
Paraffin wax is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum, coal, or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between 20 and 40 carbon atoms. It is solid at room temperature and begins to melt above approximately 37 °C (99 °F), and its boiling point is above 370 °C (698 °F). Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication, electrical insulation, and candles; dyed paraffin wax can be made into crayons. It is distinct from kerosene and other petroleum products that are sometimes called paraffin.

Polyurethane refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Silicone</span> Family of polymers of the repeating form [R2Si–O–SiR2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Caulking.jpg/320px-Caulking.jpg)
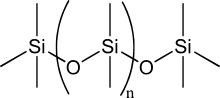
In organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane. They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, grease, rubber, resin, and caulk.

In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening ("curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and may be promoted by high pressure or mixing with a catalyst. Heat is not necessarily applied externally, and is often generated by the reaction of the resin with a curing agent. Curing results in chemical reactions that create extensive cross-linking between polymer chains to produce an infusible and insoluble polymer network.

Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand — known as casting sand — as the mold material. The term "sand casting" can also refer to an object produced via the sand casting process. Sand castings are produced in specialized factories called foundries. In 2003, over 60% of all metal castings were produced via sand casting.

Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), also known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, is a silicone polymer with a wide variety of uses, from cosmetics to industrial lubrication.

A primer or undercoat is a preparatory coating put on materials before painting. Priming ensures better adhesion of paint to the surface, increases paint durability, and provides additional protection for the material being painted.

Rotational molding involves a heated mold which is filled with a charge or shot weight of the material. It is then slowly rotated, causing the softened material to disperse and stick to the walls of the mold forming a hollow part. In order to form an even thickness throughout the part, the mold rotates at all times during the heating phase, and then continues to rotate during the cooling phase to avoid sagging or deformation. The process was applied to plastics in the 1950s but in the early years was little used because it was a slow process restricted to a small number of plastics. Over time, improvements in process control and developments with plastic powders have resulted in increased use.
Spin casting, also known as centrifugal rubber mold casting (CRMC), is a method of utilizing inertia to produce castings from a rubber mold. Typically, a disc-shaped mold is spun along its central axis at a set speed. The casting material, usually molten metal or liquid thermoset plastic, is then poured in through an opening at the top-center of the mold. The filled mold then continues to spin as the metal solidifies.
An antistatic agent is a compound used for treatment of materials or their surfaces in order to reduce or eliminate buildup of static electricity. Static charge may be generated by the triboelectric effect or by a non-contact process using a high voltage power source. Static charge may be introduced on a surface as part of an in-mold label printing process.
Silicate mineral paints or mineral colors are paint coats with mineral binding agents. Two relevant mineral binders play a role in the field of colors: Lime and silicate.

Silicone rubber is an elastomer composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations. Silicone rubbers are often one- or two-part polymers, and may contain fillers to improve properties or reduce cost. Silicone rubber is generally non-reactive, stable, and resistant to extreme environments and temperatures from −55 to 300 °C while still maintaining its useful properties. Due to these properties and its ease of manufacturing and shaping, silicone rubber can be found in a wide variety of products, including voltage line insulators; automotive applications; cooking, baking, and food storage products; apparel such as undergarments, sportswear, and footwear; electronics; medical devices and implants; and in home repair and hardware, in products such as silicone sealants.
Electronic packaging is the design and production of enclosures for electronic devices ranging from individual semiconductor devices up to complete systems such as a mainframe computer. Packaging of an electronic system must consider protection from mechanical damage, cooling, radio frequency noise emission and electrostatic discharge. Product safety standards may dictate particular features of a consumer product, for example, external case temperature or grounding of exposed metal parts. Prototypes and industrial equipment made in small quantities may use standardized commercially available enclosures such as card cages or prefabricated boxes. Mass-market consumer devices may have highly specialized packaging to increase consumer appeal. Electronic packaging is a major discipline within the field of mechanical engineering.
Injection molding of liquid silicone rubber (LSR) is a process to produce pliable, durable parts in high volume.

Decorative concrete is the use of concrete as not simply a utilitarian medium for construction but as an aesthetic enhancement to a structure, while still serving its function as an integral part of the building itself such as floors, walls, driveways, and patios.
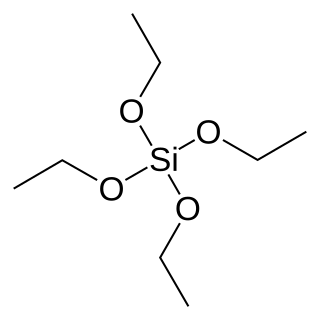
Tetraethyl orthosilicate, formally named tetraethoxysilane (TEOS), ethyl silicate is the organic chemical compound with the formula Si(OC2H5)4. TEOS is a colorless liquid. It degrades in water. TEOS is the ethyl ester of orthosilicic acid, Si(OH)4. It is the most prevalent alkoxide of silicon.

A defoamer or an anti-foaming agent is a chemical additive that reduces and hinders the formation of foam in industrial process liquids. The terms anti-foam agent and defoamer are often used interchangeably. Strictly speaking, defoamers eliminate existing foam and anti-foamers prevent the formation of further foam. Commonly used agents are insoluble oils, polydimethylsiloxanes and other silicones, certain alcohols, stearates and glycols. The additive is used to prevent formation of foam or is added to break a foam already formed.
RTV silicone is a type of silicone rubber that cures at room temperature. It is available as a one-component product, or mixed from two components. Manufacturers provide it in a range of hardnesses from very soft to medium—usually from 15 to 40 Shore A. RTV silicones can be cured with a catalyst consisting of either platinum or a tin compound such as dibutyltin dilaurate. Applications include low-temperature over-molding, making molds for reproducing, and lens applications for some optically clear grades. It is also used widely in the automotive industry as an adhesive and sealant, for example to create gaskets in-place.
Cast urethanes are similar to injection molding. During the process of injection molding, a hard tool is created. The hard tool, made of an A side and a B side, forms a void within and that void is injected with plastics ranging in material property, durability, and consistency. Plastic cups, dishware, and toys are most commonly made using the process of injection molding because they are common consumer items that need to be produced on a mass scale, and injection molding is designed for mass production.


![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Silicone</span> Family of polymers of the repeating form [R2Si–O–SiR2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Caulking.jpg/320px-Caulking.jpg)






