
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease.

Inflammation is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function.

Diclofenac, sold under the brand name Voltaren among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammatory diseases such as gout. It can be taken orally, inserted rectally as a suppository, injected intramuscularly, injected intravenously, applied to the skin topically, or through eye drops. Improvements in pain last up to eight hours. It is also available as the fixed-dose combination diclofenac/misoprostol (Arthrotec) to help protect the stomach.

Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It is available in immediate and delayed release formulations. Onset of effects is within an hour and lasts for up to twelve hours. Naproxen is also available in salt form, naproxen sodium, which has better solubility when taken orally.
Anti-inflammatory or antiphlogistic is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system to block pain signaling to the brain.
Lactucarium is the milky fluid secreted by several species of lettuce, especially Lactuca virosa, usually from the base of the stems. It is known as lettuce opium because of its sedative and analgesic properties. It has also been reported to promote a mild sensation of euphoria. Because it is a latex, lactucarium physically resembles opium, in that it is excreted as a white fluid and can be reduced to a thick smokable solid.

Lumiracoxib is a COX-2 selective inhibitor nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.

Piroxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam class used to relieve the symptoms of painful inflammatory conditions like arthritis. Piroxicam works by preventing the production of endogenous prostaglandins which are involved in the mediation of pain, stiffness, tenderness and swelling. The medicine is available as capsules, tablets and, in some countries, as a prescription-free gel 0.5%. It is also available in a betadex formulation, which allows a more rapid absorption of piroxicam from the digestive tract. Piroxicam is one of the few NSAIDs that can be given parenteral routes.
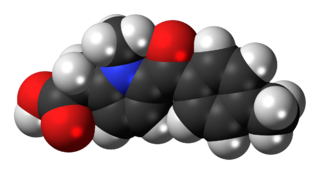
Loxoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) in the propionic acid derivatives group, which also includes ibuprofen and naproxen among others. It is available in some countries for oral administration. A transdermal preparation was approved for sale in Japan in January 2006; medicated tape and gel formulations followed in 2008 and 2010.

Benzopyran is a polycyclic organic compound that results from the fusion of a benzene ring to a heterocyclic pyran ring.

Lenabasum (also known as ajulemic acid, 1',1'-dimethylheptyl-delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol-11-oic acid, DMH-D8-THC-11-OIC, AB-III-56, HU-239, IP-751, CPL 7075, CT-3, JBT-101, Anabasum, and Resunab) is a synthetic cannabinoid that shows anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects in pre-clinical studies without causing a subjective "high". Although its design was inspired by a metabolite of delta-9-THC known as delta-9-THC-11-oic acid, lenabasum is an analog of the delta-8-THC metabolite delta-8-THC-11-oic acid. It is being developed for the treatment of inflammatory and fibrotic conditions such as systemic sclerosis, dermatomyositis and cystic fibrosis. It does not share the anti-emetic effects of some other cannabinoids, but may be useful for treating chronic inflammatory conditions where inflammation fails to resolve. Side effects include dry mouth, tiredness, and dizziness. The mechanism of action is through activation of the CB2 receptor leading to production of specialized proresolving eicosanoids such as lipoxin A4 and prostaglandin J2. Studies in animals at doses up to 40 mg/kg show minimal psychoactivity of lenabasum, compared to that produced by tetrahydrocannabinol. Lenabasum is being developed by Corbus Pharmaceuticals (formerly JB Therapeutics) for the treatment of orphan chronic life-threatening inflammatory diseases. Development since been discontinued.
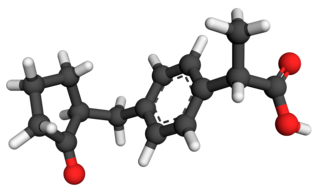
Tolmetin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the heterocyclic acetic acid derivative class.
COX-inhibiting nitric oxide donators (CINODs), also known as NO-NSAIDs, are a new class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) developed with the intention of providing greater safety than existing NSAIDs.

Salsalate is a medication that belongs to the salicylate and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) classes.

Pranoprofen (INN) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used in ophthalmology.

VUF-6002 (JNJ-10191584) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist at the histamine H4 receptor. It has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects in animal studies of inflammatory diseases.

Licofelone is a dual COX/LOX inhibitor that was studied in clinical trials as a treatment for osteoarthritis and which was under development by Merckle GmbH with partners Alfa Wassermann and Lacer.

Fomitopsis quercina is a species of mushroom in the order Polyporales. Commonly known as the thick-walled maze polypore, maze-gill fungusoak-loving maze polypore, or oak mazegill, the specific epithet refers to the oak genus Quercus, upon which it frequently grows, causing a brown rot. It is found in Europe, Asia, Northern Africa and Australasia. Though inedible, it can be used as a natural comb and has been the subject of chemical research.

Sargachromanols are a group of related chemical compounds isolated from the brown alga Sargassum siliquastrum. At least 20 members of the class have been identified, named sargachromanol A through T. Sargachromanol G has in vitro anti-inflammatory effects in isolated mouse macrophage cells.
A drug class is a group of medications and other compounds that share similar chemical structures, act through the same mechanism of action, have similar modes of action, and/or are used to treat similar diseases. The FDA has long worked to classify and license new medications. Its Drug Evaluation and Research Center categorizes these medications based on both their chemical and therapeutic classes.
















