A caldera is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the structural integrity of such a chamber, greatly diminishing its capacity to support its own roof, and any substrate or rock resting above. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface. Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur over the course of a century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times within a given window of 100 years. Only eight caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2018, with a caldera collapse at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018. Volcanoes that have formed a caldera are sometimes described as "caldera volcanoes".

Mount Shasta is a potentially active volcano at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California. At an elevation of 14,179 ft (4,322 m), it is the second-highest peak in the Cascades and the fifth-highest in the state. Mount Shasta has an estimated volume of 85 cubic miles, which makes it the most voluminous stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. The mountain and surrounding area are part of the Shasta–Trinity National Forest.

Catron County is a county in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2020 census, the population was 3,579, making it New Mexico's third-least populous county. Its county seat is Reserve. Catron County is New Mexico's largest county by area.

The Ring of Fire is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes.
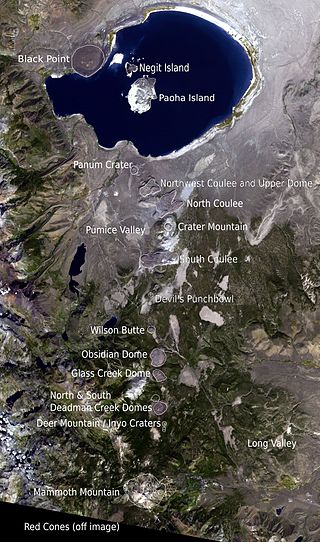
The Mono–Inyo Craters are a volcanic chain of craters, domes and lava flows in Mono County, Eastern California. The chain stretches 25 miles (40 km) from the northwest shore of Mono Lake to the south of Mammoth Mountain. The Mono Lake Volcanic Field forms the northernmost part of the chain and consists of two volcanic islands in the lake and one cinder cone volcano on its northwest shore. Most of the Mono Craters, which make up the bulk of the northern part of the Mono–Inyo chain, are phreatic volcanoes that have since been either plugged or over-topped by rhyolite domes and lava flows. The Inyo volcanic chain form much of the southern part of the chain and consist of phreatic explosion pits, and rhyolitic lava flows and domes. The southernmost part of the chain consists of fumaroles and explosion pits on Mammoth Mountain and a set of cinder cones south of the mountain; the latter are called the Red Cones.

Mount Adams, known by some Native American tribes as Pahto or Klickitat, is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range. Although Adams has not erupted in more than 1,000 years, it is not considered extinct. It is the second-highest mountain in Washington, after Mount Rainier.

Indian Heaven is a volcanic field in Skamania County in the state of Washington, in the United States. Midway between Mount St. Helens and Mount Adams, the field dates from the Pleistocene to the early Holocene epoch. It trends north to south and is dominated by six small shield volcanoes; these shields are topped by small spatter and cinder cones, and the field includes a number of subglacial volcanoes and tuyas. The northernmost peak in the field is Sawtooth Mountain and the southernmost is Red Mountain; its highest point is Lemei Rock at an elevation of 5,925 feet (1,806 m).
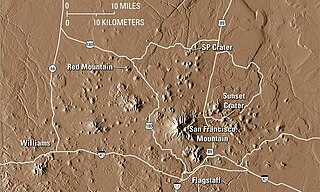
The San Francisco volcanic field is an area of volcanoes in northern Arizona, north of Flagstaff, US. The field covers 1,800 square miles (4,700 km2) of the southern boundary of the Colorado Plateau. The field contains 600 volcanoes ranging in age from nearly 6 million years old to less than 1,000 years, of which Sunset Crater is the youngest. The highest peak in the field is Humphreys Peak, at Flagstaff's northern perimeter: the peak is Arizona's highest at 12,633 feet and is a part of the San Francisco Peaks, an active stratovolcano complex.
A monogenetic volcanic field is a type of volcanic field consisting of a group of small monogenetic volcanoes, each of which erupts only once, as opposed to polygenetic volcanoes, which erupt repeatedly over a period of time. The small monogenetic volcanoes of these fields are the most common subaerial volcanic landform.

Goat Rocks is an extinct stratovolcano in the Cascade Range, located between Mount Rainier and Mount Adams in southern Washington, in the United States. Part of the Cascade Volcanoes, it was formed by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate under the western edge of the North American Plate. The volcano was active from 3.2 million years ago until eruptions ceased between 1 and 0.5 million years ago. Throughout its complex eruptive history, volcanism shifted from silicic explosive eruptions to voluminous, mafic activity.

The Almolonga volcano, also called "Cerro Quemado" or "La Muela" due to its distinct shape, is an andesitic stratovolcano in the south-western department of Quetzaltenango in Guatemala. Part of the mountain range of the Sierra Madre, the volcano is located near the town of Almolonga, just south of Quetzaltenango, Guatemala's second largest city.

Sierra Grande is an extinct stratovolcano in northeastern New Mexico that rises 2,200 feet above the surrounding plain. It is part of the inactive Raton-Clayton volcanic field.

Zuñi Salt Lake, also Zuni Salt Lake is a rare high desert lake, and a classic maar, located in Catron County, New Mexico, United States, about 60 miles (97 km) south of the Zuni Pueblo, New Mexico.
The Bridge River Cones, sometimes referred to as the Lillooet Cones and Salal Creek Cones, is the name given to a volcanic field located on the north flank of the upper Bridge River, about 40 km (25 mi) west of the town of Gold Bridge. The cones are in the lee of the Lillooet Icecap and sit astride a group of passes between the Bridge River, which flows W-E to their south, and the Lord River, which flows north to the Taseko Lakes in the Chilcotin District.

Volcanic activity is a major part of the geology of Canada and is characterized by many types of volcanic landform, including lava flows, volcanic plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes, and maars, along with less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds.

The Raton-Clayton volcanic field is a volcanic field located in the state of New Mexico, United States. Capulin Volcano National Monument is located in the volcanic field. It is the northeasternmost volcanic field of the Jemez Lineament and the easternmost Cenozoic volcanic field of North America.

Cat Hills volcanic field is a monogenetic volcanic field located in New Mexico, US.

Red Hill volcanic field, also known as Quemado volcanic field, is a monogenetic volcanic field located in the vicinity of the ghost town of Red Hill in Catron County New Mexico. Red Hill is 24 kilometers (15 mi) east of the larger Springerville volcanic field and includes Zuñi Salt Lake. The area is made up of scoria cone and silicic dome fields. Over 40 volcanic vents have been identified in the field. These erupted basaltic flows, with no other rock types evident in the field.

Aden Crater is a small shield volcano located in Doña Ana County, about 25 miles (40 km) southwest of Las Cruces, New Mexico. It is located in the northwest part of the Aden-Afton basalt field, which is part of the central area of the Potrillo volcanic field.
The Salton Buttes are a group of volcanoes in Southern California, on the Salton Sea. They consist of a 7-kilometer (4.3 mi)-long row of five lava domes, named Mullet Island, North Red Hill, Obsidian Butte, Rock Hill and South Red Hill. They are closely associated with a fumarolic field and a geothermal field, and there is evidence of buried volcanoes underground. In pre-modern times Obsidian Butte was an important regional source of obsidian.

















