
Novartis AG is a Swiss multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland. Consistently ranked in the global top five, Novartis is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world and was the fourth largest by revenue in 2022.

The Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited is a Japanese multinational pharmaceutical company. It is the third largest pharmaceutical company in Asia, behind Sinopharm and Shanghai Pharmaceuticals, and one of the top 20 largest pharmaceutical companies in the world by revenue. The company has over 49,578 employees worldwide and achieved US$19.299 billion in revenue during the 2018 fiscal year. The company is focused on oncology, rare diseases, neuroscience, gastroenterology, plasma-derived therapies and vaccines. Its headquarters is located in Chuo-ku, Osaka, and it has an office in Nihonbashi, Chuo, Tokyo. In January 2012, Fortune Magazine ranked the Takeda Oncology Company as one of the 100 best companies to work for in the United States. As of 2015, Christophe Weber was appointed as the CEO and president of Takeda.

Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20–24 base pairs in length, similar to microRNA (miRNA), and operating within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. It interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences by degrading messenger RNA (mRNA) after transcription, preventing translation. It was discovered in 1998 by Andrew Fire at the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington, D.C. and Craig Mello at the University of Massachusetts in Worcester.

Biocon Limited is an Indian biopharmaceutical company based in Bengaluru, India. It was founded by Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw in 1978. The company manufactures generic active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that are sold in approximately 120 countries, including the United States and Europe. It also manufactures novel biologics as well as biosimilar insulins and antibodies, which are sold in India as branded formulations. Biocon's biosimilar products are also sold in both bulk and formulation forms in several emerging markets.

Jerini AG was a pharmaceutical company based in Berlin, Germany, which focused on the discovery and development of novel peptide-based drugs. Using a proprietary technology platform, Peptides-to-Drugs (P2D), Jerini pursued disease indications for which limited, inadequate, or no treatment options exist. As a result, Jerini established a drug pipeline composed of its own programs as well as others in collaboration with partners. Jerini's commercialization strategy was to market new drugs in niche indications independently and in larger indications with partners. Jerini was acquired by Shire plc in 2008.
RNA silencing or RNA interference refers to a family of gene silencing effects by which gene expression is negatively regulated by non-coding RNAs such as microRNAs. RNA silencing may also be defined as sequence-specific regulation of gene expression triggered by double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). RNA silencing mechanisms are conserved among most eukaryotes. The most common and well-studied example is RNA interference (RNAi), in which endogenously expressed microRNA (miRNA) or exogenously derived small interfering RNA (siRNA) induces the degradation of complementary messenger RNA. Other classes of small RNA have been identified, including piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) and its subspecies repeat associated small interfering RNA (rasiRNA).
Lucatumumab is a human monoclonal antibody against CD40 development of which was discontinued by Novartis in 2013 after it was investigated for the treatment of various types of cancer like multiple myeloma and follicular lymphoma.
MorphoSys AG is a German biopharmaceutical company founded in 1992. The company is headquartered near Munich, Germany, and has a wholly owned subsidiary, MorphoSys US Inc., in Boston, Massachusetts, in the US. The company has various antibody, protein and peptide technologies that it uses to discover and develop both proprietary and partnered drug candidates. The company has more than 100 drugs in its wider pipeline that are being investigated for a variety of diseases. While many of these are being developed in partnership with pharma and biotech companies, MorphoSys also has a proprietary pipeline with a focus on cancer and autoimmune diseases.

ALK inhibitors are anti-cancer drugs that act on tumours with variations of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) such as an EML4-ALK translocation. They fall under the category of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, which work by inhibiting proteins involved in the abnormal growth of tumour cells. All the current approved ALK inhibitors function by binding to the ATP pocket of the abnormal ALK protein, blocking its access to energy and deactivating it. A majority of ALK-rearranged NSCLC harbour the EML4-ALK fusion, although as of 2020, over 92 fusion partners have been discovered in ALK+ NSCLC. For each fusion partner, there can be several fusion variants depending on the position the two genes were fused at, and this may have implications on the response of the tumour and prognosis of the patient.
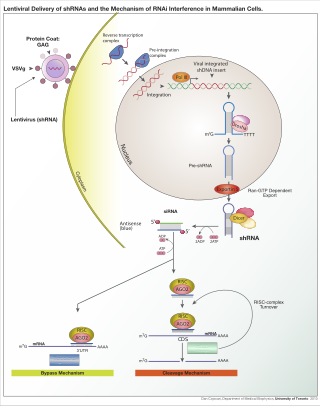
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector may be developed and find utility as novel therapeutic agents.

Santaris Pharma A/S was a biopharmaceutical company founded in 2003 in Copenhagen, Denmark. The company also had a branch in San Diego, California that opened in 2009. Created by a merger between Cureon and Pantheco, Santaris developed RNA-targeted medicines using a Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) Drug Platform and Drug Development Engine.
Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutics for genetically defined diseases. The company was founded in 2002 and is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. In 2016, Forbes included the company on its "100 Most Innovative Growth Companies" list.
Ceritinib is a prescription-only drug used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It was developed by Novartis and received FDA approval for use in April 2014.

Arbutus Biopharma Corporation is a publicly traded Canadian biopharmaceutical company with an expertise in liposomal drug delivery and RNA interference, and is developing drugs for hepatitis B infection.

Arcturus Therapeutics Holdings Inc. is an American RNA medicines biotechnology company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of therapeutics for rare diseases and infectious diseases. Arcturus has developed proprietary lipid nanoparticle RNA therapeutics for nucleic acid medicines including small interfering RNA (siRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), gene editing RNA, DNA, antisense oligonucleotides, and microRNA.
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals is a publicly traded biopharmaceutical company based in Pasadena, California. Arrowhead’s products in development act through RNA interference (RNAi) mechanisms of action. The company focuses on treatments for hepatitis B, liver disease associated with alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency and cardiovascular disease.

Emricasan is a potential drug invented in 1998 by Idun Pharmaceuticals. The drug was acquired by Pfizer in 2005 and then sold to Conatus Pharmaceuticals in 2010. Conatus in turn licensed emricasan to Novartis in 2017 for exclusive development and commercialization.
Inclisiran, sold under the brand name Leqvio, is a medication used for the treatment of high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and for the treatment of people with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), ASCVD risk-equivalents, and heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH). It is a small interfering RNA (siRNA) that acts as an inhibitor of a proprotein convertase, specifically, inhibiting translation of the protein PCSK9.
Portola Pharmaceuticals is an American clinical stage biotechnology company that researches, develops, and commercializes drugs. The company focuses primarily on drugs used in the treatment of thrombosis and hematological malignancies. Founded in 2003 and headquartered in South San Francisco, California, Portola Pharmaceuticals is a member of the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index.
DB-OTO is an experimental gene therapy for otoferlin-related hearing loss developed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. It is delivered via adeno-associated virus.












