Related Research Articles

Libya is fourth in size among the countries of Africa and sixteenth among the countries of the world. It is on the Mediterranean between Egypt and Tunisia, with Niger and Chad to the south and Sudan to the southeast. Although the oil discoveries of the 1960s have brought immense wealth, at the time of its independence it was an extremely poor desert state whose only important physical asset appeared to be its strategic location at the midpoint of Africa's northern rim.

Cyrenaica is the eastern coastal region of Libya. Also known as Pentapolis in antiquity, it formed part of the Roman province of Crete and Cyrenaica, later divided into Libya Pentapolis and Libya Sicca. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as Barqa, after the city of Barca.

The Libyan Desert is a geographical region filling the north-eastern Sahara Desert, from eastern Libya to the Western Desert of Egypt and far northwestern Sudan. On medieval maps, its use predates today's Sahara, and parts of the Libyan Desert include the Sahara's most arid and least populated regions; this is chiefly what sets the Libyan Desert apart from the greater Sahara. The consequent absence of grazing, and near absence of waterholes or wells needed to sustain camel caravans, prevented Trans-Saharan trade between Kharga close to the Nile, and Murzuk in the Libyan Fezzan. This obscurity saw the region overlooked by early European explorers, and it was not until the early 20th century and the advent of the motor car before the Libyan Desert started to be fully explored.

Benghazi is a city in Libya. Located on the Gulf of Sidra in the Mediterranean, Benghazi is a major seaport and the second-most populous city in the country, as well as the largest city in Cyrenaica, with an estimated population of 632,937 in 2019.

The Mojave Desert is a xeric desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is the smallest and driest desert of the four American deserts. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily in southeastern California and southwestern Nevada, with small portions extending into Arizona and Utah.
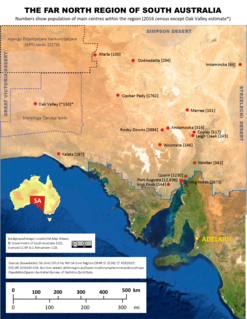
The Far North is a large region of South Australia close to the Northern Territory border. Colloquial usage of the term in South Australia refers to that part of South Australia north of a line roughly from Ceduna through Port Augusta to Broken Hill. The South Australian Government defines the Far North region similarly with the exception of the Maralinga Tjarutja Lands. the Yalata Aboriginal community and other unincorporated crown lands in the state's far west, which are officially considered part of the Eyre and Western region.

Tataouine Governorate is the southernmost of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia, the only one to border both Algeria and Libya. It is also the largest, covering an area of 38,889 km². It had a population of 149,453, nearly tied for second least-populated with Kebili (156,961) after Tozeur (107,912). The capital is Tataouine.

The Italian colonizationof Libya began in 1911 and it lasted until 1943. The country, which was previously an Ottoman possession, was occupied by Italy in 1911 after the Italo-Turkish War, which resulted in the establishment of two colonies: Italian Tripolitania and Italian Cyrenaica. In 1934, the two colonies were merged into one colony which was named the colony of Italian Libya. In 1937, this colony was divided into four provinces, and in 1939, the coastal provinces became a part of metropolitan Italy. The colonization lasted until Libya's occupation by Allied forces in 1943, but it was not until the 1947 Paris Peace Treaty that Italy officially renounced all of its claims to Libya's territory.

Ancient Aethiopia, first appears as a geographical term in classical documents in reference to the upper Nile region, as well as certain areas south of the Sahara desert. Its earliest mention is in the works of Homer: twice in the Iliad, and three times in the Odyssey. The Greek historian Herodotus specifically uses the appellation to refer to such parts of Africa as were then known within the inhabitable world.

The wildlife of Libya is spread over the Mediterranean coastline and encompasses large areas of the Saharan desert. The protection of wildlife is provided through appropriate legislation in seven national parks, five reserves, 24 protected areas, two wetlands under Ramsar Convention, and also in other areas. Apart from these, there are also five UNESCO World Heritage Sites related to culture. The most important national parks are the El-Kouf National Park and Karabolli National Park. The well known nature reserves are the Benghazi Reserve and the Zellaf Reserve. The wildlife species recorded in the country are 87 mammals and 338 species of birds.

Rājmā[raːdʒmaː], also known as Rāzmā or Lal Lobia, is a vegetarian dish, originating from the Indian subcontinent, consisting of red kidney beans in a thick gravy with many Indian whole spices, and is usually served with rice. It is a part of regular diet in India, Nepal and Punjab province of Pakistan. The dish developed after the red kidney bean was brought to the Indian subcontinent from Mexico. Rajma chawal is kidney beans served with boiled rice.

Al Jufra Airbase is a Libyan Air Force base 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) northeast of Hun, a desert city in the Jufra District of Libya. It was originally used by the Libyan Arab Air Force from 1969 to 2011.

Martuba Airbase is a Libyan Air Force base in the Derna District of Libya, located approximately 27 kilometres (17 mi) south-southeast of Derna, and 268 kilometres (167 mi) east-northeast of Benghazi.
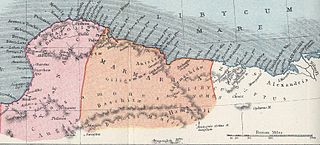
Marmarica in ancient geography was a littoral area in Ancient Libya, located between Cyrenaica and Aegyptus. It corresponds to what is now the Libya and Egypt frontier, including the towns of Bomba, Timimi, Tobruk, Acroma, Bardiya, As-Salum, and Sidi Barrani. The territory stretched to the far south, encompassing the Siwa Oasis, which at the time was known for its sanctuary to the deity Amun. The eastern part of Marmarica, by some geographers considered a separate district between Marmarica and Aegyptus, was known as Libycus Nomus. In late antiquity, Marmarica was also known as Libya Inferior, while Cyrenaica was known as Libya Superior.
Jebil is a national park in Tunisia situated within the Sahara desert. Covering an area of 150,000 hectares, it is the country's second-largest national park, after Senghar-Jebbes National Park. Though large, it is relatively new having been designated a national park in 1994. Until Senghar-Jebbes was declared, it was the only national park within the Sahara desert proper.

Ar Rajma, Er Rajma, or Er Regima is a village in eastern Libya. It is located 27 km (17 mi) east of Benghazi.
Protected areas of Libya include any geographical area protected for a specific use.
Harouj Mountain, also Gebel-Harouj or the Black Harouj Mountains, is a mountain and protected area of Libya.
Rajma plantations is a protected area of Libya.

The Western Desert of Egypt is an area of the Sahara that lies west of the river Nile, up to the Libyan border, and south from the Mediterranean sea to the border with Sudan. It is named in contrast to the Eastern Desert which extends east from the Nile to Red Sea. The Western Desert is mostly rocky desert, though an area of sandy desert, known as the Great Sand Sea, lies to the west against the Libyan border. The desert covers an area of 680,650 km2 (262,800 sq mi) which is two-thirds of the land area of the country. Its highest elevation is 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in the Gilf Kebir plateau to the far south-west of the country, on the Egypt-Sudan-Libya border. The Western Desert is barren and uninhabited save for a chain of oases which extend in an arc from Siwa, in the north-west, to Kharga in the south. It has been the scene of conflict in modern times, particularly during the Second World War.
References
- ↑ Davis, Ethel (2009). North Africa: The Roman Coast. Bradt Travel Guides. p. 326. ISBN 978-1-84162-287-3 . Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ↑ "The National Parks Of Libya". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 2021-01-19.