
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical technologies corporation headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, and publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange. Its common stock is a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and the company is ranked No. 40 on the 2023 Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations. In 2023, the company was ranked 40th in the Forbes Global 2000. Johnson & Johnson has a global workforce of approximately 130,000 employees who are led by the company's current chairman and chief executive officer, Joaquin Duato.
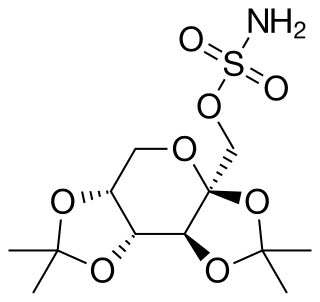
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence and essential tremor. For epilepsy this includes treatment for generalized or focal seizures. It is taken orally.

The pharmaceutical industry is a medical industry that discovers, develops, produces and markets pharmaceutical goods such as medications and medical devices. Medications are then administered to patients for curing or prevention of disease, as well as alleviating symptoms of illness or injury.

Valdecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and painful menstruation and menstrual symptoms. It is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. It was patented in 1995.
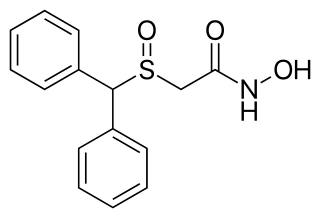
Adrafinil, sold under the brand name Olmifon, is a wakefulness-promoting medication that was formerly used in France to improve alertness, attention, wakefulness, and mood, particularly in the elderly. It was also used off-label by individuals who wished to avoid fatigue, such as night workers or others who needed to stay awake and alert for long periods of time. Additionally, the medication has been used non-medically as a novel vigilance-promoting agent.

Ofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. When taken by mouth or injection into a vein, these include pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infections, prostatitis, plague, and certain types of infectious diarrhea. Other uses, along with other medications, include treating multidrug resistant tuberculosis. An eye drop may be used for a superficial bacterial infection of the eye and an ear drop may be used for otitis media when a hole in the ear drum is present.
Off-label use is the use of pharmaceutical drugs for an unapproved indication or in an unapproved age group, dosage, or route of administration. Both prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs (OTCs) can be used in off-label ways, although most studies of off-label use focus on prescription drugs.

Takeda Oncology is a biopharmaceutical company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is a fully owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical.

Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine is a Belgian pharmaceutical company headquartered in Beerse, Belgium, and wholly-owned by Johnson & Johnson. It was founded in 1953 by Paul Janssen.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Office of Criminal Investigations (OCI) provides the FDA with a specific office to conduct and coordinate its criminal investigations.
Ortho Pharmaceutical was initially formed in the United States in 1931 as a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson to market the first prescription spermicidal contraceptive jelly, Ortho-Gynol.
Ortho-McNeil-Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc is a healthcare company of Johnson & Johnson composed of two divisions:

Phentermine/topiramate, sold under the brand names Qsymia or QSIVA, is a combination drug of phentermine and topiramate used to treat obesity. It is used together with dietary changes and exercise. If less than 3% weight loss is seen after 3 months it is recommended the medication be stopped. The weight loss is modest. Effects on heart related health problems or death is unclear.

Dapoxetine, sold under the brand name Priligy among others, is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) used for the treatment of premature ejaculation (PE) in men ages 18 to 64 years old. Dapoxetine works by inhibiting the serotonin transporter, increasing serotonin's action at the postsynaptic cleft, and as a consequence promoting ejaculatory delay. As a member of the SSRI family, dapoxetine was initially created as an antidepressant. However, unlike other SSRIs, dapoxetine is absorbed and eliminated rapidly in the body. Its fast-acting property makes it suitable for the treatment of PE, but not as an antidepressant.

Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd. is a pharmaceuticals and biotechnology company established in December 1997, headquartered in Allschwil near Basel, Switzerland. The company is part of Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine business segment.
Health care fraud includes "snake oil" marketing, health insurance fraud, drug fraud, and medical fraud. Health insurance fraud occurs when a company or an individual defrauds an insurer or government health care program, such as Medicare or equivalent State programs. The manner in which this is done varies, and persons engaging in fraud are always seeking new ways to circumvent the law. Damages from fraud can be recovered by use of the False Claims Act, most commonly under the qui tam provisions which rewards an individual for being a "whistleblower", or relator (law).
Pharmaceutical fraud is when pharmaceutical companies engage in illegal, fraudulent activities to the detriment of patients and/or insurers. Examples include counterfeit drugs that do not contain the active ingredient, false claims in packaging and marketing, suppression of negative information regarding the efficacy or safety of the drug, and violating pricing regulations.
Guselkumab, sold under the brand name Tremfya, is a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-23 used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis.
Marketing of off-label use is advertising the use of drugs for purposes not approved by the regional government. The practice is often illegal and has led to most of the largest pharmaceutical settlements after Franklin v. Parke-Davis, in which a court ruled off-label marketing a violation of the False Claims Act.











