Related Research Articles

Etowah Indian Mounds (9BR1) are a 54-acre (220,000 m2) archaeological site in Bartow County, Georgia south of Cartersville, in the United States. Built and occupied in three phases, from 1000–1550 AD, the prehistoric site is located on the north shore of the Etowah River.

Ocmulgee Mounds National Historical Park in present-day Macon, Georgia, United States preserves traces of over ten millennia of culture from the Native Americans in the Southeastern Woodlands. Its chief remains are major earthworks built before 1000 CE by the South Appalachian Mississippian culture These include the Great Temple and other ceremonial mounds, a burial mound, and defensive trenches. They represented highly skilled engineering techniques and soil knowledge, and the organization of many laborers. The site has evidence of "17,000 years of continuous human habitation." The 3,336-acre (13.50 km2) park is located on the east bank of the Ocmulgee River. Present-day Macon, Georgia developed around the site after the United States built Fort Benjamin Hawkins nearby in 1806 to support trading with Native Americans.
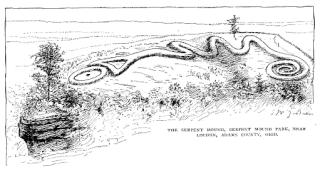
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico.

Moccasin Bend Archeological District is an archeological site in Chattanooga, Tennessee, that is part of the Chickamauga and Chattanooga National Military Park unit. The National Park Service refers to it as one of the "most unique units found in the entire National Park Service." The area contains remnants of 12,000 years of continuous human habitation and therefore serves as a fascinating area with a rich history and unique cultural significance. For many years, there was little recognition of the historical significance of the area, and years of industrial development occurred on and around sites of archeological importance. After decades of campaigning by concerned citizens, private organizations, local officials, the Friends of Moccasin Bend National Park, and finally a state representative, the area was officially recognized as a National Archeological District in 2003. Moccasin Bend is currently undergoing a process of renovation and restoration that will allow the area to fulfill the National Park Service's mission of preserving "natural and cultural resources" for the "enjoyment, education, and inspiration of this and future generations."
Indian Mound Park, also known as Shell Mound Park or Indian Shell Mound Park, is a park and bird refuge located on the northern shore of Dauphin Island, a barrier island of Mobile County, Alabama in the United States. In addition to the many birds which visit, a wide variety of botanical species contribute to the natural offerings. The site is historically significant due to the presence of prehistoric Indian shell middens, mounds composed of discarded oyster shells. The park was added to the National Register of Historic Places on August 14, 1973. It is administered by the Alabama Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.

The Hickory Ridge Cemetery Archeological Site (8ES1280) is an archaeological site in Pensacola, Escambia County Florida. It is located north of Big Lagoon and west of Pensacola. During excavations in the 1980s carbon dating was done on burnt wood fragments associated with burials in the mound, with a determination that the site had been used c. 1450. Analysis of ceramics suggested it was a Mississippian culture site, probably from the Late Bottle Creek Phase or Early Bear Point Phases of the Pensacola culture. It was a cemetery associated with a village nearby, (8ES1052). On September 22, 2000, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

The Shawnee Lookout Archeological District is a historic district in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of Ohio. Located southwest of Cleves in Hamilton County's Miami Township, the district is composed of forty-six archaeological sites spread out over an area of 2,000 acres (810 ha). Thirty-four of these sites are located in the 1,000-acre (400 ha) Shawnee Lookout Park, which has been called one of the most beautiful parks in southwestern Ohio.

The Kincaid Mounds Historic Site c. 1050–1400 CE, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located at the southern tip of present-day U.S. state of Illinois, along the Ohio River. Kincaid Mounds has been notable for both its significant role in native North American prehistory and for the central role the site has played in the development of modern archaeological techniques. The site had at least 11 substructure platform mounds, and 8 other monuments.

Bottle Creek Indian Mounds (1BA2) is an archaeological site owned and monitored by the Alabama Historical Commission located on a low swampy island within the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta north of Mobile, Alabama, United States. It was occupied by the peoples of the Pensacola culture, a regional Mississippian culture variant, and is the largest site of the Mississippian culture on the central Gulf Coast. It is important to understanding the history and culture of the Mobile-Tensaw delta in late prehistoric times and was designated as a National Historic Landmark on March 10, 1995, making it one of only two such sites in Alabama.
Hester Site is a major prehistoric archaeological site in Monroe County, Mississippi. It is a multicomponent site whose major occupation took place during the Archaic period with artifacts dating from 9000-8000 BCE, and other occupations during the Woodland and Mississippian periods. The site is one of the largest Archaic sites in the southeastern United States, and its well-stratified nature was critical in providing for accurate relative dating of finds at other sites throughout the region. The site was declared a National Historic Landmark in 2001.

Jaketown Site is an archaeological site with two prehistoric earthwork mounds in Humphreys County, Mississippi, United States. While the mounds have not been excavated, distinctive pottery sherds found in the area lead scholars to date the mounds' construction and use to the Mississippian culture period, roughly 1100 CE to 1500 CE.

The Dry Creek Archeological Site is an archaeological site not far outside Denali National Park and Preserve. It is a multi-component site, whose stratified remains have yielded evidence of human occupation as far back as 11,000 years ago. The site is located on the northern flanks of the Alaska Range, near Healy, Alaska, in the Nenana River watershed. There are four major components to the site, layered in an outwash terrace overlooking Dry Creek, with layers of loess separating them.

The Mines of Spain State Recreation Area and E. B. Lyons Nature Center is a state park in Dubuque County, Iowa, United States. It is near Dubuque, the eighth-largest city in the state. The park features picnic areas, 15 miles (24 km) of walking/hiking trails, 4 miles (6.4 km) of ski trails, and the Betty Hauptli Bird and Butterfly Garden. It also includes archaeological sites of national importance as an early lead mining and smelting venture led by French explorer Julien Dubuque, as well as Dubuque's gravesite. These sites were collectively designated a National Historic Landmark District as Julien Dubuque's Mines.

The Sommerheim Park Archaeological District includes a group of six archaeological sites west of Erie, Pennsylvania in the United States. The sites are in Sommerheim Park, one of the few undeveloped areas of the Lake Erie shoreline, in Millcreek Township. This district has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places. This is one of the leading archaeological sites in the Erie area and along the southern shoreline of Lake Erie, due to the amount of artifacts and the lack of disturbance on the site.

Pocahontas Mounds is an archaeological site from the Plaquemine Mississippian culture in Hinds County, Mississippi, dating from 800 to 1300 CE. Two mounds from the site were added to the NRHP on two separate occasions, Pocahontas Mound A on November 25, 1969 as NRIS number 69000365 and Pocahontas Mound B on April 11, 1972 as NRIS number 72000694.

Judaculla Rock is the name of an archeological site that features a curvilinear-shaped outcrop of soapstone known for its ancient carvings and petroglyphs. It is located on a 0.85-acre rectangular-shaped property, now owned by Jackson County. It is approximately 60 meters east of Caney Fork Creek, a major branch of the northwestward-trending Tuckasegee River, in the mountains of Western North Carolina.

The Collins Archeological District is a pre-Columbian archaeological site located in Kennekuk County Park in Vermilion County, Illinois. The site dates from the Late Woodland period and was used roughly from 900 to 1100 A.D. The core of the site includes two mounds and a ceremonial area. The inhabitants of the region used the site for ceremonial purposes, and the ceremonies conducted at the site were influenced by Mississippian traditions. The site provides evidence of the spread of Mississippian culture from Cahokia to other peoples and regions.
The Seven Mile Island Archeological District is an archeological site on an island in the Tennessee River in Colbert and Lauderdale County, Alabama. The island is believed to have been inhabited for about 9,000 years, with the earliest artifacts dated to the early Archaic Period. Out of 18 sites identified on the island, two have had extensive study. The Perry Site (1Lu25) is a seven-foot (2.1-meter) thick midden containing ceramic potsherds from the Archaic period. The Seven Mile Island site (1Lu21) is a Mississippian village site and mound. A number of arrowheads and flint knives, as well as a bottle with an engraved bird have been found at the site. 41 burials from the Mississippian era were also unearthed.
The Schilling Archeological District is a prehistoric Native American archaeological site on private property on Lower Grey Cloud Island in Cottage Grove, Minnesota, United States. It consists of a habitation site and mound group with artifacts that date from the Early Woodland Period to the Late Prehistoric Period. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978 for having state-level significance in the theme of archaeology. It was nominated for its rare Early Woodland component, Middle Mississippian cultural influences, and potential to show climatic adaptations over time.
The Black Mountain Archeological District is a region of the Bighorn Basin near Shell, Wyoming that contains archeological sites associated with chert deposits used in making tools and weapons. Covering 530 acres (210 ha), the area was occupied from about 11,500 years ago in the Paleoindian Period to the Late Prehistoric Period of 1500 to 400 years ago. The sites have not yielded more recent artifacts. The area contains six rock shelters, two campsites at canyon bottoms and one interfluve campsite, as well as the Black Mountain and East Spring Creek chert quarries. The local chert comes from the Phosphoria Formation, and is red in color. The district was placed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 2, 1987.
References
- 1 2 "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places . National Park Service. July 9, 2010. Retrieved February 26, 2014.
- ↑ Barnes, Mark R.; C. Hamilton (September 22, 1988), "Rock Creek Archeological District (ACt44, ACt45", National Register of Historic Places Registration Form, National Park Service

