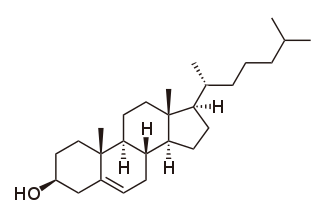
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol, a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid.

Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL is involved in atherosclerosis, a process in which it is oxidized within the walls of arteries.

Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.

Margarine is a spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The spread was originally named oleomargarine from Latin for oleum and Greek margarite. The name was later shortened to margarine.

Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia, hyperlipoproteinemia, and dyslipidemia.

Raisio Oyj, known internationally as Raisio Group, is a Finnish company specialised in healthy, responsibly produced food and ingredients.

Atorvastatin, sold under the brand name Lipitor among others, is a statin medication used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and to treat abnormal lipid levels. For the prevention of cardiovascular disease, statins are a first-line treatment. It is taken by mouth.

HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia.

Stanol esters is a heterogeneous group of chemical compounds known to reduce the level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in blood when ingested, though to a much lesser degree than prescription drugs such as statins. The starting material is phytosterols from plants. These are first hydrogenated to give a plant stanol which is then esterified with a mixture of fatty acids also derived from plants. Plant stanol esters are found naturally occurring in small quantities in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, cereals, legumes, and vegetable oils.
Becel is a brand of margarine produced by Dutch company Upfield. In France, it is sold as Fruit D'or and in the United States as Promise.
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally elevated levels of any or all lipids or lipoproteins in the blood. The term hyperlipidemia refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbrella term covering any of various acquired or genetic disorders that result in that finding. Hyperlipidemia represents a subset of dyslipidemia and a superset of hypercholesterolemia. Hyperlipidemia is usually chronic and requires ongoing medication to control blood lipid levels.
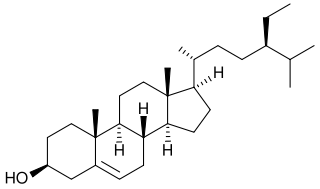
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phytosterols extracted from oils are insoluble in water, relatively insoluble in oil, and soluble in alcohols.
Sterol esters are a heterogeneous group of chemical compounds. They are created when the hydroxyl group of a sterol and a fatty acid undergo an esterification reaction. They can be found in trace amounts in every cell type but are highly enriched in foam cells and are common components of human skin oil.

Campesterol is a phytosterol whose chemical structure is similar to that of cholesterol, and is one of the ingredients for E number E499.
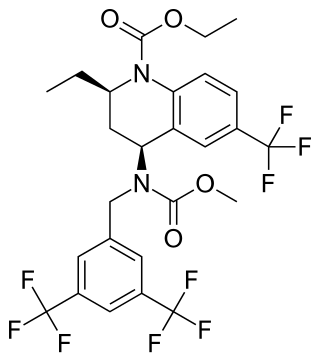
Torcetrapib was a drug being developed to treat hypercholesterolemia and prevent cardiovascular disease. Its development was halted in 2006 when phase III studies showed excessive all-cause mortality in the treatment group receiving a combination of atorvastatin (Lipitor) and torcetrapib.

Sitosterolemia is a rare autosomal recessively inherited lipid metabolic disorder. It is characterized by hyperabsorption and decreased biliary excretion of dietary sterols. Healthy persons absorb only about 5% of dietary plant sterols, but sitosterolemia patients absorb 15% to 60% of ingested sitosterol without excreting much into the bile. The phytosterol campesterol is more readily absorbed than sitosterol.

Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, in the blood and early cardiovascular diseases. The most common mutations diminish the number of functional LDL receptors in the liver or produce abnormal LDL receptors that never go to the cell surface to function properly. Since the underlying body biochemistry is slightly different in individuals with FH, their high cholesterol levels are less responsive to the kinds of cholesterol control methods which are usually more effective in people without FH. Nevertheless, treatment is usually effective.
The chronic endothelial injury hypothesis is one of two major mechanisms postulated to explain the underlying cause of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease (CHD), the other being the lipid hypothesis. Although an ongoing debate involving connection between dietary lipids and CHD sometimes portrays the two hypotheses as being opposed, they are in no way mutually exclusive. Moreover, since the discovery of the role of LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, the two hypotheses have become tightly linked by a number of molecular and cellular processes.
Portfolio Diet is a therapeutic plant-based diet created by Canadian researcher David J. Jenkins in 2003 to lower blood cholesterol. The diet emphasizes using a portfolio of foods or food components that have been found to associate with cholesterol lowering to enhance this effect. Soluble fiber, soy protein, plant sterols, and nuts are the four essential components of Portfolio diet. The diet is low in saturated fat, high in fibre. Researches have found it has comparable blood cholesterol effect to statin treatment.
Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes, also known as the TLC Diet, is a dietary pattern recommended by the National Cholesterol Education Program, part of the National Institutes of Health, to control hypercholesterolemia. This pattern focuses on saturated fats and cholesterol, dietary options to enhance LDL cholesterol lowering, weight control, and physical activity.














