Related Research Articles

Anemia, also spelled anaemia and sometimes called erythrocytopenia, is a decrease in the total amount of red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin in the blood or a lowered ability of the blood to carry oxygen. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague and may include feeling tired, weakness, shortness of breath, and a poor ability to exercise. When the anemia comes on quickly, symptoms may include confusion, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. For people who require surgery, pre-operative anemia can increase the risk of requiring a blood transfusion following surgery.

A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, so do not become healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, bleeding disorders, anemia, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia.
Aplastic anemia is a disease in which the body fails to produce blood cells in sufficient numbers. Blood cells are produced in the bone marrow by stem cells that reside there. Aplastic anaemia causes a deficiency of all blood cell types: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.

Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a rare genetic disease resulting in impaired response to DNA damage. Although it is a very rare disorder, study of this and other bone marrow failure syndromes has improved scientific understanding of the mechanisms of normal bone marrow function and development of cancer. Among those affected, the majority develop cancer, most often acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), and 90% develop aplastic anemia by age 40. About 60–75% have congenital defects, commonly short stature, abnormalities of the skin, arms, head, eyes, kidneys, and ears, and developmental disabilities. Around 75% have some form of endocrine problem, with varying degrees of severity.
Cytopenia is a reduction in the number of mature blood cells. It is common in cancer patients being treated with radiation and/or chemotherapy.
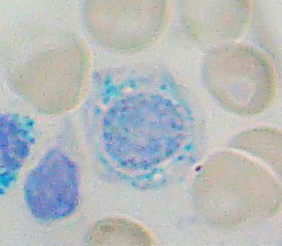
Sideroblastic anemia, or sideroachrestic anemia, is a form of anemia in which the bone marrow produces ringed sideroblasts rather than healthy red blood cells (erythrocytes). In sideroblastic anemia, the body has iron available but cannot incorporate it into hemoglobin, which red blood cells need in order to transport oxygen efficiently. The disorder may be caused either by a genetic disorder or indirectly as part of myelodysplastic syndrome, which can develop into hematological malignancies.
Myelophthisic anemia is a severe type of anemia found in some people with diseases that affect the bone marrow. Myelophthisis refers to the displacement of hemopoietic bone-marrow tissue by fibrosis, tumors, or granulomas. The word comes from the roots myelo-, which refers to bone marrow, and phthysis, shrinkage or atrophy.
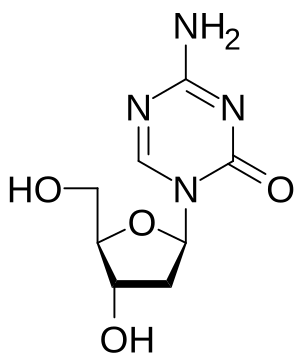
Decitabine, sold under the brand name Dacogen, acts as a nucleic acid synthesis inhibitor. It is a medication for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes, a class of conditions where certain blood cells are dysfunctional, and for acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Chemically, it is a cytidine analog.
Pearson syndrome is a mitochondrial disease characterized by sideroblastic anemia and exocrine pancreas dysfunction. Other clinical features are failure to thrive, pancreatic fibrosis with insulin-dependent diabetes and exocrine pancreatic deficiency, muscle and neurologic impairment, and, frequently, early death. It is usually fatal in infancy. The few patients who survive into adulthood often develop symptoms of Kearns–Sayre syndrome. It is caused by a deletion in mitochondrial DNA. Pearson syndrome is very rare, less than a hundred cases have been reported in medical literature worldwide.
Refractory anemia with excess of blasts (RAEB) is a type of myelodysplastic syndrome with a marrow blast percentage of 5% to 19%.
Erythroid dysplasia is a condition in which immature red blood cells in the bone marrow are abnormal in size and/or number. Erythroid dysplasia may be caused by vitamin deficiency or chemotherapy, or it may be a sign of refractory anemia, which is a myelodysplastic syndrome. Also called erythrodysplasia.
Normocytic anemia is a type of anemia and is a common issue that occurs for men and women typically over 85 years old. Its prevalence increases with age, reaching 44 percent in men older than 85 years. The most common type of normocytic anemia is anemia of chronic disease.
Sideropenic hypochromic anemia is primarily characterized by low serum iron concentration. Non-sideropenic hypochromic anemia is the ineffective utilisation of iron stores, usually from chronic infection/inflammation. It is very important to distinguish iron deficit anemia from the anemia of chronic disorders so as to ensure specific treatment.

Ghosal hematodiaphyseal dysplasia, is a rare, autosomal recessive disease, characterized by diaphyseal dysplasia and metaphyseal dysplasia of the long bones and refractory anemia.

Polychromasia is a disorder where there is an abnormally high number of immature red blood cells found in the bloodstream as a result of being prematurely released from the bone marrow during blood formation. These cells are often shades of grayish-blue. Polychromasia is usually a sign of bone marrow stress as well as immature red blood cells. 3 types are recognized, with types (1) and (2) being referred to as 'young red blood cells and types (3) as 'old red blood cells'. Giemsa stain is used to distinguish all three types of blood smears. The young cells will generally stain gray or blue in the cytoplasm. These young red blood cells are commonly called reticulocytes. All polychromatophilic cells are reticulocytes, however, not all reticulocytes are polychromatophilic. In the old blood cells, the cytoplasm either stains a light orange or does not stain at all.
Bone marrow failure occurs in individuals who produce an insufficient amount of red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets. Red blood cells transport oxygen to be distributed throughout the body’s tissue. White blood cells fight off infections that enter the body. Bone marrow also contains platelets, which trigger clotting, and thus help stop the blood flow when a wound occurs.

A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. Almost all vertebrate organisms have hemoglobin-containing cells in their blood, and with the exception of mammals, all of these red blood cells are nucleated. In mammals, NRBCs occur in normal development as precursors to mature red blood cells in erythropoiesis, the process by which the body produces red blood cells. NRBCs are normally found in the bone marrow of humans of all ages and in the blood of fetuses and newborn infants. After infancy, RBCs normally contain a nucleus only during the very early stages of the cell's life, and the nucleus is ejected as a normal part of cellular differentiation before the cell is released into the bloodstream. Thus, if NRBCs are identified on an adult's complete blood count or peripheral blood smear, it suggests that there is a very high demand for the bone marrow to produce RBCs, and immature RBCs are being released into circulation. Possible pathologic causes include anemia, myelofibrosis, thalassemia, miliary tuberculosis, cancers involving bone marrow, and in chronic hypoxemia.
Refractory cytopenia of childhood is a subgroup of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), having been added to the World Health Organization classification in 2008. Before then, RCC cases were classified as childhood aplastic anemia. RCC is the most common form of MDS in children and adolescents, accounting for approximately half of all MDS cases.

Decitabine/cedazuridine, sold under the brand name Inqovi, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of adults with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). It is a combination of decitabine, a nucleoside metabolic inhibitor, and cedazuridine, a cytidine deaminase inhibitor.
Naxitamab, sold under the brand name Danyelza, is an anti-cancer medication. It is a monoclonal antibody used in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) for people one year of age and older with relapsed or refractory high-risk neuroblastoma in the bone or bone marrow demonstrating a partial response, minor response, or stable disease to prior therapy.
References
- ↑ Fedoriw, Yuri. "Pathology of Refractory Anemia With Ring Sideroblasts" . Retrieved 28 August 2013.