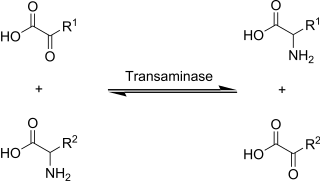
Transamination is a chemical reaction that transfers an amino group to a ketoacid to form new amino acids. This pathway is responsible for the deamination of most amino acids. This is one of the major degradation pathways which convert essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids.

Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates.

Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme that was first described by Arthur Karmen and colleagues in 1954. AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells and gall bladder. Serum AST level, serum ALT level, and their ratio are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels.
In enzymology, a 2-aminoadipate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, 4-aminobutyrate transaminase, also called GABA transaminase or 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase, or GABA-T, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxyglutamate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 5-aminovalerate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cysteine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-amino-acid transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a diamine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a dihydroxyphenylalanine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a histidinol-phosphate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a leucine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-lysine 6-transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyridoxamine-oxaloacetate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyridoxamine-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a taurine-2-oxoglutarate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction.
Phosphoserine transaminase is an enzyme with systematic name O-phospho-L-serine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Putrescine aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.82, putrescine-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase, YgjG, putrescine:alpha-ketoglutarate aminotransferase, PAT, putrescine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase, putrescine transaminase) is an enzyme with systematic name butane-1,4-diamine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction





