
Eleodes is a genus of darkling beetles, in the family Tenebrionidae. They are endemic to western North America ranging from southern Canada to central Mexico with many species found along the Mexico-United States border. Some species have been introduced to Colombia. The name pinacate is Mexican Spanish, derived from the Nahuatl (Aztec) name for the insect, pinacatl, which translates as "black beetle".

Polycestinae is a subfamily of beetles in the family Buprestidae: known as "jewel beetles".

Scaphinotus is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae. There are at least 60 species, all native to North America. They eat snails and are generally limited to the moist environments where snails live. These beetles are flightless.

Platyninae is a subfamily of ground beetles.
Mexisphodrus is a genus of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. There are about 12 described species in Mexisphodrus, found in North America.

Xylotrechus a genus of longhorned beetles of the family Cerambycidae, containing some 200 described species.

Cyclotrachelus is a genus in the beetle family Carabidae. There are more than 40 described species in Cyclotrachelus, found in North America.
Mexaphaenops is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae, containing the following species:

Mexitrechus is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae, containing the following species:
Paratrechus is a genus in the beetle family Carabidae. There are more than 50 described species in Paratrechus, found in Mexico, and Central and South America.

Judolia is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Phymatodes is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Pseudocellus is an arachnid genus in the order Ricinulei, first described by Norman Platnick in 1980. It is native to the Neotropics.

Ophryastes is a genus of broad-nosed weevils in the family Curculionidae. There are at least 30 described species in Ophryastes.

Apostasimerini is a tribe of flower weevils in the family of beetles known as Curculionidae. There are over 240 genera and nearly 1700 described species in Apostasimerini.

Trechini is a large tribe of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. There are more than 270 genera and over 2,400 described species in Trechini, found throughout the world.
Onychobaris is a genus of flower weevils in the beetle family Curculionidae. There are more than 40 described species in Onychobaris.
Rhadine caudata is a species of beetle native to the eastern United States. It is a brachypterous habitat specialist, occurring in only two of five forest classes in a North Carolina study. R. caudata is a considered a Vulnerable species at the global level on NatureServe, Imperiled in Alabama, and Vulnerable in Virginia.
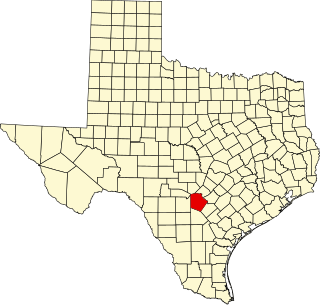
Rhadine infernalis is a species of troglobitic beetle of the family Carabidae. They are endemic to the county of Bexar, Texas. Within this county, R. infernalis has been found in 39 caves. There are 2 named subspecies of R. infernalis: R. infernalis infernalis and R. infernalis ewersi. There is a third possible subspecies that has not been officially described. R. infernalis was classified in 2000 as endangered under the IUCN Endangered Species Act of 1973, along with 8 other karst invertebrates in the same region. It has the widest known range of the endangered karst invertebrates.















