist Richard Owen in 1853. Since then, and throughout the late 19th century, many fossil turtles were incorrectly assigned to this genus, though only two are currently considered valid.

The Lacertoidea is a group of squamate reptiles that includes the Lacertidae, Teiidae, Gymnophthalmidae, and Amphisbaenia. The finding from molecular phylogenetic studies that the burrowing Amphisbaenia were nested in a clade with the lizard forms led Vidal & Hedges (2005) to propose a new name for the group based on shared morphogical characters, Laterata, "referring to the presence of tile-like scales that form the rings in Amphisbaenia, and are also present ventrally in Lacertiformata and Teiformata".

The Lulworth Formation is a geologic formation in England. It dates from the late Tithonian to the mid Berriasian. It is a subunit of the Purbeck Group. In Dorset, it consists of three members, which are in ascending order, the Mupe Member, the Ridgway Member, and the Warbarrow Tout Member. The Mupe Member is typically 11 to 16 m thick and largely consists of marls and micrites with interbeds of calcareous mudstone. The Ridgeway Member is about 3 to 7 m thick and consists of in its western portion carbonaceous muds, marls and micrites, in the east the muds are replaced by micritic limestone. The Warbarrow Tout Member is 17 to 39 m thick and consists of limestone at the base and micrite and mudstone for the rest of the sequence, this member is the primary source of the vertebrate fossils within the formation. Elsewhere the unit is undifferentiated.

Triconodon is a genus of extinct mammal from the Early Cretaceous of England and France with two known species: T. mordax and T. averianovi. First described in 1859 by Richard Owen, it is the type genus for the order Triconodonta, a group of mammals characterised by their three-cusped (triconodont) molar teeth. Since then, this "simplistic" type of dentition has been understood to be either ancestral for mammals or else to have evolved multiple times, rendering "triconodonts" a paraphyletic or polyphyletic assemblage respectively, but several lineages of "triconodont" mammals do form a natural, monophyletic group, known as Eutriconodonta, of which Triconodon is indeed part of.

Eichstaettisaurus is a genus of lizards from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Germany, Spain, and Italy. With a flattened head, forward-oriented and partially symmetrical feet, and tall claws, Eichstaettisaurus bore many adaptations to a climbing lifestyle approaching those of geckoes. The type species, E. schroederi, is among the oldest and most complete members of the Squamata, being known by one specimen originating from the Tithonian-aged Solnhofen Limestone of Germany. A second species, E. gouldi, was described from another skeleton found in the Matese Mountains of Italy. Despite being very similar to E. schroederi, it lived much later, during the Albian stage. Fossils of both species show exceptional preservation due to deposition in low-oxygen marine environments.
Sunnybatrachus is a genus of extinct frog that lived during the Berriasian epoch of the Early Cretaceous of England. The only known material, including the holotype ilium as well as bones of the skull, vertebral column, forelimb, pelvis, and hindlimb was named Sunnybatrachus purbeckensis by Susan E. Evans and Gerard J. McGowan in 2002. The species name describes the Purbeck Limestone Group, while the genus name is for the Sunnydown Farm locality of the Lulworth Formation, where the fossils were found.
Hylaeochelys is an extinct genus of plesiochelyid turtle that lived during the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous in Portugal, Spain, France, and southern England. The type species was originally named by Richard Owen as Pleurosternon latiscutatum in 1853, before being moved to the new genus Hylaeochelys by Richard Lydekker in 1889. Other species included in the genus are H. belli, H. kappa and H. lata, originally named under different genera by Gideon Mantell and Owen, respectively. All species are represented by carapaces, primarily from the Lulworth Formation of the Purbeck Limestone Group that was deposited during the Berriasian.
Kouriogenys is a genus of extinct mammal from the Early Cretaceous of southern England. The type and only species was originally described as Spalacotherium minus by Richard Owen in 1871 for a dentary with teeth from the Berriasian Lulworth Formation, although it was given its own genus in 2012 by Brian Davis. The genus name is taken from the Ancient Greek "youthful" and "jaw" in reference to the replacement method of the premolars. Kouriogenys is closely related to coexisting genera Peramus and Peramuroides, and along with other genera these make up the family Peramuridae, a group of extinct zatherians.
Durotrigia is a genus of extinct lizard from the Early Cretaceous of southern England. The type and only species is Durotrigia triconidens, named in 1967 by R. Hoffstetter for jaw material in a review of the lizard fauna of the Berriasian Lulworth Formation. The genus was found in the Mammal Bed near the base of the formation alongside the other lizards Paramacellodus, Becklesius, Pseudosaurillus, Dorsetisaurus, Saurillus and Parviraptor. Durotrigia is likely a genus within the family Globauridae.
Parasaurillus is a genus of extinct lizard from the Early Cretaceous of southern England. The type and only species is Parasaurillus pseudobtusus, named in 2002 by Susan E. Evans and Belinda Searle for extensive jaw and tooth material that has previously been classified as either Saurillus obtusus or Pseudosaurillus from the Berriasian Lulworth Formation. The taxon was found in the Mammal Bed near the base of the formation alongside the other lizards Becklesius, Dorsetisaurus, Durotrigia, Paramacellodus, Pseudosaurillus, Parviraptor and Saurillus obtusus. It is likely closely related to Scincoidea, more so than other contemporary taxa.
Pseudosaurillus is a genus of extinct lizard from the Early Cretaceous of southern England. The type and only species is Pseudosaurillus becklesi, named in 1967 by R. Hoffstetter limited jaw and tooth material from the Berriasian Lulworth Formation. A large amount of material that was additionally referred to Saurillus by Hoffstetter was reassigned to Pseudosaurillus in 1983 by Estes, but this has since been reclassified within its own genus Parasaurillus by Susan E. Evans and Belinda Searle in 2002. The taxon was found in the Mammal Bed near the base of the formation alongside the other lizards Becklesius, Dorsetisaurus, Durotrigia, Paramacellodus, Parasaurillus, Parviraptor and Saurillus. Like Becklesius, Pseudosaurillus may be a member of the family Paramacellodidae.











