
Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name means "crow" in Latin. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it depicts a raven, a bird associated with stories about the god Apollo, perched on the back of Hydra the water snake. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi, form a distinctive quadrilateral or cross-shape in the night sky.

R Leporis (R Lep), sometimes called Hind's Crimson Star, is a well-known variable star in the constellation Lepus, near its border with Eridanus. It is designated "R" in the chart to the right.

The descriptive term long-period variable star refers to various groups of cool luminous pulsating variable stars. It is frequently abbreviated to LPV.

Delta Corvi, also named Algorab, is a third magnitude star at a distance of 86.9 light-years from the Sun in the southern constellation of Corvus.

R Hydrae, abbreviated R Hya, is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra, about 2.7° to the east of Gamma Hydrae. It is a Mira-type variable that ranges in apparent visual magnitude from 3.5 down to 10.9 over a period of 389 days. At maximum brightness the star can be seen with the naked eye, while at minimum a telescope of at least 5 cm is needed. This star is located at a distance of approximately 480 light-years from the Sun but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −10 km/s.

S Carinae is a variable star in the constellation Carina.

R Centauri is a Mira variable star in the constellation Centaurus.

T Cephei is a Mira variable star in the constellation Cepheus. Located approximately 600 light-years distant, it varies between magnitudes 5.2 and 11.3 over a period of around 388 days.

R Reticuli, also listed under the duplicate variable star designation S Reticuli, is a Mira variable star in the southern constellation Reticulum. It is an aging red giant star on the asymptotic giant branch with a stellar classification that varies between M4e to M7.5e, being hottest near maximum visual magnitude. The brightness of the star varies between apparent visual magnitudes 6.35 and 14.2 with an average period of 281.08±0.58 d. The mean maximum magnitude is 7.57 and the mean minimum magnitude 13.80.
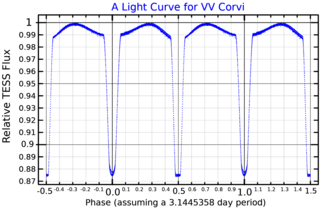
VV Corvi is a close spectroscopic binary in the constellation Corvus. It is also an eclipsing binary, varying from magnitude 5.19 to 5.34 over 3.145 days. The two stars orbit each other with a period of 1.46 days and an eccentricity of 0.088. The mass ratio of the two stars is 0.775±0.024. The primary is 1.978 ± 0.010 times as massive as the Sun, 18.253 ± 2.249 its luminosity and has 3.375 ± 0.010 the Sun's radius. The secondary is 1.513 ± 0.008 times as massive as the Sun, 4.745 ± 0.583 its luminosity and has 1.650 ± 0.008 the Sun's radius. Both are yellow-white main sequence stars of spectral type F5V, though the primary has begun expanding and cooling as it nears the end of its time on the main sequence. A tertiary companion was discovered during the Two Micron All-Sky Survey.

S Pegasi is a Mira variable star in the constellation Pegasus. It varies between magnitude 7 and 13 with a period of 319.22 days. It is believed to be pulsating in the first overtone. First overtone pulsators have masses less than 1.8 M☉ at a temperature of 2,107 K, and less than 1.4 M☉ at the luminosity of S Pegasi.

T Ursae Minoris is a variable star in the constellation Ursa Minor, located 2′30″ west-southwest of 3 Ursae Minoris toward the western border of the constellation with Draco.

BH Crucis, also known as Welch's Red Variable, is a star in the constellation Crux. A long period (Mira-type) variable, its apparent magnitude ranges from 6.6 to 9.8 over 530 days. Hence at its brightest it is barely visible with the unaided eye in a rural sky. A red giant, it had been classified ranging between spectral types SC4.5/8-e and SC7/8-e, but appears to have evolved into a C-type spectrum by 2011.

V Coronae Borealis is a Mira-type long period variable star and carbon star in the constellation Corona Borealis. Its apparent magnitude varies between 6.9 and 12.6 over a period of 357 days

R Normae is a Mira variable star located near Eta Normae in the southern constellation of Norma. This is an intermediate-mass red giant star that is generating part of its energy through hydrogen fusion. Because this fusion is thought to be occurring under conditions of convection, it is generating an excess of lithium. The star ranges from magnitude 6.5 to 12.8 and has a relatively long period of 496 days. Located around 2,900 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity 7764 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 3161 K.
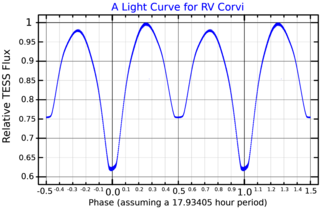
RV Corvi is an eclipsing binary star system in the southern constellation of Corvus. The brightness of the pair regularly ranges in apparent visual magnitude from 8.6 down to 9.16 over a period 18 hours, even the brightest of which is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. The system is located at a distance of approximately 690 light-years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of ~19 km/s.

R Capricorni (R Cap) is a star in the constellation of Capricornus. It has an apparent visual magnitude which varies between 9.4 and 14.9. A mira variable and ageing red giant, it is in the asymptotic giant branch stage of its lifespan.

R Octantis, also known as HD 40857, is a solitary, red hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude that varies in-between 6.4 and 13.2 within 405 days. At is maximum, it is barely visible to the naked eye. The object is located relatively far at a distance of about 1,900 light years based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 46 km/s.

S Cassiopeiae is a Mira variable and S-type star in the constellation Cassiopeia. It is an unusually cool star, rapidly losing mass and surrounded by dense gas and dust producing masers.

V Crucis is a carbon star in the constellation Crux. A Mira variable, its apparent magnitude ranges from 8.7 to 11.1 over 376.5 days. The fact that this star's period is nearly equal to one year makes it hard to get good observational coverage over the entire cycle. Its near-infrared light curve shows a contribution from the first harmonic of the fundamental period.




















